CALCULATIONS OF ENTHALPIES BY USING ATOMIZATION DATA
During the reaction reactants are atomization (changed to atoms) while the product energy. Calculate from bond energy.
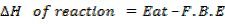
Example1
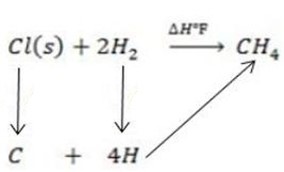
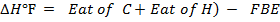
Example 2
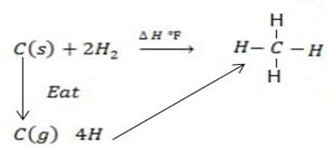
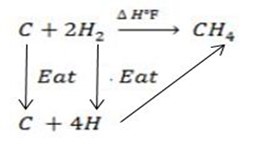
Calculate the following of formation of CH4 given that,
Enthalpy of atomization of carbon = 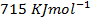
Enthalpy of atomization of hydrogen 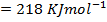
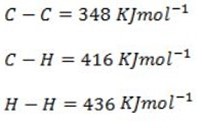
Solution
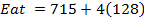
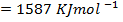
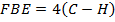
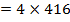
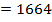
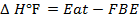
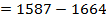
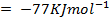
Example 3
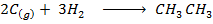
Use the information provided in the above example. Then calculate the heat of formation of ethane.
Solution
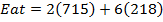
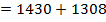
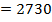
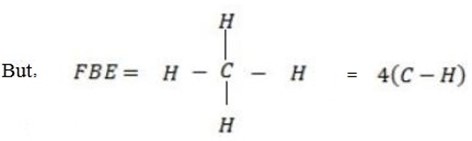
F.B.E
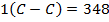
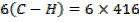
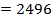
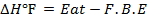
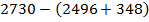
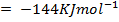
Example 4
The energy required to atomize 6g of carbon is 357.5 KJ. Calculate the energy required to atomize hydrogen atom. If the heat of formation of methane is 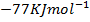 given that,
given that,
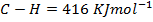
Solution
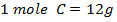
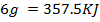
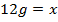
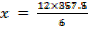
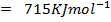
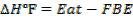
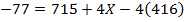
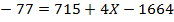
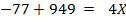
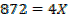
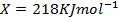
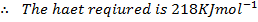
CALCULATION OF ENTHALPIES BY CALORIMETRY
Calorimetry Is the method determined the heat change reaction by the using calorimeter.
Example of enthalpies that can be determined by calorimetry method;-
i) Enthalpy of hydrogen.
ii) Enthalpy of neutralization.
DETERMINATION OF ENTHALPIES OF NEUTRALIZATION BY CALORIMETRY
What is neutralization reaction?
Neutralization reaction is the reaction between acid and base to give salt and water.
Example


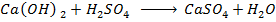
In this method the density of salt solution formed is assumed to be equal to the density of water.
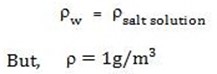
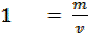
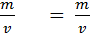
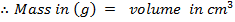
Quantity of that in this method can be calculate by using heat capacity ( C )and by using specific heat capacity ( c ) .
Let the quantity of heat be Q.
By using heat capacity
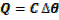
C = heat capacity.
By using specific heat capacity.
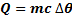
Where by 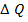 is change in temperature.
is change in temperature.
c = specific heat capacity.
If quantity of heat calculated is the same and 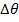 is also the same, then the relationship between c and C can be,
is also the same, then the relationship between c and C can be,
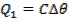
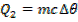
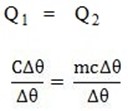
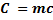
Enthalpy of neutralization is calculate with respect to the number of moles of water producer.
Reaction.
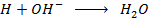
But number of moles of water depends on the moles of limiting reagent
QUESTION
What is limiting reagent?
Limiting reagent is the reactant compound in the neutralization reaction which have small number of moles.
Example 1
250c of NaOH of 0.4M were added to 250cc of the HCl of 0.4M in a calorimeter. The temperature of the two solutions and the calorimeter was
of NaOH of 0.4M were added to 250cc of the HCl of 0.4M in a calorimeter. The temperature of the two solutions and the calorimeter was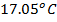 . The mass of calorimeter was 50g and its specific heat capacity was
. The mass of calorimeter was 50g and its specific heat capacity was 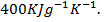 after the reaction the temperature rose to 19.5
after the reaction the temperature rose to 19.5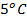
Assuming the specific heat capacity of all the solution is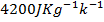 . Calculate the standard enthalpy of neutralization.
. Calculate the standard enthalpy of neutralization.
Solution
Data
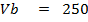
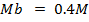
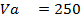
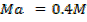
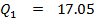
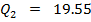
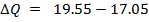
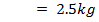
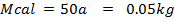
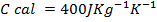
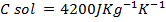
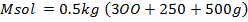
Reaction
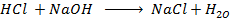
Limiting reagent
Base
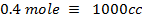
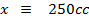
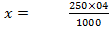
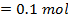
Acid
The same 0.1 mol
Both are limiting reagent.
Moles of water produced
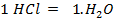
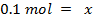
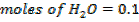
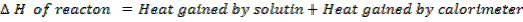
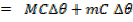
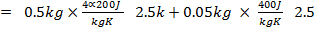 .
.
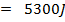
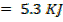
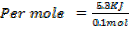
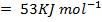
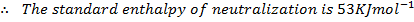
Example 2
Define
i) Heat of neutralization.
Is the heat given out when one mole of water is formed from the reaction between base and acid at standard state.
ii) Heat of Ionization.
Is the heat energy required to remove an electron from the outer most shell of a gaseous atom.
iii) Heat of sublimation.
Is the heating absorbed when one mole solid atom is converted to gaseous atom.
iv) Limiting reagent.
Is the reacted compound in the neutralization reaction which have small number of moles.
b) State Hess`s Law of heat summation.
It state’s that,
“If a reaction take place by more than are route the overall heat change is the same for which ever route may be taken”.
Question
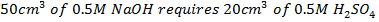 For neutralization. The reading was absorbed to rose temperature of both the calorimeter and the solution by 3.4k. Calculate the standard enthalpy of neutralization of
For neutralization. The reading was absorbed to rose temperature of both the calorimeter and the solution by 3.4k. Calculate the standard enthalpy of neutralization of 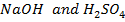 . Given that capacity of calorimeter is
. Given that capacity of calorimeter is 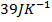 and specific heat capacity of the solution was 4.2
and specific heat capacity of the solution was 4.2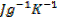 .
.