ESTIMATING STOCK
When a business firm does not maintain a perpetual inventory system, It has no way of determining the actual stock or inventory on hand unless the physical stock taking is done on a particular date. This will cumbersome and costly if it has to be done several times during an accounting period.
In order to avoid these inconveniences, the business will use an estimated figures its ending inventory.
There are occasions when it is necessary to estimate inventory. For-example when goods are lost or due to theft, a brokerage or natural deterioration or evaporation.
There are two common approaches to estimate stock;
- Gross profit method
- Retail method
- GROSS PROFIT METHOD
edu.uptymez.com
This method of estimation uses Gross profit margin or average mark up in order to determine the cost of goods sold (cost of sales).
*Margin = profit/selling price.
* Mark up = profit/cost price.
ILLUSTRATION 1
ABC LTD TRADING A/C FOR THE YEAR ENDED 30/06/2009
| Sales | 780,000 | ||
| less; Return inwards | 30,000 | 750,000 | |
| less; cost of goods sold | |||
| opening stock | 120,000 | ||
| Add; purchases | 660,000 | 780,000 | |
| less; closing stock | 180,000 | 600,000 | |
| Gross profit | 150,000 |
edu.uptymez.com
Calculate;
- Gross margin in percentage
- Average mark up in percentage
edu.uptymez.com
Solution;
-
Gross profit margin = profit/selling price x 100%
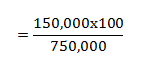
= 25%
edu.uptymez.com
ILLUSTRATION 2
Assume in illustration (i.) in the previous page during July, August, September ABC has made;
Purchases 240,000
Net sales 350,000
Calculate inventory on 30th September, use gross profit method to estimate the
Given data;-
Stock as at 30th/6 180,000
Purchases 240,000
Sales 350,’000
Margin 20%
Calculate closing stock.
| sales | 350,000 | |
| Opening stock | 180,000 | |
| Add ; purchases | 240,000 | |
| cost of goods available for sale | 420,000 | |
| less ; Closing stock | 140,000 | |
| Cost of goods`sold | ||
| Gross profit | 70,000 | |
edu.uptymez.com
ILLUSTRATION 3
On 1st January 2004, J.M valued his stock at cost, 12,300. During the first week of January 2004, his transactions in his stock were as follows;
Purchases 8,100
Sales 13,600
Returns inwards 800
Returns outwards 300
He sells his goods at 25% above cost of goods available for sale.
Calculate the cost of his stock at 7th January 2004
| Sales | 13,600 | ||
| less ; Return inwards | 800 | 12,800 | |
| less ; cost of goods sold | |||
| Opening stock | 12300 | ||
| Add ; purchases | 8100 | ||
| 20,400 | |||
| less ; Returns outwards | 300 | ||
| Cost of goods available for sale | 20100 | ||
| less; closing stock | 9860 | ||
| Cost of goods sold. | 10,240 | ||
| Gross profit | 2560 |
edu.uptymez.com
Gross profit P2?800x
Chane mark-up→Margin
25% →20%
20%x12,800→Gross profit Tshs 2560
RETAIL METHOD
- This estimation technique is employed to business with large amount of stocks of relatively low unit’s values.
- Usually all items are quoted at retail prices
edu.uptymez.com
Example of business using retail method is;
- Large chain store
- Supermarket
edu.uptymez.com
This method employs the following steps;
- obtain the cost of goods available for sale
- if sales figure is given taking the value of goods available for sale at retail the sales figure should give the value of closing stock at retail
- the value of closing stock at retail can be converted to an approximate cost figure by using the ratio of cost retail value worked out at (a) above.
edu.uptymez.com
ILLUSTRATION
On 1st June; COST RETAIL
Opening stock 180,000 288,000
30th; purchases 145,000 212,000
30th; sales ─ 170,000
Calculate;
- cost retail ratio
- closing stock at retail value
-
Conversion of closing stock at retail value to cost.
edu.uptymez.com
Solution
Cost to retail ratio
COST RETAIL
Opening stock 180,000 288,000
Add; purchases 145,000 212,000
325,000 500,000
Ratio = cost/Retail x 100
= 325,000 x 100
500,000
= 65%
Closing stock at retail value
| COST | RETAIL | |
| Opening stock | 180,000 | 288,000 |
| Add; purchases | 145,000 | 212,000 |
| 325,000 | 500,000 | |
| Less; Net sales | 170,000 | |
| Closing stock | 330,000 | |
edu.uptymez.com
Conversion of closing stock at retail value to cost
Closing stock = 330,000
65 x 330,000
100
= 214,000
Conversion of closing stock = 214,000
WEAKNESS OF ESTIMATION METHOD
- The stock estimation technique covered has assumed that the gross profit margin is stable in the period of estimation.
- They also assume that closing stock will be representative of all items which were available for sale.
- If these assumptions are not true, then misleading values will be produced.
-
These techniques have to take accounts of realities encountered if they are to yield/ to get/to gain acceptable approximation.
edu.uptymez.com
On 1st April 2012; Stock at cost was 30,000/=
Purchases 15,000/=
Sales 10,000/=
The normal rate of Gross profit on cost price is 25% however it is known that allowances of 2,000/= have been made to customers.
Calculate;
– Closing stock estimate as at 30th April 2012.
Exercise 2.
Due to administrative reasons W.mahwa, the wholesaler, had to take his stock on 28th December 2004, on which date it was valued at cost at 73,260. The following transactions took place in the next 3 days.
- Sales book 3400
- Cash sales 1940
- Purchases book total 2310
- Returns inward book 220
- Returns outward book 170
- Carriage inward 425
edu.uptymez.com
A detailed examination of the books also revealed the following information
- Sales book includes one invoice for 280/= against which goods were delivered on 2nd January 2005.
- Cash sales includes sales of an item that had a cost value of 42/= but was sold for 36/= as it has been damaged in store
- All purchases made had been dully received from supplier
- A customer returned books that has been invoiced to him at 80/= on 29th December 2004 but was issued with a credit loan on 3rd January 2005
- Carriage inward was paid in respect of goods bought in December 2004
- Stock with a cost value of 295/= had stayed in store for too long and estimated to have realizable value of only 178/=.
- Goods costing 126 were returned to a supplier on 30th December 2004 but the credit note was received four days later.
- No records have been made of drawings in the form of goods by the owner of this business, W. Mahwa of 203.
-
The usual gross profit margin is 33% on cost.
Calculate the cost, net realizable value whichever is the lowest of the stock of 31st December 2004.
edu.uptymez.com
INSURANCE CLAIM
ILLUSTRATION 1
J.A has insured a stock for 10,000/=. On 31st March 2008 when the total cost value of stock in his store was 12,000, his store caught fire, the value of stock salvaged from fire was 3,000/=. Calculate the amount he can claim from the insurance company.
NOTES
If stock is not fully insured, that is if the value of stock in store is more than the sum insured, insurance company paid the following portion of the value of stock destroyed from fire
Insurance claim = 10,000 x 9,000
12,000
Insurance claim = 7,500
- Owner J.A of the go down should claim 7,500 before his insurance company.
edu.uptymez.com
ILLUSTRATION 2
Stock on 31st March 2005 (last year end) 6200/=
Debtors on 31st March 2005 was 4600/=
Creditors on 31st March 2005 was 5400
Receipt from debtors (1st April to 5th May) was 5700/=
Discount allowed to debtors 100/=
Discount received from creditors 180/=
Payment to creditors 5120/=
Stock donated to a charity (cost value) 340/=
Stock salvaged from fire 600/=
Gross profit margin 25% cost
Calculate;
- The cost value of stock in store on 5th May 2005 considering that on that day debtors amounted to 6500 and creditors to 4900.
-
The amount to be claimed from insurance company
Solution; Exercise 2.
edu.uptymez.com
STOCK AS AT 28TH DECEMBER 2004
WORKINGS
-
NOTE (i)
Sort out all items concerning with sales
Cash sales 1940
Credit sales 3400
5340
edu.uptymez.com
Less; goods not delivered 280
5060
Less; damaged value 36
Net sales 5024
5024 x 75% = 3768
Add; cost before damage 42
COGS 3810
NOTE (ii)
Stock with a cost value = 295
Less; Realizable value = (178)
Loss in value of stock 117
ESTIMATION OF STOCK
| Stock as at 28th December 2004 | 73,200 | |
| Add; purchases | 2310 | |
| Carriage inwards | 425 | |
| (80 x 75%) | 60 | |
| Cost of value of Return inwards | ||
| (220 x 75%) | 165 | 2960 |
| 76,160 | ||
| Less; cost of goods sold .(note (i)) | 3810 | |
| Return outwards | 126 | |
| Return outward book value | 170 | |
| Drawings | 203 | |
| Loss value in stock (note (ii)) | 117 | -4426 |
| Closingstock | 71743 | |
edu.uptymez.com