Is the branch of chemistry which deals with measurable quantities.
PARTS OF PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
The physical chemistry is studied under the following sub topics. These are
1. States of matter
2. Chemical equilibrium
3. Thermochemistry/ Energetics
4. Electrochemistry
5. Chemical kinetics
1. STATE OF MATTER
This is the form in which matter do exist. There are three states of matter. These are
a) Gaseous state
b) Liquid state
c) Solid state
A. GASEOUS STATE
This is the form in which matter do exist in motion.
PROPERTIES OF GASEOUS
Properties of gases are governed by kinetic theory of gases (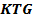 ).
).
THE KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
1. Kinetic theory of gases include the following points or postulates.
2. Gases contain large number of molecules which are in continuous random motion.
3. Molecules of gases are far away such that the force of attraction between individual molecules is negligible kinetic energy of the molecules is directly proportion to absolute temperature i.e the increase of temperature will causes the increases in kinetic energy of the molecules.
4. The values of individual molecules of gases is negligible compared to the volume of the container.
5. Pressure of the gas inside the container is due to the collision between molecules of the gas and the wall of the container.
6. The collision of molecules of gases are perfectly elastic that is kinetic energy is conserved (Kt before is equal to K.E after collision).
CLASSIFICATION OF GASES
Gases are categorized into two groups
These are
i) Ideal gases
ii) Real gases
i. IDEAL GASES
Ideal gases are gases which obey all assumption of kinetic theory and also they do obey the ideal gas equation
i.e PV = nRT.
Where by
P = Pressure of the gases
V = Volume of the gases
n = Number of moles of gases
R = Universal of gas constant
T = Temperature
ii. REAL GASES
Real gases are the gases which do not obey all the assumptions of kinetic theory of gases. Such assumptions are:
i. The volume of individual molecules of the gases is negligible compared to the volume of the container.
ii. Molecules of gases are far away such that the force of attraction between individual molecules is negligible.
From kinetic theory of gases, scientist comes up with the formula / equation that is governed by the theory the equation is
PV =  Nm
Nm 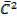
Where by
P = Pressure of the gas
V = Volume of the gas
N = Number of the molecules of the gas
m = Mass of molecules of the gas
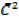 = Means square speed of the molecules
= Means square speed of the molecules
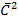 = Is given by
= Is given by
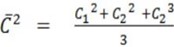
DEDUCTION OF GASES LAWS FROM KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
This is the process by which gas laws are obtained or derived from kinetic theory of gases.
Such laws to be deduced are:
i. Charles’s law.
ii. Boyle’s laws.
iii. Graham’s law of diffusion/ effusion.
iv. Dalton’s law of partial pressure.
v. Avogadro’s law.
1. DEDUCTION OF CHARLES’ LAW
It state that ” At constant pressure the volume of a fixed mass of gas is directly proportion to the absolute temperature .
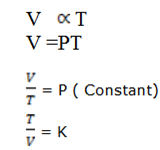
i.e The ratio of volume of temperature is constant.
Thus,
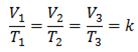
From kinetic theory of gases
PV =  Nm
Nm 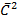
For any gas to obey charle’s law

V = k 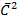
From kinetic theory of gases
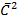 = T
= T
V = KT
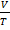 =
= 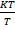
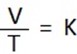
QUESTION
a) Define the following terms
i) Real gases.
ii) Ideal gases.
b) State Charles’s law.
c) Deduce Charles law from kinetic theory of gases.
2. DEDUCTION OF BOYLE’S LAW FROM KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
It state that ” At constant thermodynamic volume of a fixed mass of gas is inversely proportional to pressure.
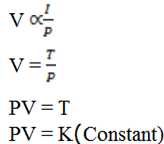
From kinetic of gases
PV =  Nm
Nm 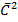
From gas to obey Boyle’s law
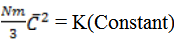
PV = K
Hence Boyle’s law deduced
3. DEDUCTION OF GRAHAM’S LAW FROM KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
Graham’s rate of diffusion or effusion: It states that,
“The rate of diffusion or effusion of gaseous material is inversely proportional to the square root of its density”
If rate is represented by r and density by ρ
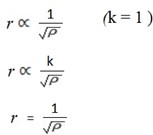
For two gases which are G1 and G2
For Gas1
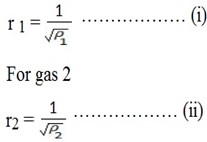
Comparison
For the ratio of their rates
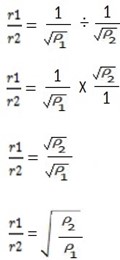
In terms of their density
If the volume is constant
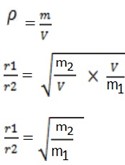
In terms of their masses
4. DEDUCTION OF GRAHAM’S LAW
From Graham’s law
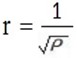
From kinetic theory of gases
Pv =  Nm
Nm 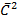
3PV = Nm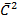
But Nm = m
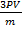 =
= 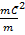
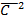 =
= 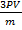
For any gases to obey graham’s law
3P = k
constant = 1
3P = 1
Now,
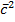 =
=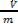
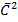 =1/
=1/ 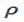
But,
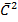 = r2
= r2
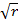 2 =
2 = 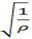
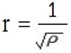
Hence grahams law deduced