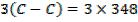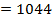2. CALCULATION OF ENTHALPIES
BASED ON BOND ENERGIES
BOND ENERGIES
Is the energy change which is obtained when one mole covalent bond is formed or broken of an atom.
Any reaction involves bond breaking and bond formation. Reactants bonds are normally broken while products bonds are formed.
Since the bonds energies are known then 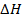 of the reaction can be calculated as the difference between broken bond energies and formed bond energies.
of the reaction can be calculated as the difference between broken bond energies and formed bond energies.
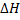 = B.B.E – F.B.E
= B.B.E – F.B.E
Where by;-
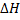 Is the heat change of reaction.
Is the heat change of reaction.
B.B.E is the broken bond energies.
F.B.E is the formed bond energies.
Example 1
(a) Define
(i) Bond energy.
Is the energy which is obtained when one mole of covalent bond is formed or broken of an atom.
(ii) Enthalpy of neutralization.
Is the heat given out when one mole of water is formed from the reaction between acid and base at standard state.
(b) Calculate the heat of formation of ethane given that:
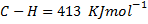
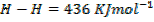
Solution
Required equation
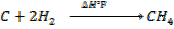
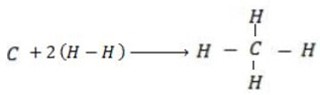
Broken bond energies
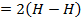
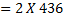
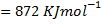
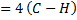
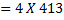
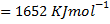
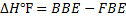
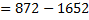
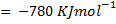
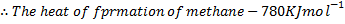
Example 2
Calculate the enthalpy of hydrogenation of ethane to ethane.
Given
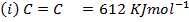
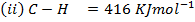
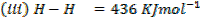
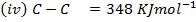
Solution
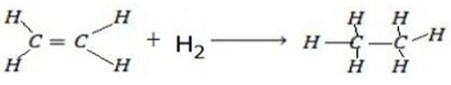
B.B.E F.B.E
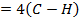
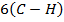
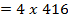
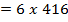
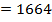
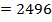
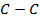
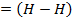
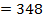 = 348
= 348
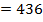
Total FBE = 2496
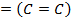 348 +
348 +
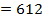 = 2844
= 2844
Total BBE = 436
612 + 1664
= 2712
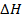 = BBE – FBE
= BBE – FBE
= 2712 – 2844
= -132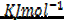
Example 3
Calculate the enthalpy of hydrogenation of prop -1 – yne to saturated if mean bond energies are: –
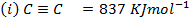
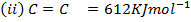
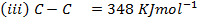
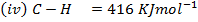
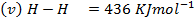
Solution
Required equation
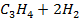
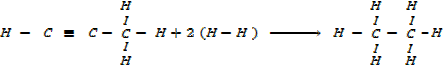
BBE
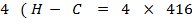
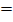 1664
1664
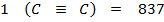


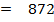
Total BBE = 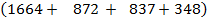
= 3721
FBE
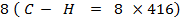

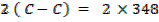

Total FBE 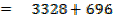

Then,
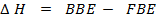
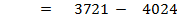
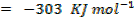
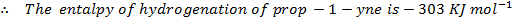
Example 4
Benzene under harsh condition undergoes hydrogenation recitation. Calculate the heat of hydrogenation of benzene if mean bond energies are;-
i) 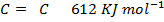
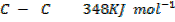
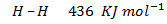
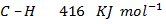
Solution
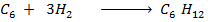
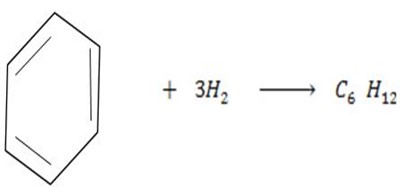
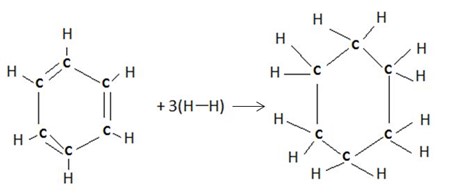

Therefore,
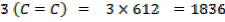
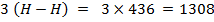
FBE
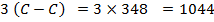
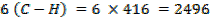
Heat of formation
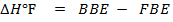
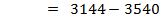
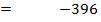
Example 5
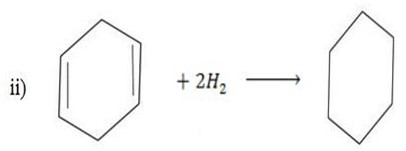
Use the data in example 4 above to calculate the enthalpy of hydrogenation of the following compounds.
i) 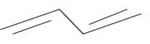 (iii)
(iii) 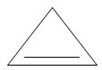
ii) 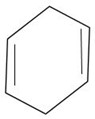 (iv)
(iv) 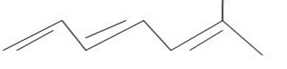
Solution
i) 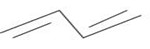
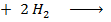
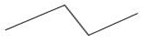
BBE
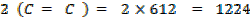
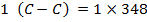
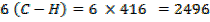
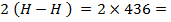 872
872
BBE 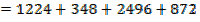
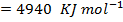
FBE
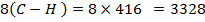
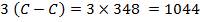
F B E 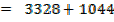
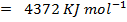
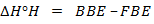
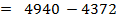
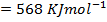
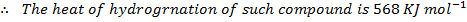
BBE
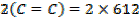
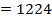
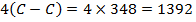
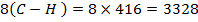
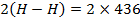
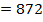
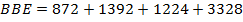
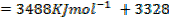
F.B.E
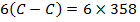
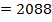
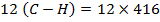
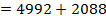
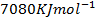
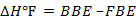
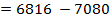
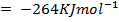
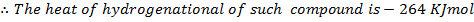
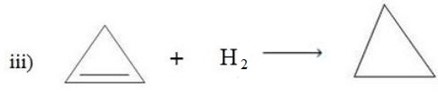
BBE
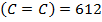
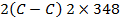
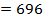
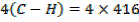
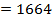
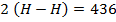
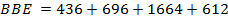
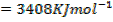
FBE