THE NETWORK TOPOLOGY
The network topology defined as layout of the network.
Is the way in which nodes are connected in a network.
NODES: are the network devices e.g.: Computer, switch, hub, server or router
NODES can be connected physically or logically
PHYSICAL TOPOLOGY
Refers to the actual physical layout of the device in a network or the way in which in nodes are connected physically.
LOGICAL TOPOLOGY
Refers to the paths that signal from one point to the network to another.
TYPES OF PHYSICAL TOPOLOGY
- BUS TOPOLOGY
- STAR TOPOLOGY
- RING TOPOLOGY
- HYBRID TOPOLOGY
edu.uptymez.com
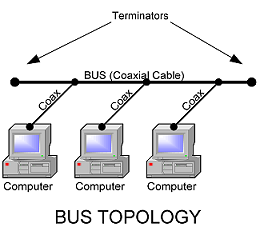
BUS TOPOLOGY
Commonly referred to as linear bus all the device on a bus topology is connected by one single cable which from one computer to the next.
This topology is rarely used and would only be suitable for a home office or small business with few hosts.
ADVANTAGES
– The thin net cabling it uses is quite inexpensive
– It uses less cable compared to other physical topologies like star or extended star
– It work well for small network
– It doesn’t need a central device such as hub , switch or route
DISADVANTAGES
– It results in slower access to the network and less bandwidth due to the sharing of the some cable by all devices.
– It is challenging to identify and isolate problems
– A break at any point in the bus can disable the entire bus network
– It needs termination.
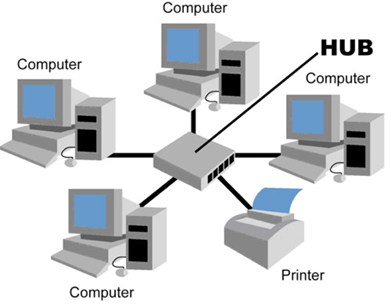
STAR TOPOLOGY
All nodes are connected to a central device.
ADVANTAGES
– It is upgradable flexible and reliable
– It is easy to design and install
– This topology makes diagnosing problem relatively easy since the problem is localized to one computer or device.
– This topology allows for more throughout than any other topology.
DISADVANTAGES
– It requires a lot of cable to connect computer since a cable is required between each device and the central location.
– It is more expensive to build because of the additional cost of cables and devices like hubs and switches that one needed to run
between.
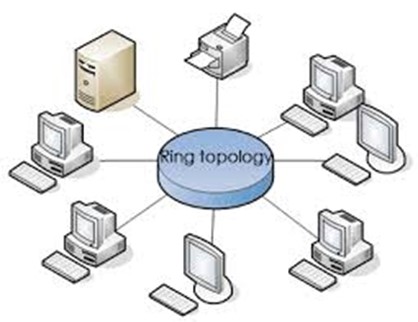
RING TOPOLOGY
Nodes are connected in a circle where by all device have equal importance.
- A frame called token, travels around the ring and stops at each node.
- If a node wants to transmit data , it adds that data and the addressing information to the frame.
- The frame continues around the ring until it finds the destination node which takes the data out of the frame.
edu.uptymez.com
Advantages of Ring topology
(i)Growth of system has minimal impact on performance
(ii)All stations have equal access
(iii)No one computer monopolize the network
Disadvantages of Ring topology
(i)Most expensive topology.
(ii)Failure of one computer may impact others.
(iii)Complex in configuration.
(iv)Difficult to troubleshoot a ring network.
(v)Adding or removing computer disrupts the network.
TYPES OF RING TOPOLOGY
1) Single ring topology
The entire device on the network shares a single cable, and the data travels in one direction only.
2) Dual ring topology
- Two rings allows data to be sent both directions
- This creates redundancy (fault tolerance) meaning that in the event of a failure of one ring, data will still be transmitted on the other ring.
edu.uptymez.com
ADVANTAGES OF RING TOPOLOGY
- Very fast because flow in one direction
- Less expensive than star topology
edu.uptymez.com
DISADVANTAGES
- If one node fail will affect whole network
edu.uptymez.com
MESH TOPOLOGY
- The mesh topology connects all devices (nodes) to each other for redundancy and fault tolerance.
- It used in WANs to interconnected LANs and critical Networks.
- The mesh topology is expensive and difficult to implement.
edu.uptymez.com
ADVANTAGES
- Redundancy
- Fault tolerance
edu.uptymez.com
DISADVANTAGES
- More cable needed
- It’s very expensive
- Needs more skills
- Difficult to implement
edu.uptymez.com
HYBRID TOPOLOGY
Combines more than one type of topology.
ADVANTAGES
- Redundancy
- Fault tolerance
- Efficient
- High speed.
edu.uptymez.com
DISADVANTAGE
- More cable are needed
- More complicated
- It’s very expensive
- Difficult to implement
- Hard to troubleshoot