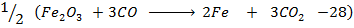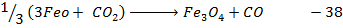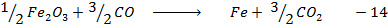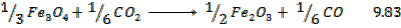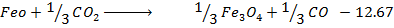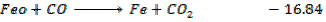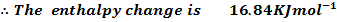11. HEAT OF DILUTION
Is the heat change when one mole of a substance is dissolved in a given mole of water
METHODS OF FINDING HEAT OF FORMATION OF A GIVEN COMPOUNDS
The calculation in thermochemistry are categorized in the following;-
(i). Calculation based on combustion Data.
(ii). Calculation based on bond energies.
(iii). Calculation based on atomization Data.
(iv). Calculation based on calorimetry information.
(v). Determination of molecular formular by combustion Data.
(vi). Calculation based on Born–Haber cycle.
CALCULATIONS BASED ON COMBUSTION DATA
Calculations involving combustion data has got the following Steps:-
(i). Identify the required equation.
(ii). Data presentation.
(iii). Data manipulation.
(iv). Conclusion.
Example 1
a) With one example in each briefly define the following terms;-
(i). Standard enthalpy of combustion.
(ii). Sublimation energy.
(iii). Standard enthalpy of formation.
(iv). Atomization energy.
(v). Lattice energy.
Solution
(i). Standard enthalpy of combustion: is the heat energy given out when 1mole of a certain substance is completely burnt in a given moles of oxygen at standard state.
(ii). Sublimation energy: Is the energy absorbed when one mole of solid atom is converted to gaseous atom.
(iii). Standard enthalpy of formation: is the heat change which occur when 1 mole of substance is formed from its element.
eg. C + O2 → CO2
(g) ΔH°f = – 393 KJmol-1
(iv). Atomization energy: is the energy absorbed when a given molecule or element is converted into gaseous atom.
(v). Lattice energy: Is the energy given out when 1 mole of ionic compound is formed from it ions.
eg. Na+(g) + Cl–(g) → NaCl
b) Calculate the enthalpy of formation of methane given that,
Enthalpy of combustion are;-
i. Carbon 394 KJmol-1.
ii. Hydrogen 286 KJmol-1.
iii. Methane 891 KJmol-1.
Solution
Required equation
C + 2H2
 CH4
CH4
Data presentation KJ mol -1
i. C + O2  CO2 – 394
CO2 – 394
ii. H2 + 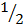 O2
O2  H2O – 286
H2O – 286
iii.CH4 + 2O2  CO2 + 2H2O 891
CO2 + 2H2O 891
Data manipulation KJmol-1
i. C + O2
 CO2 – 394
CO2 – 394
ii. H2 + 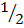 O2
O2  H2O – 286)
H2O – 286)  2
2
2H2 + O2  2H2O – 572
2H2O – 572
iii.2H2 + O2  CH4 + 2O2 891
CH4 + 2O2 891
C + 2H2
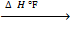 CH4 – 75
CH4 – 75
... The enthalpy of formation of methane is -75 KJmol-1.
Example 2
Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of ethane given that enthalpy of combustion.
i) C = -394 KJmol-1
ii) hydrogen = -216 KJmol-1
iii) Ethane = -1561 KJmol-1
Solution
Required equation
2C + 3H2
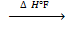 C2H6
C2H6
Given KJmol-1
(C + O2  CO2 -394
CO2 -394
H2 + 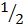 O2
O2
 2CO2 – 788
2CO2 – 788
C6H6 + 7/2 O2
 2CO2 + 3H2O -1561
2CO2 + 3H2O -1561
Data Manipulation
(C + O2  CO2 -394 )×2
CO2 -394 )×2
2C + 2O2
 2CO2 -788
2CO2 -788
(H2 + 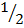 O2
O2  H2O -216)
H2O -216) 3
3
3H2 + 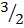 O2
O2 3H2O -648
3H2O -648
2CO2 + 3H2O  CH3 CH3 +
CH3 CH3 + 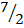 O2 1561
O2 1561
2C +3H2  C2H6 + 125
C2H6 + 125
... The standard enthalpy of formation of C2H6 is 125 KJmol-1.
Example 3
a) Define;-
i.Heat of combustion
Is the heat given out when one mole of a substance is completely burnt in given moles of O2 at standard state.
ii. Heat of neutralization
Is the heat energy given out when one mole of water is formed the reaction between acid and base at standard state.
iii.Heat of dilution
Is the heat change when one mole of a compound is dissolved in a given moles of water.
b) Calculate the heat of formation of ethanoic acid , if the enthalpy of combustion are C = -394 H2 = – 284 ethanoic acid -876 ( All in KJ mol-1).
Solution
Required equation
2C + 2H2 +O2
 CH3COOH
CH3COOH
Data presentation KJ mol-1
C + O2  CO2 -394
CO2 -394
H2 + 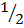 O2
O2  H2O -284
H2O -284
CH3 + 2O2
 2CO2 + 2H2O -876
2CO2 + 2H2O -876
Data manipulation
2C + 2O2
 2CO2 – 788
2CO2 – 788
2H2 + O2
 2H2O – 568
2H2O – 568
2CO2 + 2H2O  CH3COOH + 2O2 876
CH3COOH + 2O2 876
The equation obtained
2C + 2H2 + O2
 CH3COOH -480
CH3COOH -480
... The heat of formation of ethanoic acid is -480 KJmol-1.
Example 4
From the following Thermodata at 298k.
(i) 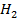 +
+ 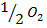
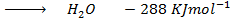
(ii) 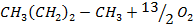
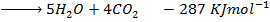
(iii) 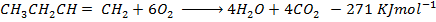
Calculate 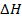 for the reaction
for the reaction
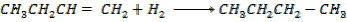
Solution
Required equation
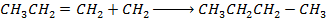
Data presentation
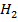 +
+ 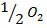
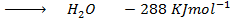
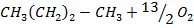
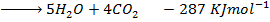
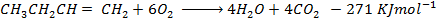
Data manipulation
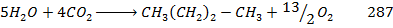
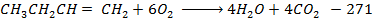
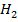 +
+ 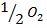
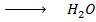 – 288
– 288
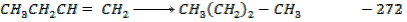
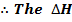 For the reaction is
For the reaction is 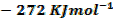
Example 5
Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction.
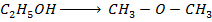
Given
Enthalpies of combustions are;-
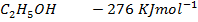
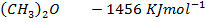
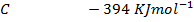
Heat of formation of water is 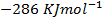
Solution
Required equation
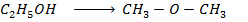
Data presentation 
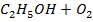
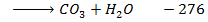
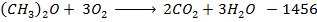
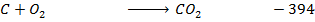
Data manipulation
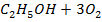
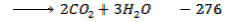
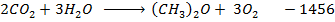
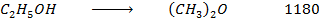
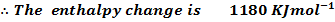
Example 6
Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction.
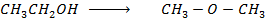
Given
Heat of combustion of 
Heat of combustion of 
Heat of combustion of 
Heat of combustion of 
Solution
Required equation
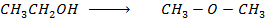
Data presentation
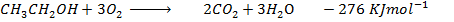
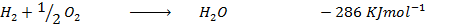
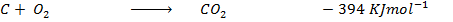
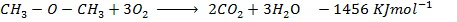
Data manipulation
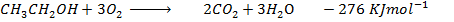
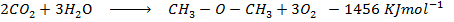
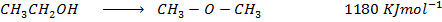
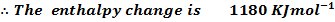
Example 7
(a) Define the following terms;-
(i) Enthalpy of sublimation.
Is the energy absorbed when one mole of solid atom is converted to gaseous atom.
(ii) Enthalpy of atomization.
Is the energy absorbed when a certain molecule or element is covered into gaseous atom.
(iii) Standard enthalpy of combustion.
Is the head given out when one mole of a substance is burnt in a given moles of Oxygen.
(b) The combustion of carbon disulphide is exothermic and the enthalpy of combustion of the compound is 1180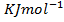 .
.
Given that carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide are exothermic compounds with enthalpies of formation of 405 and 293 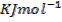 respectively.
respectively.
(i) Calculate the heat of formation of carbon disulphide.
(ii) comment on the stability of this compound at various temperature considering the results obtained in the light of Le-chaterlier`s principle.
Solution
Required equation
2S + C 
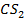
Data presentation 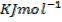
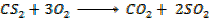 – 1108
– 1108
C + 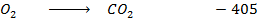
S + 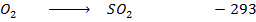
Data manipulation
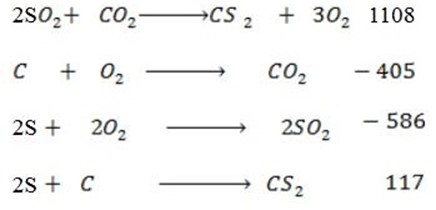
 The heat of formation of C
The heat of formation of C is 117
is 117 
ii) In high temperature the compound will be move stable.
Example 8
Given the following reaction;-
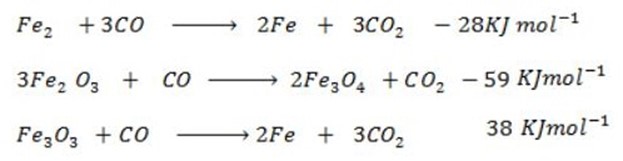
Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction 
Solution
Required manipulation