General introduction
The concept of commerce
The word commerce originates from two Latin words
(i) “CUM” which means with
(ii) “MERX” which means “MERCHANDISE”
The term refers to any study or activities dealing with merchandise. The word merchandise means things/ goods/ commodities bought and sold for gain of profit.
DEFINITION OF COMMERCE
Commerce is the subject which deals with exchange and nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution of goods and services in order to satisfy human needs or wants.
Commerce is a branch of production which concerned with exchange and nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution of goods and services from the producer to the consumer i.e. from the point of production to the profit of consumption.
Commerce is also known as “BUSINESS ECONOMICS” that means it is an art of economic activities which is mainly concerned with the exchange and all other activities which facilitate such exchange.
Exchange – is the process of buying and selling of goods and services
Distribution- movement of goods and services from where they are produced or found to where they are needed in order to satisfy human needs or wants.
THE MEANING OF SCOPE OF COMMERCE
The scope of commerce means area of study covered in commerce. It comprise the study of all activities involved in the transfer (nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution) of goods and services from producer to consumer.
These activities include trade, transportation, communication, advertising, warehousing, banking and insurance,
The scope of commerce therefore covers the following………
(i) A study of trade, which is the mainly activity in the nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution and services.
(ii) A study of auxiliary service (aids to trade) that make trade possible.
(iii) A study of how best trade and aid to trade could be organized so as to satisfy the needs of consumer in the possible and most efficient way.
 The scope of commerce can be illustrated by the chart below which shows the trade and Aids to trade.
The scope of commerce can be illustrated by the chart below which shows the trade and Aids to trade.
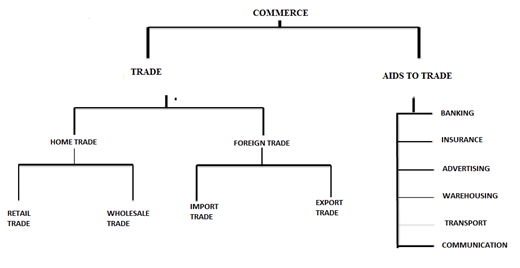
TRADE AND AIDS TO TRADE
1. 1. TRADE
Trade – refers to the buying and selling of goods and services with the aim of generating profit.The person who engages in trading activities is known as trader.
Trade is subdivided into two main branches
(i) Home trade (Internal trade).
(ii) International trade (foreign trade).
(a) HOME TRADE
This is buying and selling of goods and services within one country.
Home trade is divided into two main branches
(i) Retail trade.
(ii) Whole sale trade.
(I) RETAIL TRADE
This is buying goods in large quantities from whole sellers or producer and selling them in small quantities directly to the final consumers.
A person who engages in this type of trade is known as a retailer or retail trade.
(II) WHOLE SALE TRADE
This is the buying of goods from producers or manufacturers in a very large quantities and selling them to the retailers.
A person who engages in this type of trade is known as a wholesaler or wholesale trade.
(b) INTERNATIONAL TRADE (FOREIGN TRADE)
This is the trade between one nation and other nation it consists of all trading activities that involves exchange across national boundaries.
Foreign trade is divided into two main branches
(i) Export trade.
(ii) Import trade.
ENTER PORT TRADE
It means buying goods from one country for purpose of re-exporting/selling to another country. It is also known as – RE-EXPORT TRADE.
(i) EXPORT TRADE
This is the selling of goods and services to other countries e.g. Tanzania selling coffee as its export. Goods and services sold to other countries are known as exports.
The person or countries which carry out this type of trade is known as importer.
(ii) IMPORT TRADE
This is the buying of goods and services from other countries e.g. Tanzania buys oil as its import.
Goods and services bought from other countries are known as imports.
The person or country which carryout this type of trade is known as importer.
2. AIDS TO TRADE (Auxiliary services)
Aids to trade are all those activities which assist or help and facilitate in carrying out trade to go smoothly. they include the following:
1. TRANSPORT
This refers to the physical movement of goods and people from one place to another. The chief form of transport is land. (Roads and Railways) water and air transport assist trade by distributing raw material to manufacturers, semi – finished goods to finished goods.
This kind of transport which is road, is normally used by countries which have no harbour like Uganda, Zambia etc.
2. COMMUNICATION
Is the art of spreading or transmitting information and ideas from one point or person to another. commercial information between producer and consumer can be transmitted by means of press, wireless , radio and television.
3. WAREHOUSING
This process of storing and protecting in a warehouse until they are demanded or needed. Storage of goods make them to be available when they are required and also protect them from being stolen, going bad due to extreme weather conditions and from other hazards.
4. INSURANCE
Insurance is a system of pooling risks together by contributing small sums of money to a common pool which in long run compensates those persons who suffer the actual loss.
All business activities are exposed to a number of risks. Goods may be stolen, catch fire, be damaged in accidents. Sink in the sea etc.
Insurance undertakes to compensate this business which incurs losses from the risks insured.
5. BANKING
Banks are institutions which aim at assisting traders by safeguarding their money.
Leading them money in a form of loans and overdrafts and also provide efficient, safe and convenient method of payment using cheques and other means.
6. ADVERTISING
This is the act of making goods and services known to the public. the aim is mainly to inform, persuade and remind potential consumers about the availability of goods or services into the market.