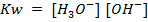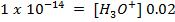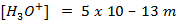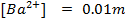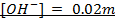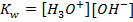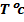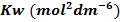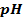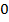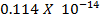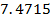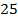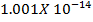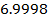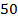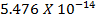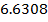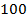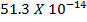LEWIS CONCEPT OF ACIDS AND BASES.
·
– Lewis proposed an even broader concept of acids and bases focusing on electron transfer rather than total transfer.
· – According to Lewis an acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons. Therefore, an acid is an electron pair acceptor.
· – A base is a substance that can donate a pair of electrons i.e base is an electrons pair donor.
NOTE
Bronsted–Lowry acids e.g. HCl, H2SO4, HNO3, are not Lewis acid.
Thus, an acid-base reaction can occur when a base provide a pair of electrons to share with an acid resulting into coordinate compound or complex.
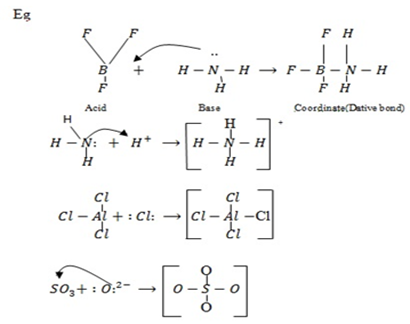
Therefore, ammonia chloride ions (AlCl3) are Lewis base, while H+, BF3 are Lewis acids.
NOTE: A Bronsted–Lowry base (like NH3) reacts by donating electron pair to a proton. Therefore Bronsted–Lowry bases are also Lewis bases
Reason:
This is because upon donating a pair of electron, it would have accepted a proton. Therefore, Bronsted – Lowry bases are also Lewis bases.
i . F– fluoride ionSO2-
ii. Sulphate ion
iii. NH+4 ammonium ion
iv. HBr Hydrogen bromid
v. H2S Hydrogen sulphide.
Reason:
These cannot accept a lone pair of electrons hence the Lewis concept of acid is usually used in special cases.
IONIC EQUILIBRIUM OF ACIDS AND BASES.
Most acids and bases are weak i.e does not ionize fully when dissolve in water. Thus a part from water equilibrium, they also establish equilibrium.
e.g.
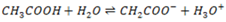
Ammonia which is a typical weak base ionizes as follows:
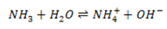
But the ionization of weak acid/ bases generally occurs to a greater extent than that of water.
STRENGTH OF WEAK ACIDS AND BASES.
The position of equilibrium of a reaction between the acid and water varies from one weak acid to another. The further to the left it lies, the weaker the acid is
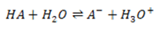
The equilibrium constant is written as;
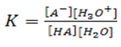
But H20 is constant at constant temperature.
Putting the constant on the same side
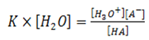
Where Ka = dissociation/ ionization constant of an acid.
for
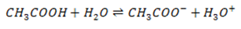
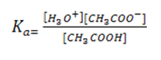
Similarly for weak base, the position of equilibrium varies from base to base. The further to the left it lies, the weaker the base is
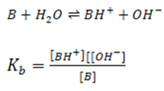
Where Kb = dissociation/ ionization constant of a base.
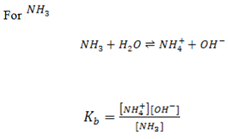
The Ka and Kb values are used to determine the strength of acids and bases i.e Ka and Kb values are quite small for a very weak acid/ base reflecting very title ionization of these acids/ base in solution.
Example:
The Kb value for C6H5NH2 is 4.17 x 10-10 ,NH3 is 1.78 x 10-5 Indicate which base is stronger than the other.
NH3 is stronger than C6H5NH2
The Kb value for C6H5NH2 is smaller than C6H5NH2NH3
The strength of weak acids and bases can also be determined from its degree of dissociation (Ostwald’s dilution law)
Since Ka and Kb values are inconvenient to handle usually pKa and pKb are used.
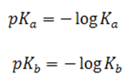
For example;
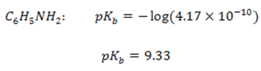
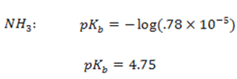
The lower the value for the stronger the acid base respectively and vice versa
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN pka AND pkθ FOR A CONJUGATE ACID–BASE PAIR.
Consider the equilibrium.
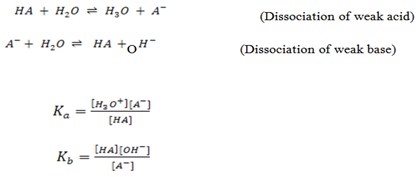
The product of Ka and Kb gives.
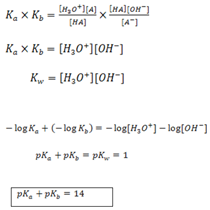
Example
Formic acid (HCOOH) has a Ka of 1.78 x 10-14 moles. Calculate the [H3O+] and the pH of 0.1M. Solution of HCOOH.
Solution
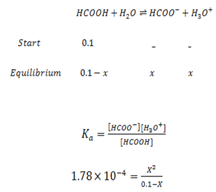
Since Ka value is small, the expression
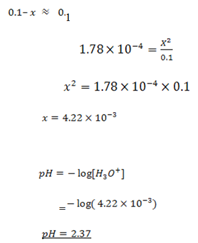
NOTE:
The approximation is done when [HA]O is greater than 100 Ka
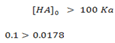
But if initial concentration [HA]O is less than 100 Ka, then the exact expression formed must be solved.
Calculate [H3O+] and pH in which has Ka value of moles/ dm3.
Solution:
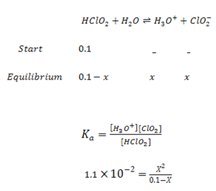
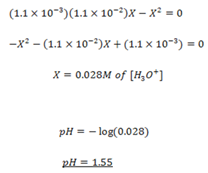
Question set 1:
Formic acid (HCOOH) has Ka of (HCOOH) 1.8 x 10-14 moles dm3. If you have0.001 m a solution of the acids. What is the pH of this solution, what is the concentration of HCOOH at equilibrium?
2. If the acid HA is 2% ionized in solution of concentration 0.01m, calculate
a) Ka
b) pKa
3.Calculate the degree of ionization 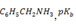 is 9.37 in a 0.1M aqueous solution
is 9.37 in a 0.1M aqueous solution 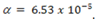
4. Calculate pH of a 0.052m acetic acid solution if Ka is 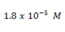
5. For a 0.1M solution of benzoic acid, calculate.
i) Concentration of ions and molecules in solution
ii) The degree of ionization of the acid.
iii) pH of the solution 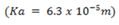
6). A hypothetical weak base (MOH) has Kb of 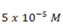 for the reaction.
for the reaction.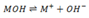
Calculate the equilibrium Concentration of MOH, M+ and OH– in a 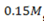 solution MOH.
solution MOH.
The weak base methylamine 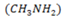 has Kb of 5 x 10– 4 .It reacts with water according to the equation.
has Kb of 5 x 10– 4 .It reacts with water according to the equation.
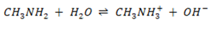
Calculate the equilibrium concentration of OH– in a 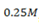 solution of base. What are the
solution of base. What are the 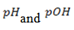 of the solution?
of the solution?
Hydroxyl amine 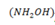 has a Kb of
has a Kb of 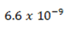 What are the
What are the 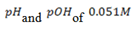 of the base ?
of the base ?
A 0.1m solution of chloroacetic acid (ClCH2COOH) has a  of 1.95. Calculate Ka for the acid.
of 1.95. Calculate Ka for the acid.
IONIC PRODUCT OF WATER AND PH.
– Water auto–ionizes i.e transfers a proton from one water molecule to another producing H3O and OH–
– 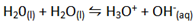
Base Acid
–
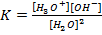
But the concentration of H2O is much larger than the two ions and is constant at constant temperature. Since the concentration of 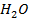 is constant it is made part of the constant.
is constant it is made part of the constant.
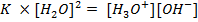
Where 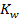 = ionic product of water constant.
= ionic product of water constant.
In pure water, Kw = 1 x 10-14 at 25°c. Since every one H3O+ ion formed also one OH– ion is formed, thus the concentrations are equal.
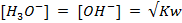
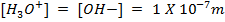
Since the concentrations are equal, this implies that pure water is neutral.
 Scale
Scale
– Is a scale which shows degree of acidity or alkalinity of a solution:
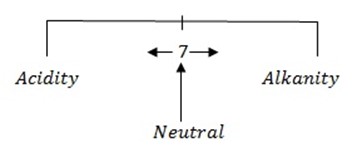
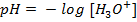
= 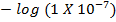
= 7
I.e pH of 7 is neutral point.
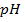 Is the negative logarithm of base 10 hydrogen ion.
Is the negative logarithm of base 10 hydrogen ion.
 Is the negative logarithm of base 10 of hydroxyl ion concentration.
Is the negative logarithm of base 10 of hydroxyl ion concentration.
For pure water
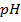 = 7 pOH= 7
= 7 pOH= 7
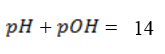
NOTE:
In acidic solution, the concentration of H3O+ is greater than [0H –].
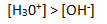
i.e 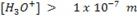
In basic solution, the concentration of 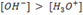
i.e [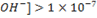
From
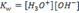 , Introducing negative log on both sides
, Introducing negative log on both sides
–
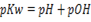
Variation of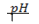 of pure water with temperature.
of pure water with temperature.
The formation of H3O+ and OH– ions from water is an endothermic process i.e the forward reaction absorbs heat.
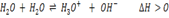
-According to Le Chatelier`s principle, when you increase the temp, the forward reaction is favoured, thus concentration of H3O+ and OH– ions will increase but in equal amounts. Thus, the pH will drop but the water will not be acidic the pH scale will also change. It won`t remain as 1 to 14 and the neutral point will also shift. The direct effect on increasing temperature is to increase Kw.
The table below shows the effect of temperature on Kw and each value of Kw a new pH must be calculated.
From the table, pH of water fall as temperature increases. This does not mean that water becomes more acidic at higher temperature. This solution is only acidic, If the concentration of 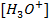 is great than
is great than 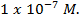
Example:
1. The value of Kw at physiological temperature of a body 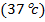 is
is 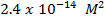 . What is the pH at neutral point of water at this temperature.
. What is the pH at neutral point of water at this temperature.
Solution:
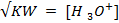
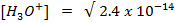
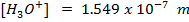
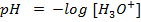
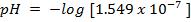
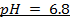
2. At  ,
, 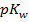 is 15. Find
is 15. Find 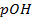 at O°c, if the [H+] is
at O°c, if the [H+] is 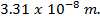
Solution:
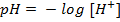
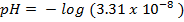
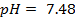
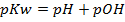
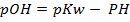
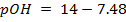
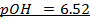
STRONG ACIDS AND BASES.
When an acid is added to water as an aqueous solution of HCl in addition to self ionization of water, the acid also ionizes.
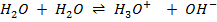
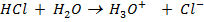
Due to common ion effect of hydroxonium ion as HCl is fully ionized, it suppresses the ionization of water hence 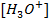 and [O
and [O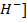 ion from water will be less than
ion from water will be less than 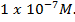
It is generally acceptable to consider the ionization of HCl to be the sole source of hydroxonium ions. This is also applicable in strong bases for OH– ions.
Example1:
If 0.001m of NaOH is added to enough amount of 1L of water, what is the concentration of OH – and H3O+ ions?
Solution:
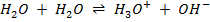


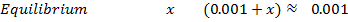
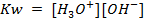
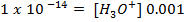
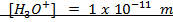
Example2:
Calculate the concentration of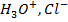 , and
, and 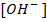 in a 100 cm3 sample of 0.015 m
in a 100 cm3 sample of 0.015 m
NOTE:
HCl is the main source of H3O+
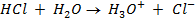

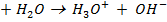

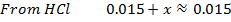
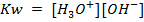
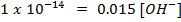
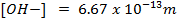
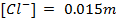
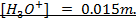
NOTE: Molar concentrations are independent of solution volume i.e [H3O+] in 0.015M HCl is the same whether we are describing 1L, 10L or 100cm3 thus the volume of acid is not involved in this calculation.
e.g. Calculate the [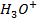 ],
],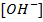 and
and 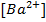 in 50 cm3 of
in 50 cm3 of 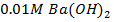
Solution:
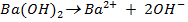
0.01M 0.01M 2 X 0.01=0.02M
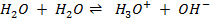



From: