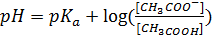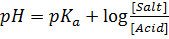NEUTRALIZATION REACTION.
This is the reaction between H3O+ from an acid and OH – ions from a base to form water. Therefore when solutions of acids and bases are mixed together, the chemical reaction must occur in which 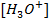 and
and 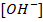 combine to form water.
combine to form water.
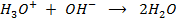
This reaction occur in order to maintain the required value of equilibrium constant Kw. The final solution can be acidic basic or neutral depending on the 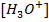 and
and 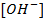 after neutralization reaction.
after neutralization reaction.
Example:
What is the [H3O+] obtained by mixing 100cm3 of 0.015m HCl and 50cm3 of 0.01m Ba(OH)2 solution, Is the final solution acidic or basic?
Solution:
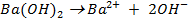
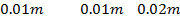
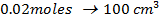
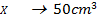
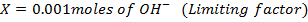
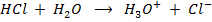

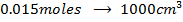
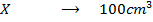
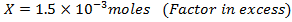
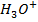 +
+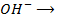 2
2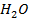
1 1
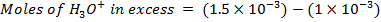
=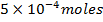
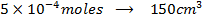
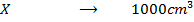
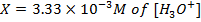
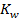 =[
=[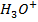 ][
][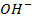 ]
]
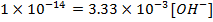
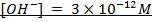
Question:
1) What is the pH of a solution obtained by dissolving 312 cm3 of HCl, measured at 30°c at 340mmHg in 3.25lL of water?
Solution:
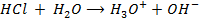
From 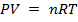
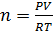
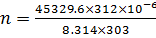
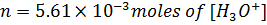
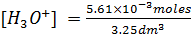
[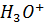 ] =1.7626
] =1.7626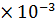
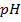
 –
–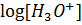
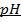
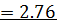
2) Calculate the pH of neutralization point when 40cm3 of 0.1m NaOH is mixed with 60cm3 of 0.1m HCl.
Solution:
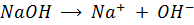
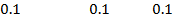
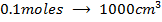
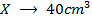
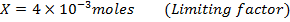
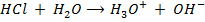
 1
1
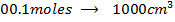
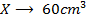
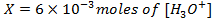
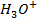 +
+ 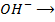
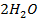

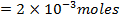
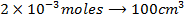
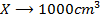
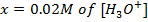
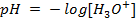
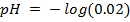
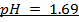
3) Calculate the pH of the solution obtained when.
a) 1cm3 of 0.1m NaOH is added to 100cm3 of 0.001m HCl
b) 1cm3 of 0.1m NaOH is added to 100cm3 of 0.1m HCl
Solution:
a) 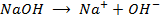
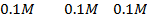
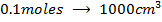
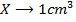
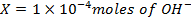
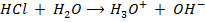
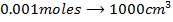
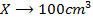
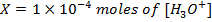
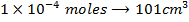
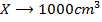
X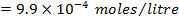
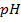
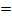 –
–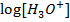
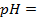 –
–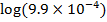
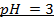
b) 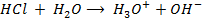
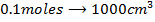
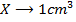
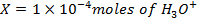
Again
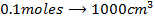
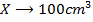
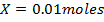
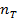 =
=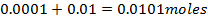
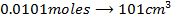
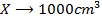
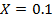
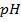
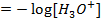
=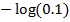
BUFFER SOLUTIONS:
A buffer solution is a solution which maintains its pH when small amount of an acid 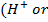
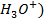 or alkali
or alkali 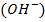 is added to it.
is added to it.
OR
Is the one that resist a change in pH when small amount of acid or alkali is added to the solution.
A buffer solution usually consists of a weak acid and one of its salt or a weak base and one of its salts.
Types of buffer solutions.
i) Acidic buffer solution.
This is the buffer solution which keeps the pH below 7.
They are formed by mixing a weak acid and its salt (of a strong base)
e.g.
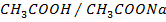
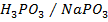
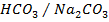
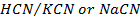
How does the buffer system work?
Consider 
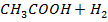 O
O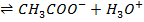
( 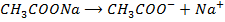 )
)
Since the salts is strong, it dissociates completely into increases the concentration of 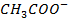 shifting the equilibrium to the left hand side suppressing the dissociation of acetic acid due to common ion effect. Hence
shifting the equilibrium to the left hand side suppressing the dissociation of acetic acid due to common ion effect. Hence 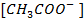 is equal to the salt concentration and due to the common ion effect
is equal to the salt concentration and due to the common ion effect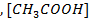 becomes equal to the initial concentration of the acid.
becomes equal to the initial concentration of the acid.
Therefore the solution will contain these important species.
i)A lot of unionized acid
ii) A lot of acetate ions from 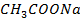
iii) Enough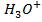 to make the solution acidic.
to make the solution acidic.
When little H+ are added, the following reaction occurs.
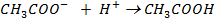
® The acetate ions concentration from the salt are large enough to consume the added hydrogen ions therefore there will be no accumulation of H+ in the solution.
® If OH– are added the following reaction occur ;
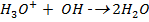
This decrease 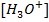 in the solution, shifting the equilibrium to the right hand side to replace
in the solution, shifting the equilibrium to the right hand side to replace 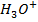 used to neutralize
used to neutralize 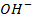 added. Therefore no accumulation of
added. Therefore no accumulation of 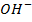 in the solution.
in the solution.
NOTE: Addition of 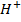 to acidic buffer increases the acid concentration, but decreases the salt concentration by the same amount of
to acidic buffer increases the acid concentration, but decreases the salt concentration by the same amount of 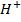 added.
added.
Addition of 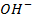 to acidic buffer decreases the acid concentration but increases the
to acidic buffer decreases the acid concentration but increases the 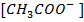 i.e salt by the same amount of
i.e salt by the same amount of 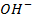 added.
added.
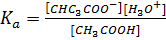
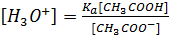
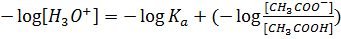
Where 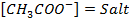
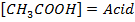
According to Henderson Hesselbach
Example:
1. 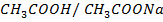 buffer solution containing 1M of acid has a
buffer solution containing 1M of acid has a 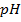 of 4.742.
of 4.742.
a) Determine the salt concentration in buffer given 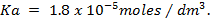
b) To 1 dm3 of a buffer, 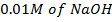 is added. Calculate the
is added. Calculate the 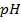 of the resulting buffer solution.
of the resulting buffer solution.
c) Calculate the 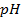 when
when 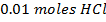 are added to 1dm-3 of the buffer.
are added to 1dm-3 of the buffer.
d) Calculate the 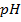 of the solution when
of the solution when 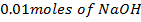 are added to 1dm3 of water sample.
are added to 1dm3 of water sample.
e) Calculate the 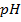 of the solution when
of the solution when 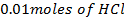 are added to 1dm3 of water sample.
are added to 1dm3 of water sample.
ANSWER:
1. Solution
a) From Henderson Hesselbach equation.
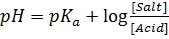
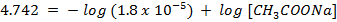
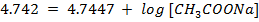
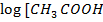 ]
] 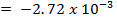
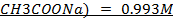
b) 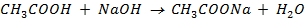
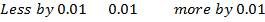
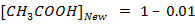
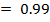
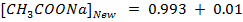
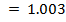
From 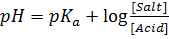
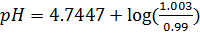
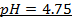
c) 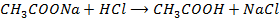
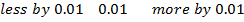
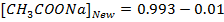
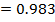

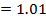
From 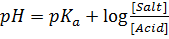
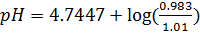
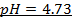
d) 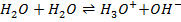

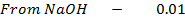
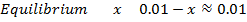
From 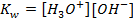
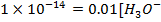
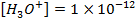
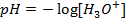
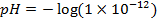
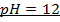
e) 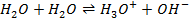

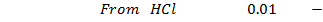
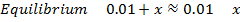
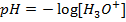
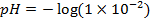
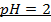
NOTE: Therefore water is not a buffer system