DETERMINATION OF MOLAR SOLUBILITY FROM Ksp VALUE
If the Ksp value is known, the molar solubility can be obtained since Ksp shows the maximum concentration of ions which exists together in a solution.
Example 1
Calculate the molar solubility of Ag2CrO4 in water at 25oC if its Ksp is 2.4 x 10-12 M3.
Ag2CrO4(s)  2Ag+ (aq) + CrO42-(aq)
2Ag+ (aq) + CrO42-(aq)
Let the solubility be S
Ag2CrO4(s)  2 Ag+ (aq) + CrO42-(aq)
2 Ag+ (aq) + CrO42-(aq)
S 2S S
From Ksp = [Ag+] 2 [CrO42+]
2.4 x 10 -12 = (2S) 2
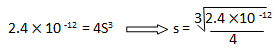
S = 8.434 x 10 -5 mol L-1
Example 2
Calculate the solubility of CaF2 in water at 25oC if its solubility product is 1.7 x 10 -10 M3
Solution
CaF2
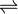 Ca 2+ + 2F –
Ca 2+ + 2F –
S S 2S
Ksp = [Ca2+] [F–] 2
=S (2S) 2
1.7 x 10 -10 = 4S3
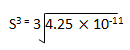
S = 3.489 x 10-4 mol L–
SOLUBILITY AND COMMON ION EFFECT
The solubility of sparingly soluble salts is lowered by the presence of second solute that furnishes (produce) common ions. Since the concentration of the common ion is higher than the equilibrium concentration, some ions will combine to restore the equilibrium (Le Chatelier’s principle)
Example 1
In solubility equilibrium of CaF2, adding either Calcium ions or F– ions will shift the equilibrium to the left reducing the solubility of CaF2.
i. Find the molar solubility of CaF2 (Ksp = 3.9 x 10 -11 M3) in a solution containing 0.01M Ca(NO3)2
Solution
Since Ca(NO3)2 is strong electrolyte, it will dissociates completely according to the equation.
Ca (NO3)2 (s)  Ca2+ (aq) + 2NO3(aq)
Ca2+ (aq) + 2NO3(aq)
0.01 0.01 2(0.01)
CaF2(s)  Ca2+(aq) + 2F–(aq)
Ca2+(aq) + 2F–(aq)
S S 2S
Letting solubility of CaF2 be S
CaF2(s)  Ca2+ (aq) + 2F–(aq)
Ca2+ (aq) + 2F–(aq)
S S 2S
0.01
From Ca (NO3)2
In absence of Ca(NO3)2
Ksp = [Ca2+] [F–]2
3.9 x 10 -11 = S (2S) 2
3.9 x 10 -11 = 4S 3
S 3 = 9.75 x 10 -12
S = 2.136 x 10 -4 molL-1
Assume the concentration of Ca2+ from Ca (NO3)2 does not affect the solubility of CaF2 then concentration of Ca2+ will be
[Ca2+] = S + 0.01
= (2.136 x 10-4) + 0.01
0.0102 M ≈ 0.01
Since the Ksp value is very small, the expression 0.01 + S is approximated to 0.01
Ksp = [Ca2+] [F–]2
3.9 x 10 -11 = 0.01 (2S) 2
3.9 x 10 -11 = 0.04S2
S2 = 9.75 x 10 -10
S = 3.122 x 10 -5 mol/l
Conclusion
Hence, because of common ions effect, the solubility of CaF2 has reduced from 2.13 x 10 -4 M to 3.122 x 10 -5 M
Example 2
Calculate the mass of PbBr2 which dissolves in 1 litre of 0.1M hydrobromic acid (HBr) at 25oC
(Ksp for PbBr2 at 25oC is 3.9 x 10 -8 M3) (Pb = 207, Br = 80)
Solution
PbBr2 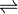 Pb2+ + 2Br—
Pb2+ + 2Br—
S S 2S
0.1 After adding HBr
At equilibrium
PbBr2 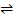 Pb2+ + 2Br
Pb2+ + 2Br
S S 2S + 0.1
2S + 0.1 = 0.1 since Ksp is very small
Ksp = [Pb2+][Br–]2
3.9 x 10 -8 = S (0.1)2
S = 3.9 x 10 -6 moll-1
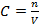
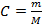
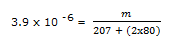
m = 1.43 x 10 -3 gl-1 of PbBr2
Example 3
The solubility product of BaSO4 in water is 10 -10 mol2l-2 at 25oC
(a) Calculate the solubility in water in moldm-3
(b) 0.1 M of Na2SO4 solution is added to a saturated solution of BaSO4. What is the solubility of BaSO4 now?
Example 4
Calculate the molar solubility of Mg (OH) 2 in
(a) Pure water
(b) 0.05M MgBr2
(c) 0.17 M KOH
(Ksp for Mg(OH)2 is 7.943 x 10 -12 M3)
(a)Solution
BaSO4 (s)  Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq)
Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq)
S S S
10-10mol2l-2 = [Ba2+] [SO4-2]
10-10mol2l-2 = S2
S = 1x 10 -5 mol/dm3
(b) Solution
Na2SO4(s)  2Na+(aq) + SO42-(aq)
2Na+(aq) + SO42-(aq)
0.1 2 x 0.1=0.2 0.1
BaSO4
(s)  Ba2+(aq) + SO4
Ba2+(aq) + SO4
2-(aq)
S S S + 0.1 after adding Na2SO4
S + 0.1 ≈ 0.1 Ksp is very small
Ksp = [Ba2+][SO42-]
1 x 10 -4 mol2/l2 = S (0.1)
S = 1 x 10 -19 mol l-1
S = 1 x 10 -9 mol l-1
The value of S has reduced after adding NaSO4
4. (a) Solution
Mg(OH)2(aq) 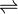 Mg2+(aq) + 2OH–(aq)
Mg2+(aq) + 2OH–(aq)
S S 2S
Ksp = [Mg2+][OH-]2
7.943 x 10 -12 = 4S3
S3 = 1.985 x 10 -12
S = 1.25 x 10 -4 moll-1
(b) Solution
KOH(aq) 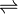 K+
K+
(aq) + OH–(aq)
0.17 0.17 0.17
Mg(OH)2 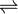 Mg2+ + 2OH–
Mg2+ + 2OH–
S S 2S
2S + 0.17
2S + 0.17 = 0.17 Ksp is very small
Ksp =[Mg2+][OH–]2
7.943 x 10 -12 M3 = S(0.17)2
S = 2.748 x 10 -10 moll-1
(c) Solution
MgBr2 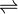 Mg2+ + 2Br–
Mg2+ + 2Br–
0.05 0.05 2 x 0.05 ≈ 0.1
Mg (OH)2 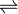 Mg2+ + 2OH–
Mg2+ + 2OH–
S S + 0.05 2S
S + 0.05 0.05 Ksp is very small
Ksp = [Mg2+][OH–]2
7.943 x 10 -12 M3 = (0.05)(2S)2
S2 = 3.9715 x 10 -11
S = 6.3 x 10 -6 moll–