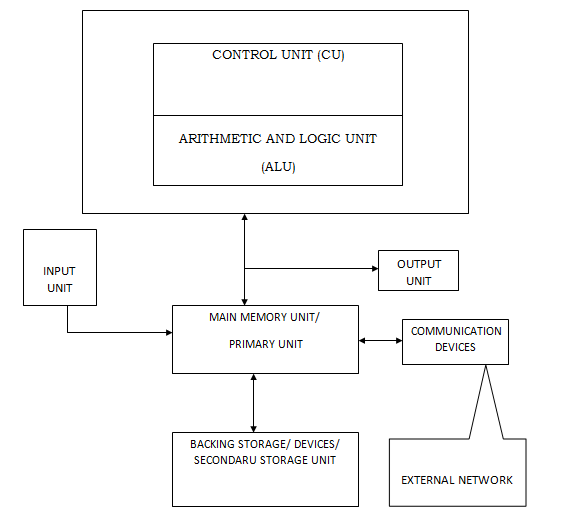
HOW A COMPUTER WORKS
All digital computers work esentially the same way.
A human operator uses input equipment to enter data and instructions into the computer. The processor then performs manipulation on the data, while the memory stores information during processing. The results then are sent to the output equipment, which presents them to the user. File storage devices enable information to be saved for future use.
CHARACTERISTICS (FEATURES) OF A COMPUTER
(i) It is very fast,
(ii) It is very accurate and reliable
(iii) It can work continuously without getting tired or bored.
(iv) It can work on and store large amounts of data items
(v) It can solve any problem if a relevant set of instructions is input,
(vi) It is able to access or recovers, retrieve large volumes of data.
(vii) It is able to communicate with other computer systems in a network.
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF COMPUTER
(a) Advantages
- It works at a very high speed
- Its results are very accurate and reliable
- It can work continuously without getting tired or bored
- It can work on the stored large amounts of data items
- It can solve any problem if a relevant set of instructions is input, (computer never think, bad programs will also produce bad output GIGO –garbage in garbage out)
- It is flexible
- It reduces paper work significantly.
- It reduces number of employees in organizations.
- It uses a small office space
- It is automatic.
- It allows fast retrieval of information from a storage space.
- It can store information efficiently
- Computers can move information very quickly from one person to another.
edu.uptymez.com
(a) Disadvantage
- It is costly
- It becomes outdated very fast due rapid changes in computer technology, hence it leads to capital loss
- It causes loss of employment in certain fields.
- It can fail. Such failures can cause loss of life e.g in traffic control system.
- Too much work at the computer causes nerve injuries.
- Loss of employment
- Loss of secrets
- Eye damage
- Loss of data.
edu.uptymez.com
APPLICATIONS OF COMPUTER IN DIFFERENT AREAS OF HUMAN LIFE
IN EDUCATION
- To teach (give courses) in different subjects
- To give Computer Assisted Instructions (CAI)
- To give Computer Assisted Learning (CAL)
- To keep records
- As a reseach tool e.g. to analyse data from experiments
- To process records
- To assist in education management.
- To keep records of books and borrowers in a library.
edu.uptymez.com
MEDICINE (HEALTH)
- To assist in hospital administration
- To keep records of employee and patients
- To monitor conditions of patients e.g. temperature, heart-beats
- To help doctors to investigate illness (diagnosis) and prescribe treatments.
- To do medical research.
edu.uptymez.com
HOME
- For recreation e.g. playing games, listening to music
- As an education tool
- To store personal information
- To access to news when connected to the internet
- To access databases
- As a home accountant to keep a track of expenses and to balance a family budget
- To protect homes against crimes from burglary vandals by using electronics security systems.
- For alert emergence services automatically e.g fire brigade, police.
edu.uptymez.com
IN INDUSTRY AND ENGINEERING
- To design drawing for products using Computer Aided Design (CAD) programs e.g. airplanes, bridges, cars, buildings, electronic circuit boards.
- To manufacture products using Computer aided Manufacturing (CAM)
- To plan and control major projects.
- To simulate (predict what will happen in real-life situation from a model situation.) e.g. turning of traffic lights.
- To control some operations in automobiles e.g mixing of fuel and air entering the engine
- A branch of computer science called artificial intelligence, uses programs that help to solve problems by applying human knowledge and experience e.g. in medicine, law etc.
edu.uptymez.com
IN BANKING AND BUSINESS
- To allow bank clerks and customers to find out bank balances in an account
- To help bank clerks to record money paid in and out
- To check computer sensitive cheques, to do reservation system for airline travel by checking of there is a free seat on a flight.
- To help retailers to check out stock at a supermarket
- To control industrial robots
- To allow people to use Automatic Teller Machines (ATM) in cash withdraw and transfer funds between accounts.
- To keep track of current prices of market stocks, bonds currency.
- Creates an effective way of producing document e.g. reports, brochures, cards.
edu.uptymez.com
MILITARY
- It can be used for planing and decision – making
- It can used by planners to stimulate wars
- It can be used to guide modern weapons such as missiles and field artillery.
edu.uptymez.com
IN GOVERNMENT
- It can be used for internal revenue services e.g to provide reports for tax purposes.
- It can be used for planning, analysis, forecast, sampling, predictions etc.
- It can be used for weather forecasting ,
- It can be used for Law enforcement
edu.uptymez.com
IN TRANSPORTATION
- It can be used for a Traffic control
- It can be used in driving stimulator
- It can be used for reservation systems
- Are embedded in aircraft to provide efficiency in flying.
edu.uptymez.com
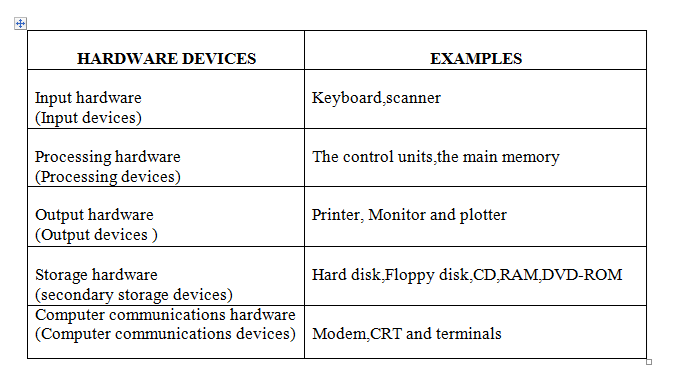
COMPUTER HARDWARE
- Is a collection of machines (physical components or elements) which form a complete computer system.
- Is the actual machinery that makes up the computer system.
- Is the collection all physical pieces of equipment (elements) that makes up a computer system.
- Is a set of devices that accept data, processes them and displays them.
- Is the set of all pyhsical parts of the computer.
edu.uptymez.com
TYPES OF COMPUTER HARDWARE
COMPUTER HARDWARE is a composed of the following components/elements according to the functions of the computer:
- Input devices or input hardware
- Central processing unit (CPU) or processing hardware
- Output devices or Output hardware
- Secondary storage devices or storage hardware
- Communication devices or Communication hardware
edu.uptymez.com
A BLOCK DIAGRAM FOR CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTER HARDWARE COMPONENTS (DEVICES or ELEMENTS)
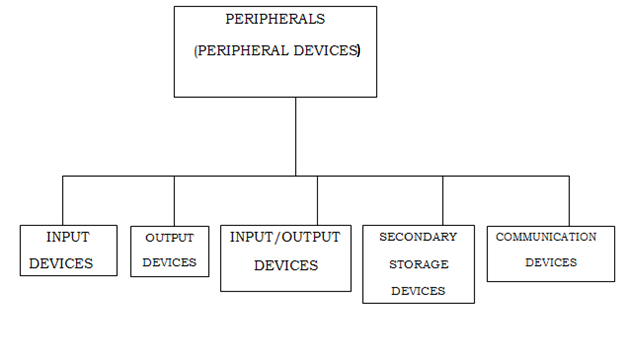
PERIPHERALS (OR PERIPHERAL DEVICES or PERIPHERAL HARDWARE)
PERIPHERAL
- Is a device that is located outside the central processing unit (CPU) but controlled by it.
- Is an attachment to a computer used mainly to feed unprocessed data into the computer and receive the output of processed information.
- Is the totality of facilities or equipments connected to the computer to assist it in satisfying its users.
edu.uptymez.com
DEVICES
- Is any machine, but particularly a computer peripheral e.g. printer
- Is a computer peripheral
edu.uptymez.com
There are two types of devices
1. AN ONLINE DEVICES – is a peripheral devices that is in use
2. AN OFFLINE DEVICES – is a peripheral that is not in use
A MEDIUM – Is a material in which data is stored on or data is output to e.g. printed paper.
Types (categories) of peripherals
There are five main types or categories of peripherals (or peripheral devices). These are: –
(i) Input devices
(ii) Output devices
(iii) Input/output devices (i.e. both input and output devices)
(iv) Backing storage (secondary storage devices
(v) Communication devices