MAGNETIC DISK STORAGE
– The circular platters on each side of the magnetic disk are about 35cm in diameter.
– The circular platters on each side of the magnetic disk are very smooth.
– The circular platters on each side of the magnetic disk are coated with a metal oxide.
Characteristics of magnetic disk units
(i) Provide fast memory search
(ii) Have large storage capacity
(iii) Use random access method to retrieve data
(iv) It is fast and to read an index
DANGERS/THREATS TO DISK (DISK ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS)
The great threats/dangers to disk are: – smoke, dust, lint and fingerprints. These items can jam under the “lightning fast” read/ write heads, causing permanent damage to the smooth surface and thereby destroying data files.
Two basic types of magnetic disk media are:
– It is a type of magnetic media that stores items using magnetic patterns.
– It consists of several inflexible, circular disks called PLATTERS (or PLATES).
A platter in a disk is made of aluminium, glass or ceramic and is coated with a magnetic substance i.e. iron oxide that allows items to be magnetically recorded on its surface. Often, several platters are stacked together to create a disk park. A disk pack is easy to handle.
Example
One type of disk pack consists of 11 to 14 – each-wide disks. It is about 6 inches high, weighs about 9 kilograms, and can store over 500 million characters.
– A disk park is easy to handle
On hard disks, the platters (or plates), the red/write heads, and the mechanism for moving the heads across the surface of the disk are enclosed (sealed) in an airlight case/ module that protects platters from contamination.
– It is also a read/write storage media; that is you can both read from and write on a hard disk any number of times).
– It can be non removable (i.e. permanent) or removable.
– On microcomputer, hard disks are permanently mounted/housed inside the computer chassis (system unit).
– The capacity of a fixed disk in modern desktop personal computers ranges from 20 MB to 50 GB.
– On minicomputers and mainframes, hard disks can be permanent (non-removable or removable.
THE HARD DISK DRIVE – SUB- DIVISIONS OF THE HARD DISK
The hard disk is further sub-divided into two types:
(a) Fixed disk or inflexible disk: It is not portable
(b) Removable disk.
FIXED DISK (FIXED HARD DISK)
– It is a type of magnetic media that stores items using magnetic patterns.
– It also a read/write storage media; that is you can both read from and write on a hard disk any number of times)
– This is non removable magnetic disk assemblages used in magnetic disk units.
– On microcomputer, fixed disks are permanently mounted/housed inside the computer chassis (system unit)
– The capacity of a fixed disk in modern desktop personal computers ranges from 20 MB to 1 GB.
– On microcomputers and mainframes, fixed disks can be permanent or removable
– It is not portable.
– It allows higher speeds greater data recording densities, and closer tolerances within a sealed, more stable environment.
– Fixed disks can be stacked together. The result is called a disk pack.
A disk pal is easy to handle.
FLEXIBLE DISK, (FLOPPY DISK), FLOPPY OR DISKETTE
OR MAGNETIC DISKETTE
– It is a disk that consists of polyester film coated with an iron oxide compound.
– It is a thin, circular, flexible, plastic disk with a magnetic coating enclosed in square-shaped plastic shell.
Characteristics of diskettes
(i) It is portable
(ii) It is not expensive
(iii) It is square shape
(iv) It is reusable
(v) It is easy to store
A floppy disk drive –is a device that can read from and write to a floppy disk.
Standard types of diskettes
There are two standard types of diskettes
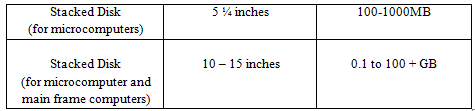
- The 5 ¼ inches diskettes
edu.uptymez.com
- This is an old type of diskettes and it is being phased out.
- It is in a soft (flexible) housing (jacket)
- Its capacity ranges from 356 KB to over 1 MG of data.
edu.uptymez.com
- The 3 ½ inches diskettes type.
edu.uptymez.com
- It is a new type and is still in use
- It is mounted in a hard plastic cover (housing)
- It is has a larger/ higher storage capacity
- It weighs less
- It consumes less power
- It is smaller, studier and easier to store. It lifts into a T- shirt pocket or purse.
edu.uptymez.com

USES OF DISKETTES
Diskettes are used:
- To move data and programs from one computer to another
- To back up critical data on the fixed disk.
edu.uptymez.com
THE MAIN FORCES THAT ARE HOSTILE TO THE DISKETTE (FLOPPY DISK OR FLOPPIES
Floppies are endangered by several factors (things, or forces)
The main forces (things) that are hostile (dangerous) to floppies are
(i) Dust
(ii) Magnetic fields
(iii) Liquid
(iv) Temperature extremes
(v) Vapours
HOW TO HANDLE DISKETTES:
RULES FOR TAKING CARE OF FLOPPIES
1. Do not touch the disk surface.it is easily contaminated, which causes errors.
- Do not use alcohol thinners or freon to clean the disk
- Do not use magnetic or magnetized objects near the disk. Data can lost from a disk exposed to a magnetic field
- Do not bend or fold the disk
- Do not place heavy objects on the disk
edu.uptymez.com
6. Do not use rubber band or paper clips on the disk
7. Do not use erasers on the disk
8. Do not expose the disk to excessive heat or sunlight
9. Apply the index label to the right of the manufacture
10. Write on the index label with left-tip pen only
11. Insert carefully by grasping upper edge
THE ARITHMETIC – LOGIC UNIT (ALU)
- Is a component of the CPU (central processing unit) that performs arithmetic operations and logical operations and controls the speed of those operations.
- Is the calculating device for the computer.
edu.uptymez.com
PARTS OF THE ALU
The ALU is made up of two sections or parts:
- THE ARITHMETIC SECTION (OR ARITHMETIC PART)
edu.uptymez.com
This is a part of the ALU, which deals with the arithmetic operations.
Some examples of arithmetic operations performed by the arithmetic section (or arithmetic part) of the ALU are: addition, substraction, multiplication and division.
- THE LOGIC SECTION (OR THE LOGIC PART)
edu.uptymez.com
This is a part of the ALU, which handles or deals with the logical operations (or decision making operations)
Some examples of logical operations performed by the logical section (or logical part) of the ALU are: comparing, selecting, matching, sorting and merging.
FUNCTIONS OF THE ALU
The Arithmentic – logical Unit has two main functions:
- To do (carry out) arithmetic operations e.g. addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
edu.uptymez.com
2. To do (perform) logic operations e.g. comparing, selecting, matching, sorting and merging.
The ALU does not store data. It merely performs the necessary manipulations. For example; if a program tells the computer to add or subtract two or more numbers; the control unit has those numbers copied into special memory areas called registers or accumulators. The ALU then manipulates these memory areas and returns the result to the appropriate memory location as directed by the control unit.
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ALU
- It receives commands from the control unit (CU)
- It contains additional storage locations called REGISTERS
edu.uptymez.com
The ALU does not store data. It merely perfoms the necessarymanipulation