1. LOWERING OF VAPOR PRESSURE
Vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by vapor against the atmospheric pressure.
Lowering of vapor pressure: Is the difference between the original pressure of liquids solvent (Po) and the pressure of the solution.
Effect of solute on the vapor pressure of the solvent
When solute particles are added in the solvent, the vapor pressure of the solution is lowered.
When solute particles dissolve in a given solvent normally they collide with the solvent molecule and hence prevent / decrease the number of solvent molecules that escape from liquid phase to vapor phase. This causes the decrease amount of vapor above the solution and normally causes the decrease in vapor pressure.
Relative lowering of vapor pressure
Relative lowering of vapor pressure is the ratio lowering vapor pressure to the vapor pressure the solvent.
RAOULT’S LAW OF VAPOR PRESSURE
It states that “The relative lowering of vapor pressure is proportional to the mole fraction of the solute added”
Mathematically
Let P o be the vapor pressure of the solvent
P be the vapor pressure of solution
Xs be the mole fraction of solute
From Raoult’s law of vapor pressure
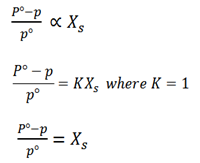
For mole fraction of solute
Let n be number of mole solute
N be number of mole solvent
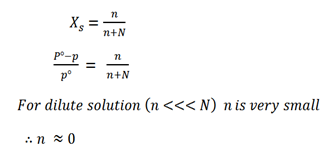
The molar mass of solute can be determined
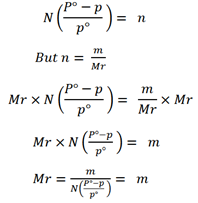
Example 1.
What do you understand by the term ” Colligative property”?
Colligative property is the property of a liquid which change depending on the number of properties of solute added but not on the nature of the solute.
A solution is prepared from 90g of water and 10.6g of non – volatile solute. If the vapor pressure of the solution at 60oC was found to be 0.1867 atm. Calculate the relative molecular mass of solute. Given that V. P of H2O at 60oC was 0.1966 atm
Solution
Mass of water (solvent) = 90g.
Mass of non – volatile solute = 10.6g.
Vapor pressure of solution (P) = 0.1867 atm.
Vapor pressure of solvent Po = 0.1966 atm.
Recall
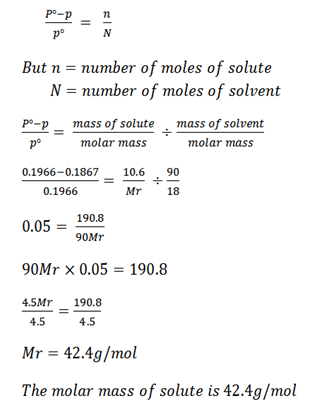
Example 2.
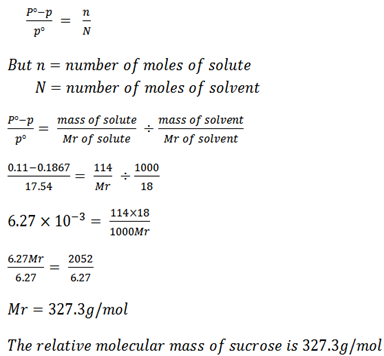
When 114g of sucrose are dissolved in 1000g at water the vapor pressure was lowered 0.11mmHg . Calculate the relative molecular mass of sucrose if the vapor pressure of water at 20oC was 17.54 mmHg.
Solution
Mass of solute = 114g
Mass of solvent = 1000g
Lower vapor pressure = 0.11mmHg (Po – P)
Vapor pressure of solvent = 17.54mmHg
Recall
Example 3.
Calculate the vapor pressure lowering caused by the addition of 100g of sucrose of molar mass 342g/mol to 1000g of water if the vapor pressure of pure water at 25oC is 23.8 mmHg.
Solution
Mass of solute = 100g
Mass of solvent = 1000g
Molar mass of solute = 342g/mol
Molar mass of solvent = 18g/mol
Vapor pressure of solvent = 23.8mmHg

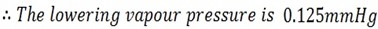
Example 4.
The vapor pressure of ether (molar mass 74g/mol) is 442mmHg at 293k. If 3g of compound A are dissolved in 50g of ether at this temperature, the vapor pressure falls to 426mmHg. Calculate the molar mass of A assuming that the solution of A in ether is very dilute.
Solution
Mass of solute = 3g
Mass of solvent = 50g
Vapor pressure of solution P = 426mmHg
V.p of solvent Po = 442mmHg
Mr of solvent = 74g/mol
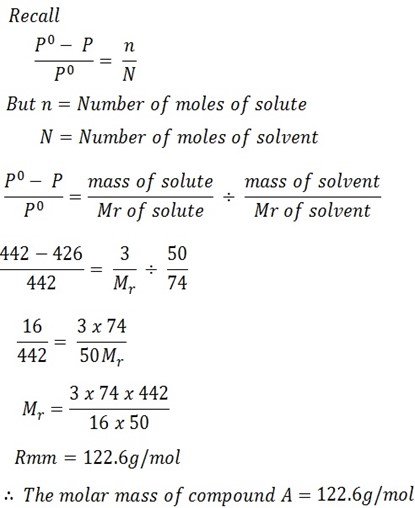
Example 5.
18. 2g of urea is dissolved in 100g of water at 50oC . The following of vapor pressure produced is 5mmHg. Calculate the molecular mass of urea if the vapor pressure of water at 50oC is 92mmHg.
Solution
Mass of solute = 18.2g
Mass of solvent = 100g
Lowering vapor pressure (Po – P) = 5mmHg
V . p of solvent (Po) = 92mmHg
Required to find Mr of solute
