MOLAR CONDUCTIVITY AND DEGREE OF DISSOCIATION
The molar conductivity of weak electrolyte is proportional to the degree of dissociation.
i.e.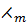
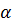
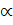
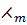 = K
= K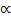 ……………. (i)
……………. (i)
At infinity dilution, the weak electrolyte is completely ionized.
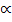 = 1 or 100%
= 1 or 100%
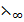 = K (Constant)……….. (ii)
= K (Constant)……….. (ii)
Taking ratio of equation (i) and (ii)
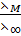
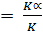
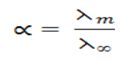
Ostwald’s dilution law
It states that
“For a weak electrolyte the degree of dissociation is proportional to the square root of reciprocal of concentration”
Consider a weak binary electrolyte AB (i.e. ethanoic acid) in solution with concentration C (mol/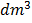 ).
).
AB  A+ (aq) + B– (aq)
A+ (aq) + B– (aq)
1mole 0 0 start
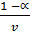

 At equilibrium
At equilibrium
But V = 
AB 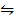 A+ (aq) + B– (aq)
A+ (aq) + B– (aq)
K = 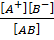
But AB = CH3 COOH
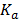 =
= 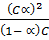
For a weak electrolyte, degree of dissociation is very small thus the expression
1 – 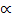
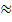 1
1
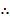 Ka =
Ka = 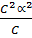
K a = C 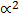
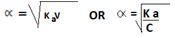
Example
1. At 250c the solution of O.1M of ethanoic acid has a conductivity of 5.0791×10-2 m-1mol-1.
m-1mol-1.
calculate the pH of the solution and dissociation constant Ka (Answer Ka=1.69 10-2M)
10-2M)
2. A 0.001 moldm-3 solution of ethanoic acid was found to have molar conductivity of 14.35Sm2mol-1. Use this value together with molar conductivity at infinity dilution of ethanoic acid 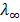 (C
(C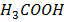 ) is 390.7Ð…
) is 390.7Ð…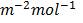 to calculate :-
to calculate :-
i. Calculate degree of dissociation of acid
ii. Equilibrium constant 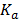
3.The resistivity of 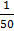 M KCl solution is 361Ω and conductivity cell containing such a solution was found to
M KCl solution is 361Ω and conductivity cell containing such a solution was found to
have a resistance of 550Ω
a.Calculate the cell constant
b.The same cell filled with 0.1M ZnSO4 solution had resistance of 72Ω. What is the conductivity of this solution?
KOHLRAUSCH’S LAW OF INDEPENDENT IONIC MOBILITY
Kohlrausch notes that the difference between molar conductivity at infinity dilution λ∞ values for the two salts which were strong electrolytes and of the same cation and anion was always constant.
Using the λ∞ values in D.. cm2 mol-1
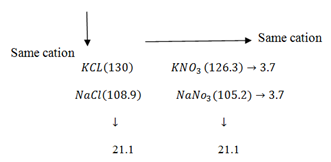
This observation shows that each type of ion (caution or anion) contribute a definite amount of molar conductivity of an electrolyte of infinity dilution independently from other ions present in the solution i.e. a fraction of current that an ion carry is always constant and it doesn’t depend on the compound in which it is contained.
Hence Kohlrausch’s law
States that;”The molar conductivity of an electrolyte at infinity dilution is equal to the sum of the molar conductivities of the caution and anion”.
OR State that the molar conductivity at infinity dilution of the solution equal to the sum of molar conductivity at infinity dilution of its components ions.
i.e. 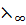 =
= 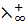 +
+ 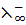
E.g. 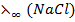 =
= 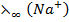 +
+ 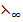 (C
(C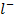 )
)
λ∞(Al2(S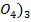 ) = 2
) = 2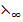 (AL3+) + 3
(AL3+) + 3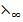 (S
(S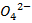 )
)
Application of Kohlrausch’s law
In direct determination of molar conductivity at infinity dilution for weak electrolytes. Thus by using strong electrolytes we can easily. Calculate the molar conductivities at infinity. Dilution for weak electrolytes.
E.g.: The 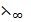 (C
(C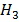 COOH) can be determined from
COOH) can be determined from 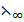 of potassium ethanoate (C
of potassium ethanoate (C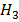 COOK) hydrochloric acid (HCl) and potassium chloride (KCl)
COOK) hydrochloric acid (HCl) and potassium chloride (KCl)
CH3COOH + KCl 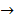 CH3COOK + HCl
CH3COOK + HCl
λ∞(CH3COOH) = 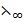 (CH3COOK) +
(CH3COOK) + 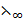 (HCl) –
(HCl) – 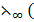 KCl)
KCl)
= 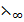 (CH3COO–) +
(CH3COO–) + 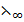 (K+) +
(K+) + 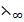 (H+) +
(H+) + 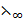 (Cl) –
(Cl) – 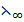 (K+) –
(K+) – 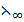 (Cl)
(Cl)
λ∞(CH3 COOH) = 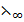 (CH3COOH–) +
(CH3COOH–) + 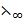 (H+)
(H+)
REVIEW QUESTIONS
1. Calculate 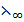 (NH4OH given that
(NH4OH given that 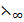 of three strong electrolyte NaCl, NaOH and NH4Cl in Ð…cm2 mol-1 are 126.4, 248.4 , 149.8 respectively.
of three strong electrolyte NaCl, NaOH and NH4Cl in Ð…cm2 mol-1 are 126.4, 248.4 , 149.8 respectively.
2.The molar conductivity of 0.093 CH3COOH solution at 298k is 536 x 10-4 Sm2mol-1 .The molar conductivity at infinity dilution of H+ and CH3COO– are 3.5 x 10-2 and 0.41 x 10-2Sm2 mol-1.what is are the dissociation constant of CH3COOH
3. A 0.05M HF solution has a conductivity of 91.81mol-1 m-1 at 298k.At the same temperature 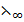 (NaF),
(NaF), 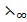 (NaoH) and
(NaoH) and 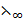 (H2O) are 493360 and 162Sm2mol-1 respectively. Calculate dissociation constant.
(H2O) are 493360 and 162Sm2mol-1 respectively. Calculate dissociation constant.
4. The λ∞(NaI), λ∞(CH3COONa) and λ∞(CH3COO2Mg) are 12.69,9.10 and 18.78Sm2 mol-1 respectively at 250C. What is the molar conductivity of MgI2 at infinity dilution.