Probability nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution is the nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution which include two main parts.
i) Discrete probability nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution function.
ii) Continuous probability nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution function.
I. DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION FUNCTION
This is the probability function (variable) which assumes separate value E.g x2 = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4…….
It consists of the following important parts;
i) Mathematical expectation
ii) Binomial probability nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution
iii) Poisson probability nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution
i) MATHEMATICAL EXPECTATION
Consider the values
x1, x2, x3,…….xn with frequencies, f1, f2, f3….. fn. respectively as shown below
| X | X1 | X2 | X3 | …………………………… | xn |
| f | f1 | f2 | f3 | …………………………… | fn |
edu.uptymez.com
From
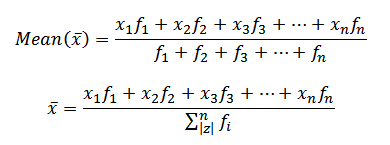
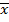 =
= 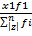 +
+ 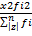 +
+ 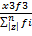 + …… +
+ …… + 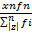
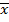 =
= 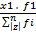 +
+ 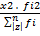 +
+ 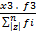 + …… +
+ …… + 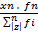
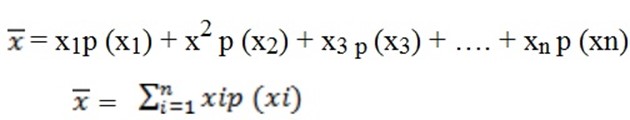
Therefore;
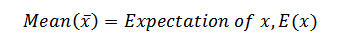
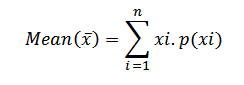
E (x) = 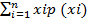
Note:
1. E (x) = 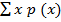
2. 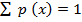
VARIANCE AND STANDARD DEVIATION
Variance
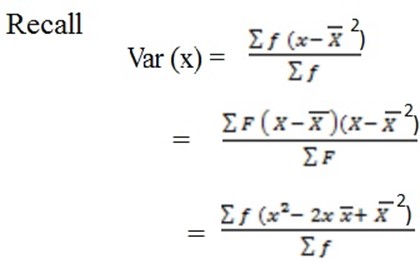
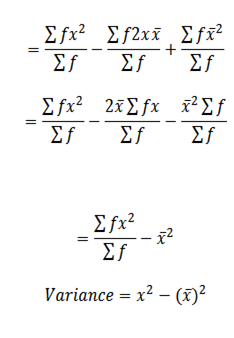
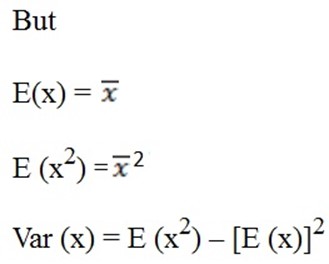
Recall
Standard deviation, S.D = 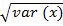
S.D = 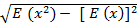
Question
i) Given the probability nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution table
| x | 8 | 12 | 16 | 20 | 24 |
| P (x) | 1/8 | 1/6 | 3/8 | 1/4 | 1/12 |
edu.uptymez.com
Find i) E (x)
ii) E (x2)
iii) 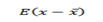
soln
Consider the nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution table below
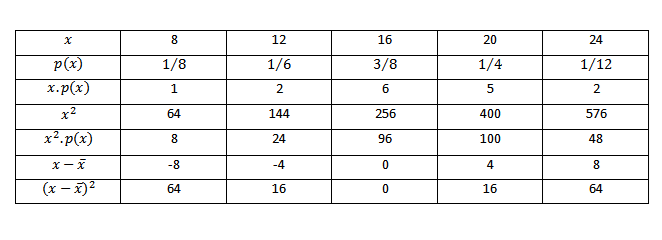
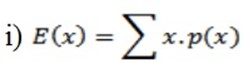
= 1 + 2 + 6 + 5 + 2
E(x) = 16
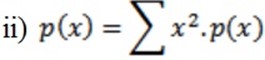
= 8 + 24 + 96 + 100 + 48
E (x2)= 276
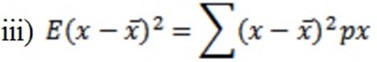
= 64(1/8) + 16 (1/16) + 0 (3/8) + 16 (1/4) + 64 (1/12)
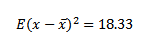
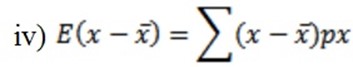
= -8 (1/8) + -4 (1/16) + 0 (3/8) + 4 (1/4) + 8 (1/2
=1 – 2/3 + 1 + 2/3.
= 0
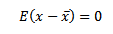
Note
Always
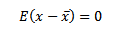
Proof
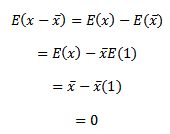
= 0 proved
OR
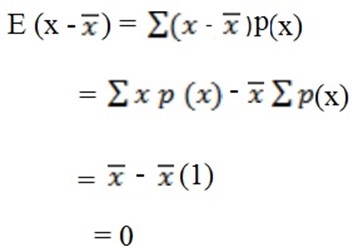
Prove
2) Given the nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution table
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| P (x) | K | 2k | 3k |
edu.uptymez.com
Find (i) The value of k
Soln
i) From the given table
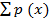 = 1
= 1
K + 2k + 3k = 1
6k = 1
K = 1/6
ii) The expected value
– Consider the nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution table below;
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| P (X) | 1/6 | 1/3 | 1/2 |
| X. PX | O | 1/3 | 1 |
edu.uptymez.com
Hence
E (x) = 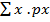
= 0 + 1/3 + 1
= 4/3
The expected value is E (x) = 4/3
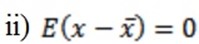
3) In tossing a coin twice where x – represents the number of heads, appear, and construct the probability table for random experiment, form the table, calculate the expected value.
Tossing a coin twice
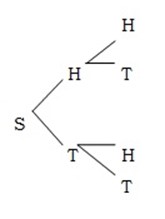
S = {HH, HT, TH, TT}
n (s) = 4
Probability nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| P (x) | ¼ | ½ | ¼ |
| Xp (x) | 0 | ½ | ½ |
edu.uptymez.com
X = 0
Hence
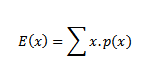
= 0 + ½ + ½
E (x) = 1
The expectation of x is E (x) = 1
4. A class consists of 8 students. A committee of 4 students is to be selected from the class of which 4 are girls. If x – represent the number of girls, construct the probability table for random variable x and from the table, calculate the expected value.
– Consider the probability nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution below;
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P (x) | 1/70 | 16/70 | 36/70 | 16/70 | 1/70 |
| Xp (x) | 0 | 16/70 | 72/70 | 48/70 | 4/70 |
edu.uptymez.com
For x = 0
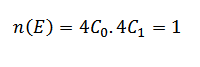
n (s) = 8C4 = 70
P (E) = 1/70
For x = 1
n (E) = 4C1. 4C3 = 16
P (B) = 16/70
For x = 2
n (E) = 4C2. 4C2 = 36
P (B) = 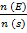 =
= 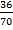
For x = 3
n (E) = 4C3. 4C1 = 16
P (E) = 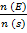 =
= 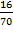
For x = 4
n (B) = 4C3. 4C0 = 1
p (E) = 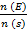
p (E) = 1/70
Hence
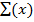 =
= 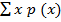
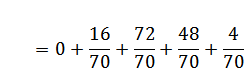
= 2
The expectation of x is 2 E (x) = 2
05. Suppose a random variable x takes on value -3, -1, 2 and 5 with respectively probability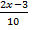 ,
, 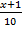 ,
, 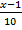 and
and 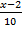 . Determine the expectation of x
. Determine the expectation of x
From the given data
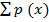 = 1
= 1
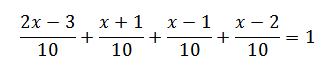
2x – 3 + x + 1 + x – 1 + x – 2 = 10
5x – 5 = 10
5x = 15
X = 3
Consider the nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution table below;
| X | -3 | -1 | 2 | 5 |
| P (x) | 3/10 | 4/10 | 2/10 | 1/10 |
| Xpx | -9/10 | -4/10 | 4/10 |
edu.uptymez.com
Hence,
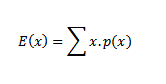
= -9/10 + -4/10 + 4/10 + 5/10
= -4/10
E (x) = -0.4
06. The random variable x has a probability nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution of 1/6 + 1/3 + 1/4.
Find the numerical values of x and y if E (x) = 14/3
Soln
From the given nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution table
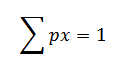
1/6 + 1/3 + 1/4 + x + y = 1
x + y = 1 – 1/6 – 1/3 – ¼
x + y = ¼ ……..i
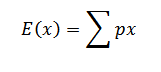
14/3 – 1/3 – 1 – 5/4 = 7x + 11y
25/12 = 7x + 11y
7x + 11y = 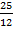 …..ii
…..ii
Solving i and ii as follows;
11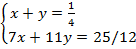
4x = 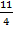 –
–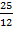
X = 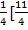 –
– 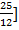
X = 1/6
Also
X + y = ¼
1/6 + y = ¼
Y = ¼ = 1/6
Y = 1/12
The numerical values of x and y are such that x = 1/6, y = ½
07. A student estimates his chance of getting A in his subject is 10%, B+ is 40%, B is 35% C is 10%, D is 4% and E is 1%. By obtaining A , the students must get % points for B+, B, C, D and E, he must get 4, 3, 2, 1 and 0 respectively. Find the student’s expectation and standard deviation.
Consider the nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution below;
| A | B+ | B | C | D | E | |
| X | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| P (x) | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.35 | 0.1 | 0.04 | 0.01 |
| X P (X) | O.5 | 1.6 | 1.05 | 0.2 | 0.04 | 0 |
| X2 | 25 | 16 | 9 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
edu.uptymez.com
From the table
E (x) = 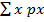
= 0.5 + 1.6 + 1.05 + 0.2 + 0.04 + 0
= 3.39
The student expectation is E (x) = 3. 39
Also
S.D = 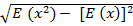
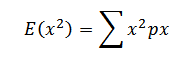
= 2.5 + 6.4 + 3.15 + 0.4 + 0.04 + 0
= 12.49
S.D = 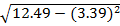
S.D = 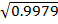
S.D = 0.99895
The standard deviation is 0.99895