TYPES OF ELECTRODES FOUND IN ALL GALVANIC CELLS
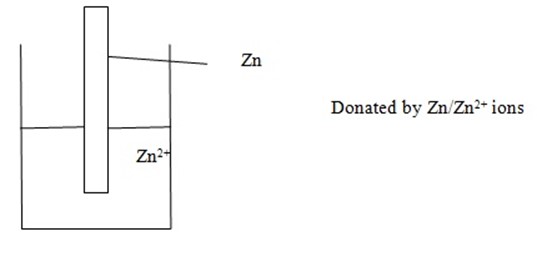
I. Metal – metal ion electrodes
This consists of metal dipped into its soluble salts.
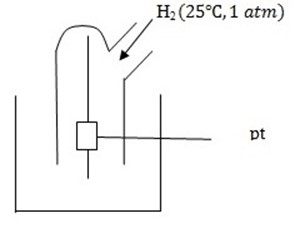
II.Gaseous electrode
This consists of platinum to which a gas at 1 atm, and 25°c is bubbled and dipped in ions of gas at a given concentration.
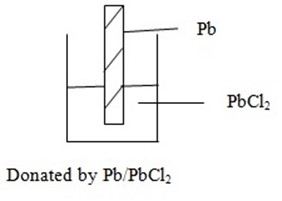
III.Metal – insoluble salt electrode
This consists of metal dipped into its insoluble salts at 
IV. Redox electrodes
It consists of platinum dipped in cations having different oxidation states at a given concentration at 25oc.
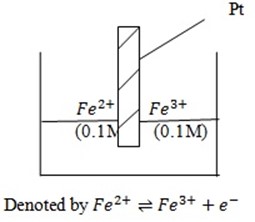
Measurements of electrode potential
We can always measure the electrode potential for an electrode in combination with standard electrode which is standard hydrogen electrode (SHE)
It was conventionally agreed that electrode potential for hydrogen is zero.
i.e. 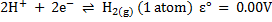
When electrode potential of any element is measured against hydrogen electrode at  1 atm and 1M concentration is called standard electrode potential.
1 atm and 1M concentration is called standard electrode potential.
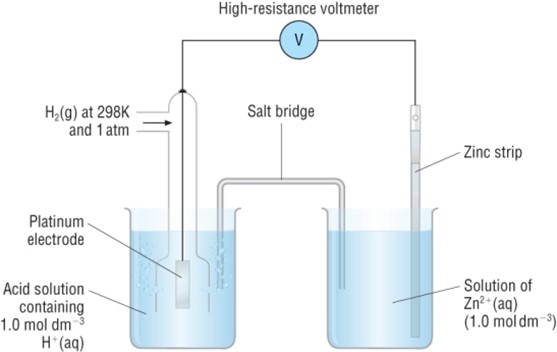
Salt Bridge
Is an inverted U-tube that contains on electrolyte (e.g. 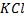 ) which connects the solution of two half cells to balance the charge and to complete the circuit.
) which connects the solution of two half cells to balance the charge and to complete the circuit.
NOTE
The standard redox potential is actually reduction potential. All elements below hydrogen have negative reduction potential and positive oxidation potential hence strong reducing agents.
All elements above hydrogen have positive reduction potential and negative oxidation potential hence strong oxidizing agents.
When writing the cell description the hydrogen electrode is placed on the left conventional to determine the polarity of the right hand electrode.
Functions of salt bridge
I.To complete the circuit
II.To balance the charge
Example
Consider the following arrangements for determine electrode potential fo
I. 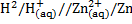
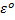 =
= 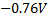
The zinc electrode is negative.
Cell reaction:
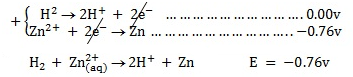
II.Copper
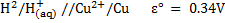
The copper electrode is positive. (It can easily be reduced)
Cell reaction:
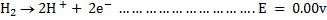
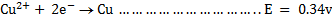
Overall: 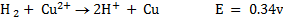
Application of standard electrode potential
I. Construction of electrochemical cells.
II. Prediction of occurrence of chemical reaction
III. Determination of  of a solution without
of a solution without  meter
meter
IV. Replacement of elements in the electrochemical series.
Electrolytic cell = produce electrical power through chemical reaction in electrochemical cells.
I. CONSTRUCTION OF ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS
Electrochemical cells are devices that use chemical reactions to produce electrical power. These are sometimes known as Galvanic or Voltaic cells.
e.g. dry cells, car batteries.
It contains two half cells connected together by external circuits.
Half cell is an arrangement which consists of an electrode dipped into a solution containing its ions. When the two half cells are connected, the resulting component is called electrochemical power. A good example is Daniel cell. It is constructed from Zinc and copper electrode.
PROCEDURE FOR CONSTRUCTION OF ELECTROCHEMICAL CELL
1. Identify between the electrodes, which electrode is supplying or gaining electrons by studying their electrode potential.
II. An electrode with negative standard electrode potential is more reactive (supplies electrodes) than the positive one.
III. If both are negative the one which has more negative electrode potential is more reactive.
E.g. Sn = -0.16
Mg = -0.25 (more reactive)
If both electrodes are positive, the one which has less positive value is more reactive.
E.g. 0.07v (more reactive)
0.2v
The electrode which supplies electrons should be placed on the left and electrode which gains electrons should be on the right hand side.
E.g. construct a Daniel cell and shows the direction of flow of electrons and current given that 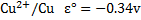
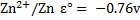
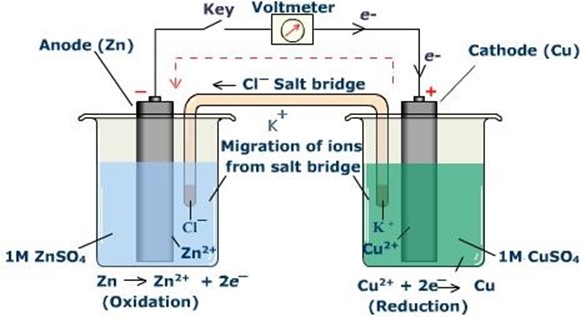
The electrode which supplies electrons oxidation takes place and the electrode is oxidized. This electrode is called ANODE. The electrode which receives electrons reduction takes place and the electrode is REDUCED. It is called CATHODE.
Zn – anode
Cu – cathode
Overall reaction is obtained by adding the two half reactions and is called cell reaction.
Anodic reaction: 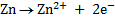
Cathodic reaction: 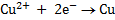
Cell reaction: 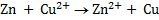
Electrochemical cell can also be represented in an abbreviation way known as cell notation.
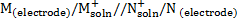
Anode cathode
I.e. for Daniel cell 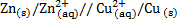
Questions
1. Given the overall reactions, write their corresponding cell notations
a) 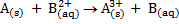
b) 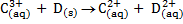
2. From the cell notation give the cell reactions
a) 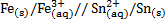
b) 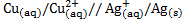
Answers
1. 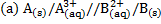
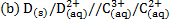
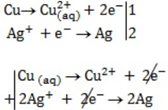 \
\
Cu(aq) + 2Ag+(aq)→Cu2+(aq) +2Ag(s)
2.
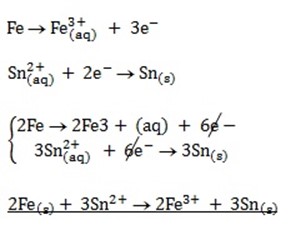
ELECTROMOTIVE (EMF) FORCE OF A CELL
The difference between electrode potential of the two electrodes constituting an electrochemical cell is known as electromotive (emf) or cell potential.
This acts as a driving force for a cell reaction and it is expressed in volts.
The emf of a cell is calculated by subtracting the standard electrode potential 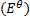 of the left electrode from that of the right electrode.
of the left electrode from that of the right electrode.
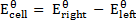
For Daniel cell 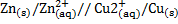
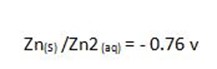
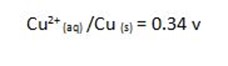
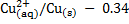
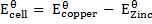
= 0.34 – (-0.76)
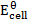 = 1.1v
= 1.1v
Alternatively
Since standard electrode potentials are in reduced form, for oxidation half reaction the sign of electrode potential should be reversed.

= 0.76 + 0.34
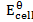 = 1.1v
= 1.1v
1.Prediction of the occurrence of chemical reaction.
If the emf of the cell calculated is negative the reaction is non spontaneous i.e. the reaction does not occur in the way it is written unless external forces apply but the reaction is spontaneous in the opposite direction.
If the emf of the cell is positive the reaction is spontaneous
Example: given the following reaction
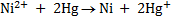
Predict the direction of the reaction given that reduction potential of nickel (Ni2+/Ni) Eo = -0.25v of mercury Hg+/Hg 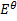 = 0.14v
= 0.14v
Solution
Cell notation
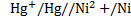
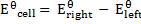
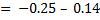
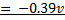
The reaction is non spontaneous since emf is negative hence backward reaction is favored.
Example
For each of the following reactions at standard condition, decide if it occurs spontaneously in the direction written.
a) 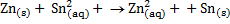
b) 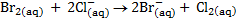
c) 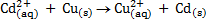
Given for 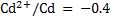 .
.
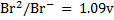
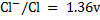
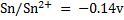
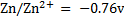
ANSWERS
I. 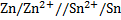
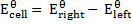
=-0.14 – (-0.76)
= 0.62V
II. Cell notation: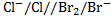
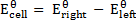
=1.09 – (1.36)
= -0.27V
III. Cell notation: 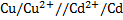
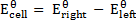
=-0.4 – 0.34
=-0.74V
Therefore reaction (1) is spontaneous while reaction (2) and (3) are non-spontaneous
Example
Briefly explain what happen when
I.Fe is dipped in CuSO4 solution
II.Cu is dipped in FeSO4 solution
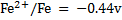
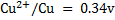
Example
Given the following 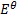 values
values
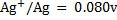
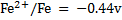
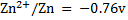
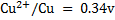
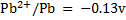
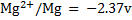
a)State which species are the strongest oxidant and which oxidant and weakest reductant.
b)State which species is the strongest oxidant and weakest reductant.
c)The lead rods are placed in a solution of each CuSO4, FeSO4, AgNO3 and ZnSO4. In which solution do you except coating of another metal on lead rod. Explain.
ANSWERS
2. (i) since Fe has a negative reduction potential then it has a positive oxidation potential and hence will displace copper metal from CuSO4 solution
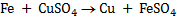
(ii)Since Cu has positive reduction potential, then it has a negative oxidation potential and hence it will NOTE displace Fe from FeSO4solution therefore no reaction will be possible.
3. (a) strongest oxidant
Weakest reductant
Maximum and minimum emf of a cell
It is possible to decide which cell has to be constructed either of great or smallest emf for a given electrodes. A cell with greatest emf is obtained by
choosing two electrodes of greatest cell reactivity difference. A cell with minimum emf, choose two electrodes with closest reactivity.
Example
Study the following electrodes.
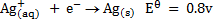
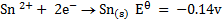
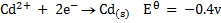
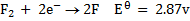
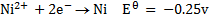
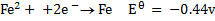
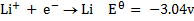
4. Explain how you can construct a cell that will yield
i. Maximum emf
ii. Minimum emf
ANSWER
For maximum emf, we choose two electrodes of greatest cell reactivity difference.
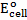 = 2.87 – (-3.04)
= 2.87 – (-3.04)
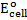 = 5.91v
= 5.91v
For minimum emf, we choose two electrodes with closest reactivity
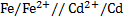
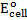 = -0.4 – (-0.44)
= -0.4 – (-0.44)
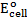 = 0.04v
= 0.04v
