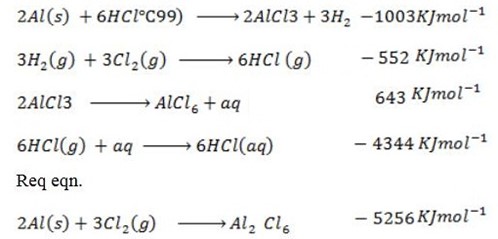HESS`S LAW OF CONSTANT HEAT SUMMATION
It State that,
“The total heat change of a chemical reaction is independent of the route taken”.
BORN HABER CYCLE
Is the cycle which is used to determine the heat of formation of a given compounds.
Example 1
a) Draw the born haber cycle for the formation of the following compounds;-
i) 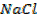 ii)
ii) 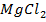
Solution
(i)
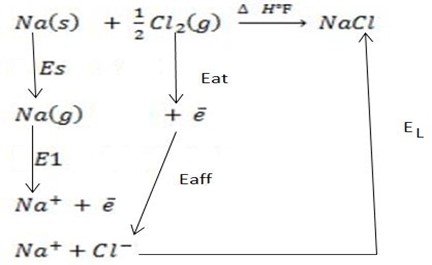
∴
ΔH°f = Es + EI + Eat + Eaff + EL
Where by,
Es is the sublimation energy.
EI is the Ionization energy.
Eat is the Atomization energy.
Eaff is the Electronic affinity energy.
EL is the lattice energy.
(ii)
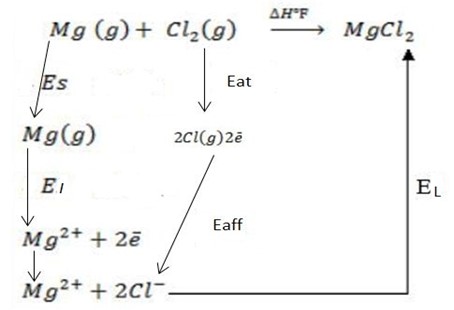
∴ ΔH°f = Es + EI + Eat + Eaff + EL
Where by,
Es is the sublimation energy.
EI is the Ionization energy.
Eat is the Atomization energy.
Eaff is the Electronic affinity energy.
EL is the lattice energy.
Example 2
Draw the born Haber cycle for the formation of the following;-
i) Aluminium Chloride ( AlCl3).
Solution
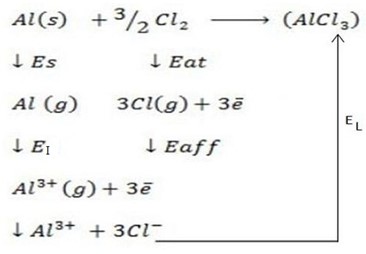
∴ ΔH°f = Es + EI + Eat + Eaff + EL
Where by,
Es is the sublimation energy.
EI is the Ionization energy.
Eat is the Atomization energy.
Eaff is the Electronic affinity energy.
EL is the lattice energy.

∴
ΔH°f = Es + EI + Eat + Eaff + EL
Where by,
Es is the sublimation energy.
EI is the Ionization energy.
Eat is the Atomization energy.
Eaff is the Electronic affinity energy.
EL is the lattice energy.
(iii) Aluminium oxide (Al2O3).
Solution
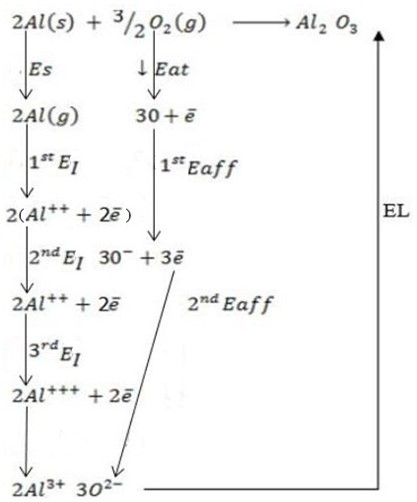
∴
ΔH°f = Es + EI + Eat + Eaff + EL
But, EI = 1st EI + 2nd EI + 3rd EI
Eaff = 1st Eaff + 2nd Eaff
Where by,
Es is the sublimation energy.
EI is the Ionization energy.
Eat is the Atomization energy.
Eaff is the Electronic affinity energy.
EL is the lattice energy.
iv) Calcium iodide (CaI2).
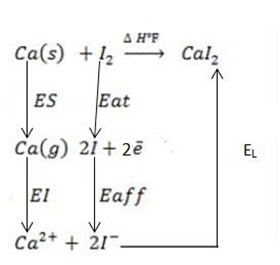
∴
ΔH°f = Es + EI + Eat + Eaff + EL
Where by,
Es is the sublimation energy.
EI is the Ionization energy.
Eat is the Atomization energy.
Eaff is the Electronic affinity energy.
EL is the lattice energy.
v) Potassium Bromide ( KBr).
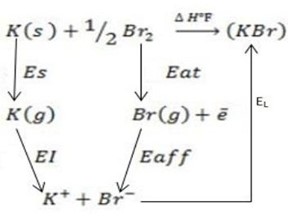
∴ ΔH°f = Es + EI + Eat + Eaff + EL
Where by,
Es is the sublimation energy.
EI is the Ionization energy.
Eat is the Atomization energy.
Eaff is the Electronic affinity energy.
EL is the lattice energy.
Example 3
a) What is “Born Haber cycle” as applied in energetic?
Solution
Born Haber cycle is the cycle which is used to determine the heat of formation of ionic compound which involves intermediate changes.
b) Construct born haber cycle for the formation of KCl.
solution
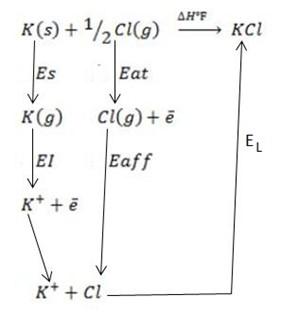
∴ ΔH°f = Es + EI + Eat + Eaff + EL
Where by,
Es is the sublimation energy.
EI is the Ionization energy.
Eat is the Atomization energy.
Eaff is the Electronic affinity energy.
EL is the lattice energy.
( c ) Using data below calculate the heat of formation of KCl.
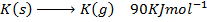
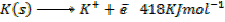
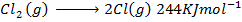
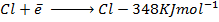
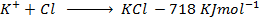
∴
ΔH°f = Es + EI + Eat + Eaff + EL
Given that,
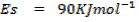
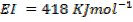
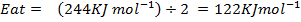
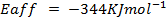
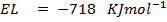
∴
ΔH°f = Es + EI + Eat + Eaff + EL
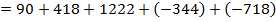
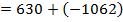
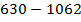
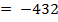
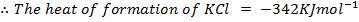
Example 4
(a) Define the following;-
(i) Atomization energy.
Atomization energy is the energy absorbed when a certain molecule or element is converted to gaseous atom.
(ii) Ionization energy.
Ionization energy is the energy required by the gaseous atom to release electron from its outer most shell.
(iii) Electron affinity.
Electron affinity is the energy requires when 1 mole of gaseous atom combine with one mole of electron.
(b) Use the following data and calculate the electron affinity of chlorine.
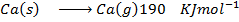
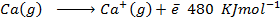
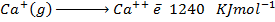
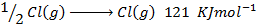
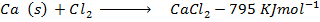
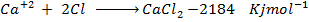
Solution
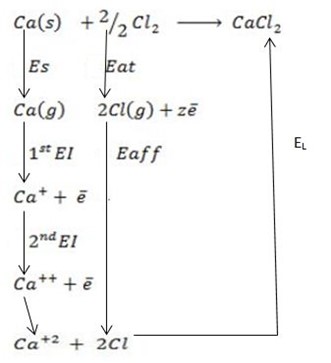
∴
ΔH°f = Es + 1st EI + 2 nd EI + Eat + Eaff + EL
Where
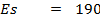
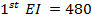
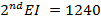
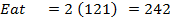
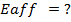
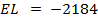
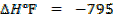
From,
∴
ΔH°f = Es + 1st EI + 2 nd EI + Eat + Eaff + EL
Eaff = ΔH°f – (Es + 1st EI + 2 nd EI + Eat + EL )
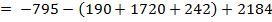
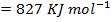
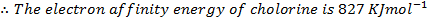
(d) Account for the differences in energies between;-
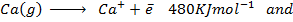
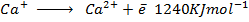
Answer
The difference in energies is due the fact that when the first electron is removed, the force of attraction becomes greater in second electron. Finally greater energy is needed to remove it from the atom. The energy is greater so as to overcome the force of attraction between the electron and the nucleus.
Example 5
1. (a) Define the following terms;-
i) Bond dissociation energy.
Bond dissociation energy is the e required to remove electron from the outer must shell of an atom.
ii) Enthalpy of dilution.
Enthalpy of dilution is the heat change when one mole of a compound dissolved in a given moles of water.
iii) Lattice energy.
Lattice energy is the heat given out when one mole of ionic compound is formed from its respective ions.
2. (a) Enthalpy of atomization.
Enthalpy of atomization is the energy absorbed when a certain gaseous molecule or elements converted to gaseous ions.
(b) State Hess`s law of constant heat summation.
It state that,
“If the reaction can take place in more than on rout, then the overall heat change is the same for which ever rout may be taken”.
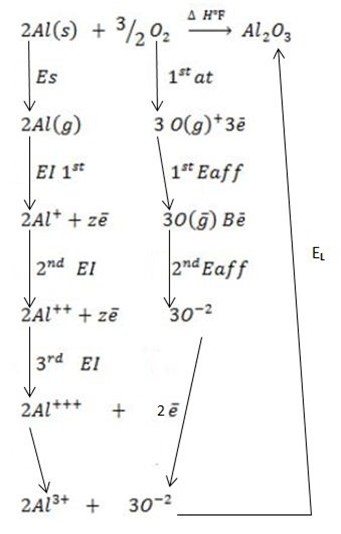
(c) (i) Draw a well labeled born Haber cycle for the reaction of formation of (Al2O3 ).
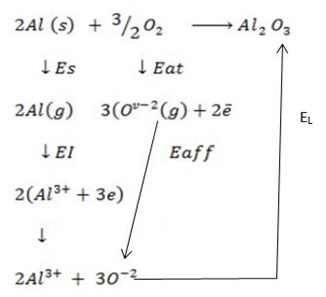
∴
ΔH°f = Es + EI + Eat + Eaff + EL
Where by,
Es is the sublimation energy.
EI is the Ionization energy.
Eat is the Atomization energy.
Eaff is the Electronic affinity energy.
EL is the lattice energy.
(ii) Calculate the heat of formation of (Al2O3) from the following;-

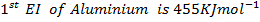
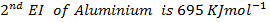
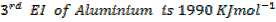
First electron affinity of oxygen is –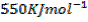
Second electron affinity of oxygen is 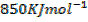
Lattice energy of 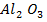 is
is 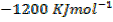
Atomization energy of oxygen is 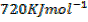
∴
ΔH°f = Es + EI + Eat + Eaff + EL
Where,
Es = 560 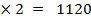
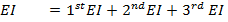
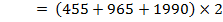
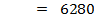
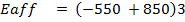
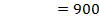
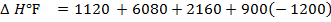
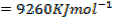
(d) Draw a born cycle for the formation of Al2Cl6 and calculate ΔH for the process.
2Al +3Cl3 → Al2Cl6 ΔH = ?
Given that,
i) 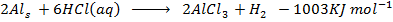
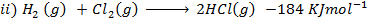
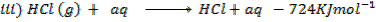
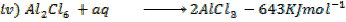
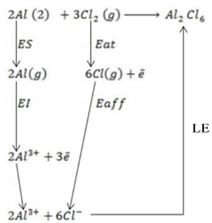
∴
ΔH°f = Es + EI + Eat + Eaff + EL
From the data,
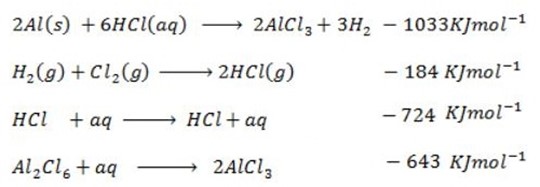
Data manipulation