SALT HYDROLYSIS
A salt is a compound which contain metallic or radicle or positive radicle rather than hydrogen (H+) and acidic or negative or anion radicle rather than hydroxyl ion (OH‾)

CLASSIFICATION OF SALTS
Salts are categorized into four major classes.
These are:
1. i. Normal salt (strong salts).
2. ii. Salts with strong cation and weak anion.
3. iii. Salts with weak cation and strong anion.
iv. Salts with weak cation and weak Anion.
i) STRONG SALTS
These are salts with strong cation and strong anions.
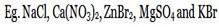
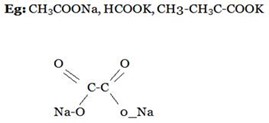
ii).SALTS WITH STRONG CATION AN WEAK ANIONS.
These are also known as basic salts mostly are organic salts or salts of carboxylic acid
iii) SALTS WITH WEAK CATION AND STRONG ANION
These salts are termed as acidic salts
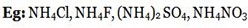
iv.) SALT WITH WEAK CATION AND WEAK ANION
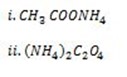
Salt hydrolysis is the reaction between salt and water to give acid and base it is a reversible reaction of neutralization reaction.
In salt hydrolysis only weak ions react with water to give the respective products.
HYDROLYSIS OF CLASSES OF SALTS
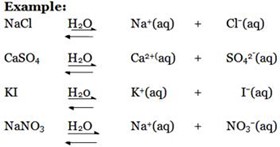
1. Hydrolysis of normal salts
The salts having strong cation and strong anion do not undergo Salt hydrolysis process, rather than ionizing in solution to give free ions.
2. Hydrolysis of basic salts
The salt having strong cation and weak anion undergo the type of hydrolysis termed as Anionic salt hydrolysis
Definition:
Anionic salt hydrolysis is the reaction between water and salt with strong cation and weak anion where by the weak anion react with water to give acid and base.
Example
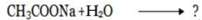
Initially the salt will ionize
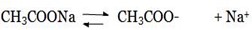
Anion will react with H2O
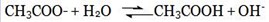
Example:
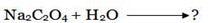
Ionization

Anion will react with H2O

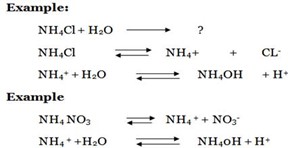
iii) Hydrolysis of salts with weak cation and strong anion. This process is also known as cationic salt hydrolysis
Definition:
Cationic salt hydrolysis is the reaction between water and salt with weak cation and strong anion in which weak cation react with water to give acid and base.
iv) Salt with weak cation and weak anion (weak salt )
This salt undergo both cationic and anionic salt hydrolysis because both weak ions will react with water to give acid and base.

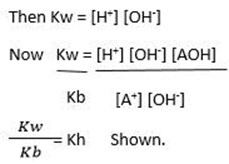
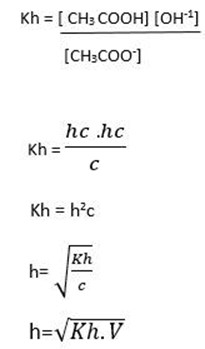
Hydrolysis constant for anionic salts hydrolysis
From hydrolysis equation Kh can be obtained
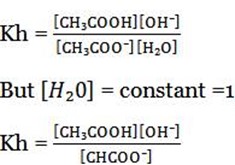
HYDROLYSIS CONSTANT (Kh)
Definition:
Kh is the ratio of product of molar concentration of the products to that concentration reactant raised to their power which is equal to the balancing number in a hydrolysis equation.
During hydrolysis the weak acid formed and water molecules will also dissociate.
The weak acid dissociation

where
ka = Dissociation constant of acid (CH3COOH)
kw = Dissociation constant of water
kh = Hydrolysis constant.
Hydrolysis constant for cationic salt hydrolysis
Consider the hydrolysis of NH4Br
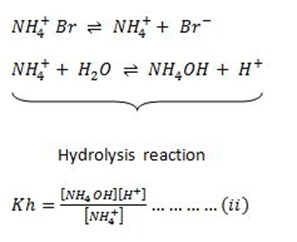
During hydrolysis the weak base is formed and water molecules will dissociate.
Weak base dissociation

where
kb = Dissociation constant of Base
Example
With examples in each briefly write short note on the following
i) Cationic salt hydrolysis
It is the reaction between water and salt with strong anion and weak cation in which the weak cation react with water to give acid and base.
Example
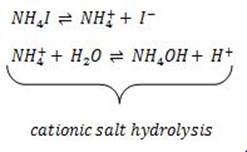
ii) Anionic salt hydrolysis
It is the reaction between water and salt with strong cation and weak anion in which the weak anion react with water to give acid and base.
Example
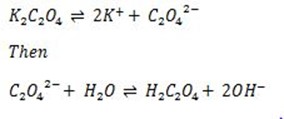
The above chemical reaction is Anionic salt hydrolysis
(iii) Hydrolysis constant
Hydrolysis constant is the ratio of the products molar concentration to the reactant concentration raised to their powers which is equal to the balancing number in the hydrolysis equation.
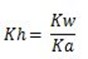 Normally it is denoted by kh
Normally it is denoted by kh
For anionic salt hydrolysis.
(iv) Acidic salt:
Acidic salt is the type of salt which contain a strong anion and weak cation.
Example:
(NH4)2SO4 , NH4Br and NH4I.
(V) Basic salt
Basic salt is the type of salt which contain a strong cation and a weak anion.
Example:
CH3COOK, Na2C2O4 and CH3CH2COONa.
(vi) Salt hydrolysis :
Salt hydrolysis is the reaction between salt and water to produce base and acid.
Under this process only weak radicals/ions are associated in the reaction.
Example
C2O42- + H2O …….. H2C2O4 + OH–
NH4+ + H2O …………………. NH4OH + H+
Example
1. Briefly differentiate cationic salt hydrolysis and anionic salt hydrolysis.
Solution
Cationic salt hydrolysis is a reaction between water and salt with weak cation and strong anion where by the weak cation react with water to produce acid and base while
anionic salt hydrolysis is a reaction between water and salt with weak anion and strong cation in which the weak anion react with water to produce acid and base.
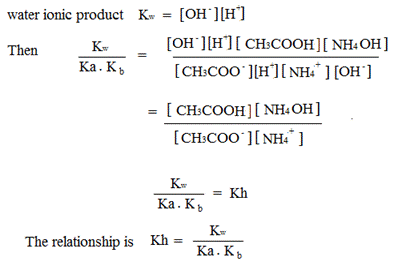
1. With an example of salt and type of hydrolysis derive the relationship between ka, kw and kh.
Solution
Consider the hydrolysis of Sodium Oxalate.
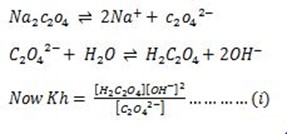
During hydrolysis acid formed together with water molecules, ionize in a solution.
Acid ionization.
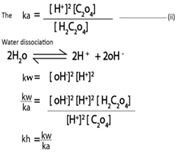
Example
During Hydrolysis the base and water molecule also ionize.
Base ionization
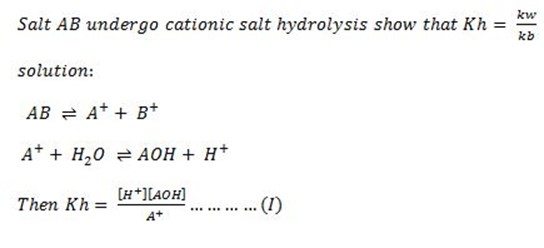
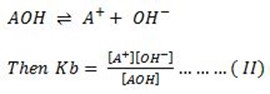
Water ionization
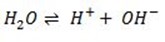
Example 4:
Calculate the Hydrolysis constant for the hydrolysis of 0.05 M NH4NO3.if its Kb is 6.67 x10-6
Solution
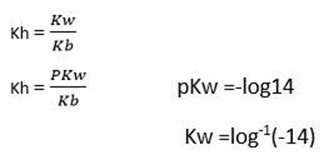
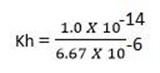

DEGREE OF HYDROLYSIS
Definition:
Is the fraction or percentage of the salts that has reacted with water to form acid and base
The degree of Hydrolysis is denoted by h.
Consider the anionic salt hydrolysis below:
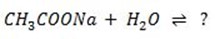
Hydrolysis Reaction:
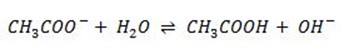

But
(1 – h)  1
1
 But c = 1/v.
But c = 1/v.
But
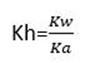
Then
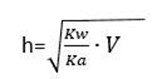
This is for anionic salt hydrolysis
Where
h is the hydrolysis constant
Kw is the water dissociation constant
Ka is the acid dissociation constant
THE HYDROLYSIS OF SALT WITH WEAK CATION AND ANION
Consider the salt of weak cation and weak anion as AB. During hydrolysis, the salt will ionize.

During the hydrolysis process there is formation of
(i) Weak acid
(ii) Weak base
Ionization of weak acid
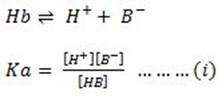
Ionization of weak base
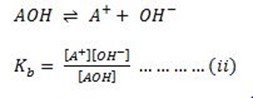
Ionization of water

For salt that undergo both cationic and anionic salt hydrolysis (weak salt)
Example
Consider the hydrolysis of ammonium acetate, then derive the relationship between Kh,Kw,Ka and Kb for such hydrolysis.
Solution
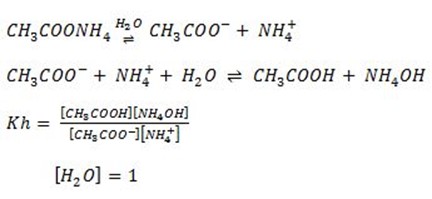
During the hydrolysis, weak acid and weak base is formed ionization of weak acid
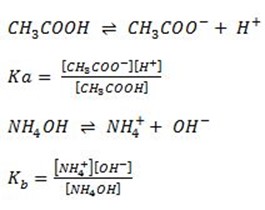
PH EQUATIONS FOR SALT HYDROLYSIS
a) FOR ANIONIC HYDROLYSIS
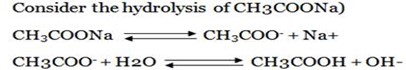
Consider the hydrolysis of CH3COONa
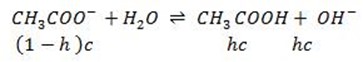
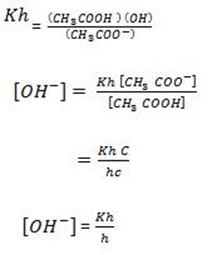
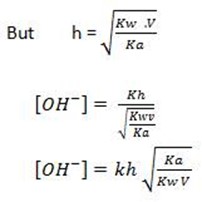
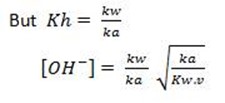
But, from water dissociation
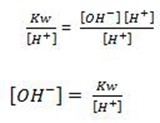
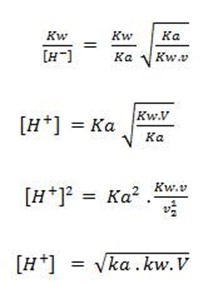
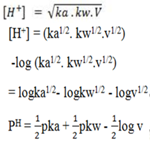
note
pH = -LOG[H+]
This is the 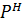 equation for anionic salt hydrolysis
equation for anionic salt hydrolysis
b) FOR CATIONIC HYDROLYSIS
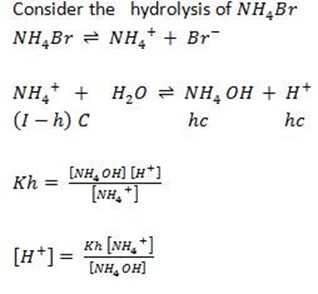
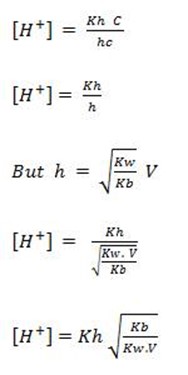
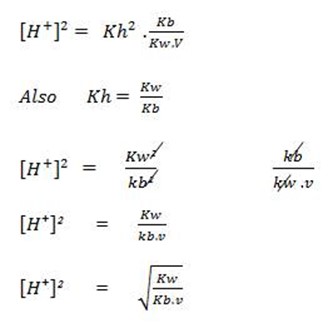
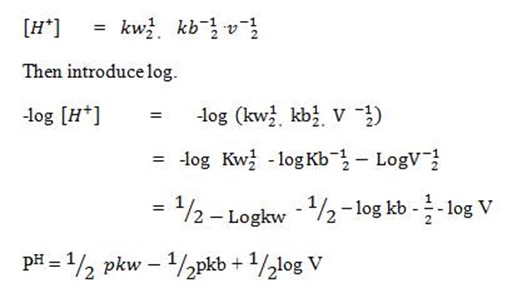
This is for the salt undergoing cationic salt hydrolysis
OR
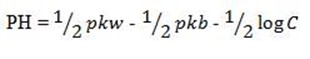
Example
a) What do you understand by
I. Salt hydrolysis
Is the reaction between water and saltl to produce acid and base.
II. Cationic hydrolysis
Is the reaction between water and salt with strong anion and weak cation at which the weak cation react with water to give acid and base.
III. Anionic hydrolysis
Is the reaction between water and salt with strong cation and weak anion in which the weak anion react with water to produce acid and base.
IV. Conjugate pair
Is the pair of conjugate acid or conjugate base or acid respectively.
b. For cationic hydrolysis show that 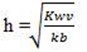
Solution. Consider the hydrolysis of NH4CL
NH4+ H20 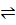 NH4 OH + H+
NH4 OH + H+
1 – h h h
At equilibrium (1 – h)c hc hc
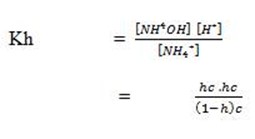
But
Assume that 1 – h 1 (h is very small)

calculate the conc. of H₃O⺠present in 0.0001M HCOOK ka. HCOOK = 2.4 X 10-4
Kw = 10-14
Solution
HCOOK 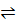 HCOOâ» + Kâº
HCOOâ» + Kâº
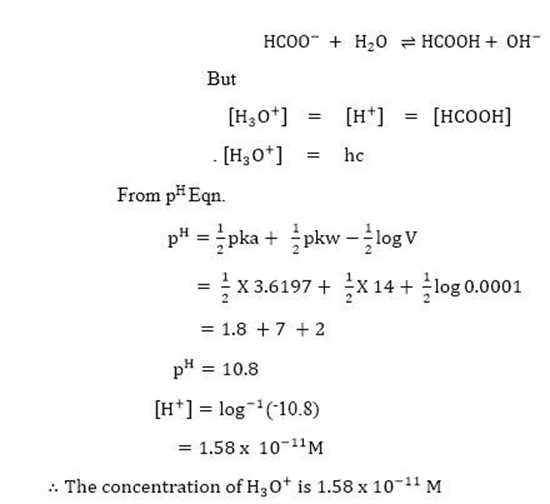
Example 2:
a. Define
pH is the negative logarithm of hydrogen molar concentration present in the solution.
Acidic salt is the type of salt that consist of strong anion and weak cation.
Basic salt is the type of salt that consist of strong cation and weak anion.
b. Normal salt do not undergo anionic or cationic salt hydrolysis. Briefly account for this statement.
Soln.
Normal salt do not undergo neither anionic nor cationic salt hydrolysis because they have strong acidic and basic radicle and the hydrolysis take place to the weak radicles only. Hence they just ionize in the water only.
c. Calculate the pH of the solution with 0.0152M. CH3COOK if KaCH3COOH =2.18 X 10-8 at a particular temperature.
Soln.
From pH equation.

Alternatively

d. Calculate the pH of the solution with 0.001M of NH4NO3 if Kb NH4OH is 1.8 x 10-4.
Soln.

Example 3:
Calculate the hydrolysis constant and the pH of 0.625M solution of CH3COONa. Kaof CH3C-OOH= 1.754 X 10-5 Kw =1 x 10-14.
Soln.
–
–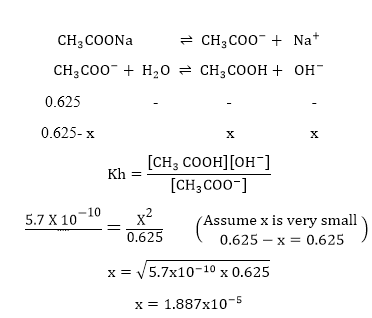
—
E-xample 4.
a. -What is the pH of 0.2M solution of NaCN? Ka for HCN =4 X 10 -10 ionic product of -water =10-14.
Soln.-
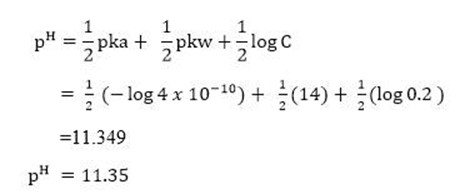
b. -Calculate the pH of 0.2M NH4Cl. Kb = 1.8×10-5.
S-oln.
–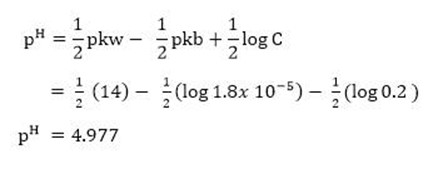
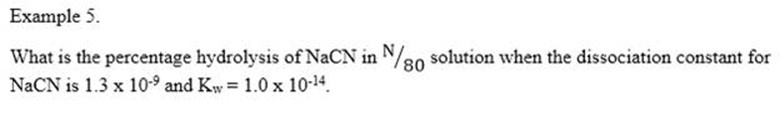
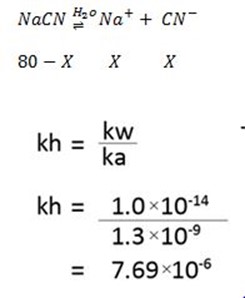
Also
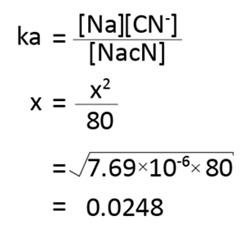
Amount dissociated = 0.0248
% hydrolysed = 0.0248 × 100%
= 2.48%
The percentage hydrolysis is 2.48%
B. calculate the hydrolysis constant and degree of hydrolysis of NH4Cl in 0.001m solution kb=1.8 × 10-5
Solution.
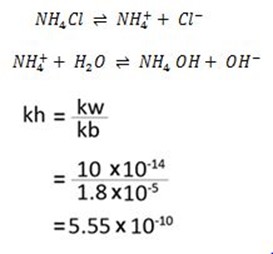
The hydrolysis constant is 5.55 × 10-10
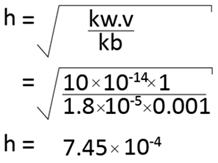
The hydrolysis constant is 7.45 × 10-4
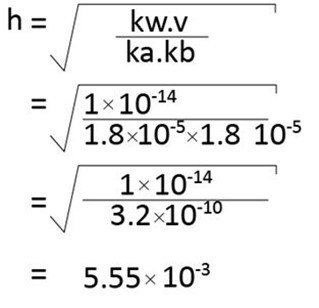
C. calculate the degree of hydrolysis of ammonium acetate if the dissociation constant of ammonium hydroxide is 1.8 × 10-5 that of acetic acid is 1.8 × 10-4 and the ionic product of H2ois 1 × 10-14 (0.55 × 10-2 ).
Solution
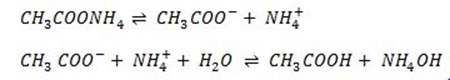
Data
Ka = 1.8 × 10-5
Kn = 1.8 × 10-5
Kw = 1 × 10-14
From hydrolysis equation
Example 6.
What is hydrolysis constant of salt?
Answer
Is the ratio of products concentration to reactant concentration in moles/dm3 raised to their powers which is equal to the balancing number in a hydrolysis equation
Why aqueous solution of sodium carbonate is alkaline derive an expression for the hydrolysis constant and pH of this solution.