INPUT DEVICES (INPUT HARDWARE)
INPUT
- Is getting (to get) data into a computer system
- Is the data that is put into the computer system for processing
- Is any data or instructions which you enter into the memory of a computer.
edu.uptymez.com
TYPES OF INPUT
Four types of computer input are: –
I. Data
II. Programs
III. Command,
IV. User responses
- DATA is a collection of unorganized (meaningless) facts, e.g. words, numbers, pictures, sound and videos.
edu.uptymez.com
– Is raw material to be processes by the computer.
- A PROGRAM is a series of instructions that tells the computer how to perform tasks which are necessary to process data into information.
- A COMMAND is an instruction given to a computer program.
- A USER RESPONSE is an instruction you issue to the computer by replying to question posed by a computer program.
edu.uptymez.com
E.g Computer question: Do you want to save the changes you have made?
Uses response: YES
AN INPUT DEVICE
– Is any hardware component that allows you to enter data, programs, commands and user responses into a computer.
– Is a peripheral (peripheral device) which accepts data and send it into the corresponding processing unit (CPU)
– Is a peripheral (peripheral device) which accepts data in a form that a computer can use and sends the data to the central processing unit (CPU).
– Is a peripheral (peripheral device) which accept data from outside the computer system and transmits (sends) it to the central processing unit (CPU).
Examples of input devices;
Keyboard, mouse, Lightpen, Joystick, Scanner, Bar-code reader, PEWS terminal,Trackball, Touch pad, Pointing stick , pen(stylus)
CHARACTERISTICS OF INPUT DEVICES
The characteristics of input devices are as follows:-
(i) They form an interface between the external environment and the computer
An interface is a hardware (and sometimes a software) that is used to connect two devices or systems in order to enable them to communicate.e.g. A modem
(ii) They’re located next to or outside the CPU. In other words, they are attached to the computer.
(iii) They can be off-line or on-line
FUNCTIONS OF INPUT DEVICES
The functions of input devices are as follows: –
(i) To accept data from the user into the computer system
(ii) To accept instructions from the users.
(iii) To accept commands for running or aborting or halting a program from the user.
OUTPUT DEVICE / OUTPUT HARDWARE
OUTPUT
– Is data that has been processed into meaning form called information.
– Is usable information
– Is raw input data that has been processed of the computer into information.
Some examples of output
– Words, numbers, sentences, paragraphs
– Drawings, charts and photographs
– Music synthetic speech
– Played back images
Types (categories or groups) of output
Two principal kinds of output are
(i) Softcopy
(ii) Hardcopy
Soft copy
Is a material (data) shown on the display screen (monitor) or data that is in audio or voice form.
This kind of output is not tangible; it cannot be touched.
Hardcopy
Is printed copy (printout) on paper.
Examples of printouts (hardcopy output)
(i) Text and graphics from printers
(ii) Film (including microfilm and microfiche)
Forms of output
Computers generate (produce) several forms of output. They are: –
(i) Text e.g. words, sentences, charts and paragraphs
(ii) Graphics e.g. drawing, charts and photographs
(iii) Audio e.g. music speech etc
(iv) Video e.g. played back images
COMMUNICATIONS DEVICES
COMMUNICATIONS HARDWARE
COMMUNICATIONS:
- Is the process of sending and receiving data and programs from one computer to another or secondary storage device to another.
- Is the process of transmitting (or sending) data from one person to another or from one device to another.
edu.uptymez.com
Examples of communications devices
(i) Modem
(ii) Multiplexor
A MODEM
-Is a device by which computers exchange information over telephone lines.
-Is a piece of hardware that converts (changes) digital signals into analog signal and vice versa.
COMPUTER COMMUNICATION
Is the transfer of information between computers.
DATA COMMUNICATION
Is the process of transmitting (or sending) data from one user to another or from one computer to another.
TELECOMMUNICATIONS
– Is data communication over large distances.
SECONDARY STORAGE DEVICES / SECONDARY STORAGE MEDIA
A STORAGE MEDIUM/STORAGE DEVICE – is a physical material on which items (data, Instructions and information) are kept for future use e.g. disks.
Examples of secondary storage devices/ secondary storage media
– Floppy disk (diskette), magnetic diskette.
– Magnetic disk or hard disk
– Magnetic tape
– Optical disks e.g. CD,CD-ROM WORM and DVD, DVD-ROM, DVD-RAM and rewritable optical disks (cailed floptical, magneto-optic)
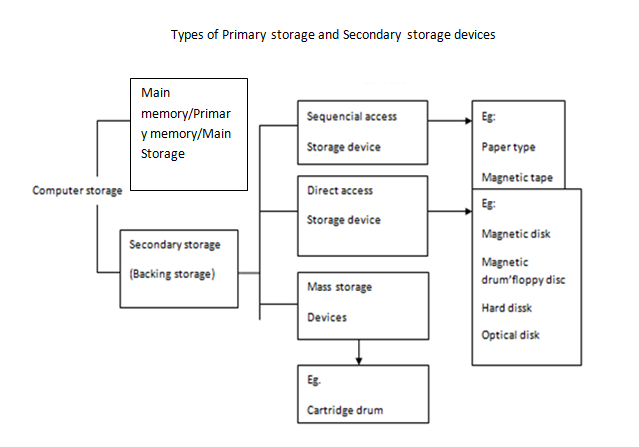
CHARACTERISTICS OF SECONDARY STORAGE DEVICES
Secondary storage devices have a several common characteristics:
- It is less expensive (i.e. it is cheaper)
- They cost less per byte.
- It is slow (the access time of storage devices are measured in milliseconds i.e thousands of a second). It has low speed.
- It is not part of the CPU
- It has a higher/larger storage capacity.
- It is used to store large quantities of data.
- It is non-volatile (its contents are retained even when the power is switched off from the computer.
- It is permanent. (I.e. record storage is permanent). It is a permanent type of storage.
- It is used to store data that are not needed for immediate processing.
- It is made up of magnetic bubbles
- It is called backing storage
- It is used for mass storage needs
- It operates on the principle of magnetism.
edu.uptymez.com
Types of magnetic storage hardware
Two common types of magnetic storage hardware are: –
1. Disks (magnetic disks)
2. Tapes (magnetic tapes)
MAGNETIC DISK STORAGE
– The circular platters on each side of the magnetic disk are about 35cm in diameter.
– The circular platters on each side of the magnetic disk are very smooth.
– The circular platters on each side of the magnetic disk are coated with a metal oxide.
Characteristics of magnetic disk units
(i) Provide fast memory search
(ii) Have large storage capacity
(iii) Use random access method to retrieve data
(iv) It is fast and to read an index
DANGERS/THREATS TO DISK (DISK ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS)
The great threats/dangers to disk are: – smoke, dust, lint and fingerprints. These items can jam under the “lightning fast” read/ write heads, causing permanent damage to the smooth surface and thereby destroying data files.
Two basic types of magnetic disk media are:
– It is a type of magnetic media that stores items using magnetic patterns.
– It consists of several inflexible, circular disks called PLATTERS (or PLATES).
A platter in a disk is made of aluminium, glass or ceramic and is coated with a magnetic substance i.e. iron oxide that allows items to be magnetically recorded on its surface. Often, several platters are stacked together to create a disk park. A disk pack is easy to handle.
Example
One type of disk pack consists of 11 to 14 – each-wide disks. It is about 6 inches high, weighs about 9 kilograms, and can store over 500 million characters.
– A disk park is easy to handle
On hard disks, the platters (or plates), the red/write heads, and the mechanism for moving the heads across the surface of the disk are enclosed (sealed) in an airlight case/ module that protects platters from contamination.
– It is also a read/write storage media; that is you can both read from and write on a hard disk any number of times).
– It can be non removable (i.e. permanent) or removable.
– On microcomputer, hard disks are permanently mounted/housed inside the computer chassis (system unit).
– The capacity of a fixed disk in modern desktop personal computers ranges from 20 MB to 50 GB.
– On minicomputers and mainframes, hard disks can be permanent (non-removable or removable.