What is Speaking?
Is simply the act of talking which maybe in either a formal or informal situation.
This kind of speech one would decide to undertake would depend on the relationship one has with audience, also the way you speak tells people more about you. Whenever one initiate communication its because he/she want to deliver something that means there must be intention of that communication, to wake your speaking more effectively and successful there many factor to be observe but the most important things will be determined by how you pronounce words, stressing them and the appropriate intonation.
PRONUNCIATION
Every language in this would has its sound system hence has it’s the way of pronouncing them. Linguists use special alphabet called phonetic symbols to represent sound or phonemes. This symbol are enclosed in slanted lines [//]. Some of this symbol are normal alphabet letters like /S/,/Z/,/t/,/d/,/k/,/g/,/f/,/v/ etc but others are different from normal alphabet letters we know
e.g. -/^/,/æ/,/ÊŠ/,/dÊ’/,/3:/,/ʃ/,/ð/,/Å‹/,/tʃ/,/Ê’/,/θ/
It is in this point then we are going to learn how to pronounce words correct.
See how we can pronounce the following words
-cat /cut
/kæt/ k^t/
-shoot/shut
/∫ut/∫^t/
-See/sea
/si//si/
-heart/ hurt
/cha:t//h3:t/
As you have observed the example given, there are some word who have different spelling but pronounced the same and those which have slightly different in spelling as well as in pronunciation
Sounds are shown by using phonetic symbols that are enclosed between two slanted lines // e.g. caught /kÉ”:t/
There are two main types of British standard English phomes namely, vowel and consonants
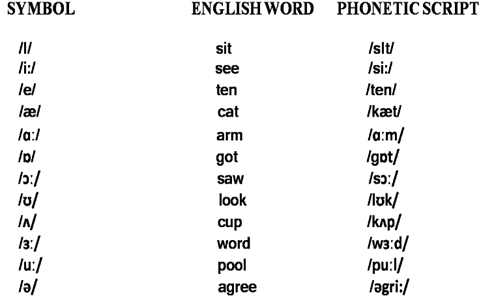
I.VOWELS
There are three kinds of monophthong diphthongs and triphthongs
i. Monophthongs (pure vowels) there can be long or short
TASK
Transcribe the following words;
- doctor
- work
- hurt
- money
- room
- just
- small
- pull
- put
- read
- chest
- kill
- feet
- market
edu.uptymez.com
ii. Diphthongs
Two short vowel sounds that are combined and pronounced as one
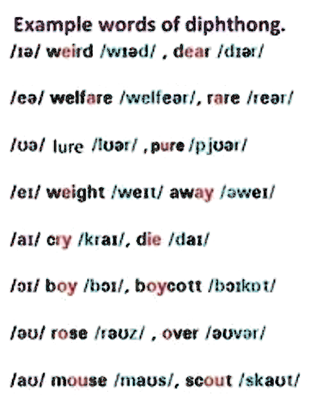
TASK
Read the following pronunciations then write them in normal letters:-
/meIn/laIt/,/heIt/,leIt/,/streIt ;
/na┧n/t┧∂/we∂/meI,/eIbl/,/eIt/
Sometimes we combine three sounds which are then pronounced as one .These are diphthong plus schwa sound /∂/ for example:-
/eI∂/ in words like player /pleI∂/, layer/ leI∂/
/∂I2/ in the words like higher /haI∂/, tire/taI∂/
/∂I∂/ in the words like soya /s∂I∂/
/a┧∂/ in the words like hour/a┧∂/,flower/fla┧∂/
/∂┧∂/ in the words like lower/l∂┧∂/,
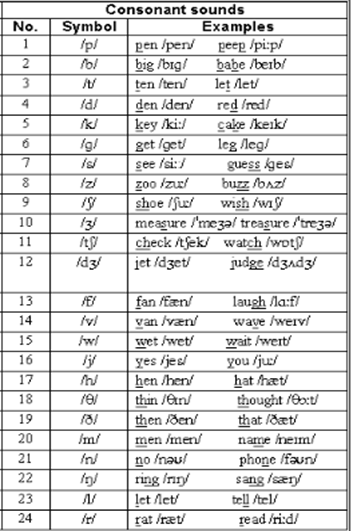
II. CONSONANTS
There are twenty four consonants sounds in British standard English . The following are the examples and sounds.
Test yourself.
Show phonetic transcription of the following sentences.
- They are going to see them today.
- She will help you.
edu.uptymez.com
3. That man is very clever.
4. We are going to meet her again.
5. The management will take it.
STRESS AND INTONATION
Are all concerned with perception or relative prominence.
STRESS
A word is made up of individual sound, within those sounds are combined, they form a syllable e.g /d/ /e×–/ /t/= date/ deIt/ i.e a one syllable word.
So a word can be of one syllable or more than one syllable e.g.- “selection” /s×–lek∫n/ has three syllabi. In pronouncing a word which has more than one syllable you will find that one syllable receive more energy and it is heard than others.
Now the one which receive prominence than the other is what we call a stressed syllable and it is shown by the mark (‘)behind the stressed syllable.
Observe the following words, the capitalized syllable is the one which receive more effort in pronunciation.
Phonemic – Pho.NE.mic
Movement – MOVE.ment
Moment – MO.ment.
Supplementary- Suple.MEN.tary.
Tremendous – tre.MEN.dous
Examination – examination.
Meeting – ME.E.ting
Thus,
Stress: Is the degree of emphasis given to a sound or syllable in speech.
OR
Is the prominence with which one part of a words or of a longer utterance is distinguished from other parts.
NB
Every word has primary stress [‘]some longer words have another stress which is not strong as the primary one, this stress is called Secondary stress. It is marked by [Ù«]. Study the following words.
Understand /,Ù¨nd∂×™stænd/
Contribution /,kontriÙ¡bju∫n/
Controlled /,k∂nÙ¡tr∂┧ld/
Graphology /,græÙ¡∫ol∂d3×–/
Machinery /,m∂Ù¡∫inkt/
Disconnect /,d×–sk∂Ù¡nekt/
In the examples given above the high vertical stroke[‘] before the syllable is for primary stress and the low vertical stress (,)before the syllable is for secondary stress [,].
Stress within a word
Native words and early French adoptions tend to have the main stress on the root syllable and to keep it there, regardless of the affixes that word formation may add.
E.g.:- ‘Kingly, ‘Kingliness, Un’kingliness
‘Stand- ‘Standing
Under’standing
‘Passion-‘Passionately
dis’passionate
With more recently adaptations and coinages especially those based on words from the classical languages, the place of the stress varies according to the affixation.
For example.
| Word | Antepenultimate | Penultment |
| ×™telegraph ×™photo ×™transport ×™argument |
te×™legraphy ph×™otography trans×™portable argu×™mentative
|
tele×™ graphic photo×™ graphic transpor’tation argumen’tation
|
edu.uptymez.com
Similar penultimate with adjectival –ic
‘Phoneme pho’nemic
E’conomy eco’nomic
E’mblem emble’matic
S’ympathy sympa’thetic
Antepenultimate with-ity (noun) or adjectivival-ian
E.g.: U’nanimous Una’nimity
‘library lib’rarian
‘grammar gram’marian
‘curious curi’osity
U’tility utili’tarian
‘Cromwell crom’welian
Stress and Meaning of words.
A fairly numerous set of words that can oparate without affixial change as a noun or adjective on the other hand and as a verb on the other have an accentual difference in the two function.
For example.
‘conduct /kondÙ¨kt/ (n)
‘contact / ×™kontrækt/ (n)
‘attribute/×™ætribjut/ (n)
‘present /×™preznt/ (adj)
‘impact /×™×–mpækt/ (n)
‘insert /×–ns3:t/ (n)
‘absent /×™æbsent (adj)
‘record /×™rekod/ (n)
Stress and Compound words.
Corresponding compound nouns are generally stressed on the first element but with a strong secondary stress on the second element.
When such compound, the primary and secondary stress is redistributed to give the same rhythm.
E.g.:’Light,house –’lighthouse,keeper.
‘Bed,room -×™bedroom ,chamber
Compounds words which are not nouns are stressed on the second element.
E.g: ,Back ‘fire (V)
,Hence ‘forth (Adj)
,Knee ‘deep (Adj)
,Flat ‘footed (Adj)
NB: Some examples are variable
,field’Marshal Or
‘Field ,Marshal
,Over ‘seas Or
‘Over ,seas
In any case, the stress often shifts from second component to first component when the compound is being used attributive in a noun phrase.
E.g.: The room is ,down ‘stair.
A’down ,stairs ‘room
His work is ,first ‘class
His ‘firstclass ,work
Function of stress
- To provide a way of distinguish degree of emphasis or contrast in sentence or line.
- To make word understandable.
- It also serves to differentiate words that are similar e.g.: REcord (N) and reCOrd (V)
- Helps us focus our listener’s attention on what is most important in our message.
edu.uptymez.com
Grammatically or communicative function i.e. distinguish between statement and question.
E.g. your name is Asha (statement)
Your name is Asha? (Question)
It’s raining (statement)
It’s raining? (Question)
Generally, pronunciation, Stress and intonation are very important component in communication.
As we have seen that, stress makes the word understandable, point of emphasis but also it differentiates words which are similar. Likewise intonation as it tells us how to say things (message) rather than what we say.
Pronunciation also play a very great role in communication as poor pronunciation of words may mislead the listeners, take an example of the following words.
Laugh /rÙ¨f/ instead of /lÙ¨f/
Read /lid/ instead of/rid/
Lead /rid/ instead of /lid/
TONE
Refer to the distinctive pitch of voice (high or low) during utterance.
It is a feature of intonation which affects the system meaning as well as grammatical categories of sentences or calves (utterances) in spoken language.
Types of tone
In spoken language, there are four major types of tone
- Fall/ falling tone (\)
edu.uptymez.com
This occurs in intonation of a syllable or longer utterance in which the pitch changes from relatively high to relatively low.
This tone has the following uses
- It is used to make statements that are complete and definite
edu.uptymez.com
E.g.:- they arrived today.
This boy is our neighbor.
It was done accidentally.
He came and left.
- It is used in making the commands
edu.uptymez.com
E.g.: – take the chair
Leave me alone
Eat that food
Go out
- It is used in making the question that are neither polite nor impolite
edu.uptymez.com
E.g.:- what are you doing?
Where do you live?
How did you do it?
- It is used in making exclamations or exclamatory sentences.
edu.uptymez.com
E.g.: – wonderful
What a beautiful lady
Oh my god
- It is used in tag question meant to force the listener agree with the speaker
edu.uptymez.com
E.g.:- we are tired, aren’t we?
She didn’t come here yesterday, did she?
2. Rise/ Rising tone (/)
This occurs when the pitch change from relatively low to relatively high (the pitch arises at the end of the Utterance)
This tone has the following uses
- It is used for yes/ no question
edu.uptymez.com
E.g.:-Do you know what happened in South Africa recently?
Oh no, can you kindly tell me about that
Have you seen my father over there?
Yes, I have
- It used for statements intending to be questions
edu.uptymez.com
E.g.: – your brother came yesterday
We were supposed to do the test yesterday
You did it
- It is used when giving request
edu.uptymez.com
E.g.:- Given me a glass of water please
Wait for me for a minute
May you please lend me your pen
- It is used for commands intending to be requests
edu.uptymez.com
E.g.:- open the door
Don’t disturb me
Go to the market and don’t be late
- It is used in incomplete statements
edu.uptymez.com
E.g.:- If James comes here ……………………….. (Tell him I’ll solve the problem)
Unless he arrives earlier ………………….. (I will call him)
When he came here yesterday ………… (I was out)
3. Fall – rise tone
This tone occurs when the pitch fall and then rises again.This tone has the following uses
- It is used for statements which show reservation or only particular agreement.
edu.uptymez.com
E.g.:- A – will you lend me your book
B – Yes, but
X – Was the film enjoyable?
Y – Yes, but
- It is used in incomplete statement leading to another tone group.
edu.uptymez.com
Tone group – group of words that are pronounced with one tone
E.g.:- if Mwita leaves tomorrow, he will get to Kampala in time
Unless he leaves now he will be late.
When I entered the class, I found them making noise.
- It is used for statement that show warning, disapproval or concern
edu.uptymez.com
Oh! Don’t behave like that
Be careful
You say you want many you might to it next
- It is used for imperatives meant to be pleating requests (imperatives – sentence which is introduced with a verb)
edu.uptymez.com
E.g.:- Don’t disturb me
Come and see the children
Go there immediately
- Is used for statement that show a kind of reservation
edu.uptymez.com
E.g.:- He won (but he didn’t preserve)
I can come tomorrow (but not today)
She is beautiful (but I don’t love her)
4. Rise / Rising – fall tone
This tone occurs when the pitch rises and then falls again.This tone has the following uses
- For statements showing enthusiastic agreement, when you agree on something with excitement
edu.uptymez.com
E.g.: – Of course, that’s what I wanted
Yes, that u right
- For exclamation showing sarcasm
edu.uptymez.com
E.g.:- How beautiful you are
Good afternoon
Intonation
Refer to the relative rising and falling of the pitch of voice in speech or utterance
I.e. it is the pitch variation
Intonation may affect
- The meaning of spoken utterance
- The grammatical category of the sentence of clause
- Stress of the syllable and speech rhythm
- It also conveys the attitude of the speakers
edu.uptymez.com
NB: Intonation is the feature of spoken language which marks the Boundary and the mood in the same way punctuation does in the written language.
Functions of intonation
Introduction as the feature of spoken language has several conversational or grammatical functions, there are four major functions conserved by intonation
- Grammatical function
edu.uptymez.com
It is used to mark the boundaries between grammatical units or structures such as phrases, clauses and sentences
E.g. that book on the table has been there for a day
It is used to determine or identify the type of sentence in language such as whether the sentence is a statement question, command or request.
2. Accentual function
It is used to determine the category to which the word belongs such as whether the word is a noun, verb or adjective
E.g. Present – v
Present – N
Indicates emphasis on certain words in the utterance by so doing it affects the meaning of the utterance
E.g. those who sold quickly made profit
Those who sold quickly made profit
3. Attitudinal function
Intonation conveys the attitude of the speaker as it can be noted by the listener such as anger, happiness, surprise, approval or shock.
Usually this may be marked by the fall-rise or rise-fall tone
4. Discourse function
Intonation helps to indicate a connection and chances of participants in the discourse {spoken conversation i.e. Its helps the participants in the conversation to take turns in a regular order, hence helping them to speak in order.
Usually each participant in speech begins the conversation with high path or rise tone and ends with lower pitch or fall tone. That will alert the second participant to take the turn the conversation.