DIGITAL COMPUTER
These are computers that use digital signals only. Digital computers recognized data by counting discrete of O’S and 1’S.
HYBRID COMPUTER
These computers are combination of both digital and analog computers. In this type of computer, the digital segments perform process control by conversion of analog signals to digital ones.
B: TYPES OF COMPUTER BASED ON THE SIZE OF COMPUTER
MICROCOMPUTER
A computer with a microprocessor and its central processing unit is known as microcomputer. They don’t occupy space as much as mainframes. When supplemented with a keyboard and a mouse, microcomputer can be called as personal computers.
Desktop, laptop, personal digital assistant (PDA’s)
MINICOMPUTERS
A minicomputers a term no longer much used , is a computer of a size intermediate between a microcomputer and a main frame , Typically microcomputers have been stand – alone computer
MAIN FRAME COMPUTER
Large organizations use mainframes for highly critical applications such as bulk data processing and ERP. Most of the mainframe computer has the capacities to host multiple operating systems and operate as a number of virtual machines and can this substitute for several small servers.
SUPER COMPUTERS
The highly calculation – intensive tasks can be effectively performed by means of super computer.
E.g.: Quant ion physics, Mechanics, Weather forecasting and molecular theory is best studied by means super computers.
STORAGES UNIT.
Bit = Smallest unit of computer data
Byte = Collection of 8 bits
1 bit = 2 characters (0 or 1)
1 byte = 8 bits
1 kb = 1000 bytes
1mb = 1000kb
1 GB = 1000 mb
1 terabyte (tb) = 1000 GB
Example: 1
40 GB hard disk contains 8 files @ with 3kb.
Calculate
a) Free space
b) Space occupied by 8 files in a hard disk
Solution
Given = 40 GB hard disk (HDD)
Step 1 = 8 files @ 3kb
Space occupied
1file = 3kb
8 files = x
8fils x 3kb = 24 kb
Total space occupied or needed by 8 files = 24kb
If 1 GB = 1000 mb
40 GB = a
= 40000mb
1mb = 1000 kb
40000mb = x
x = 40000000kb
- 40gb = 40000000kb
edu.uptymez.com
Free space = hard disk – total files
= 40,000,000 – 24
= 39,999,976kb
b) Space occupied by 8 files in a hard disk is 24kb
Example 2:
Calculate number of bits, bytes and kb required to present the following words.
a)Said katinga.
Solution
i) 1 bit = 2 character
x = 12 characters
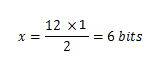
ii) 1 byte = 8 bits
x = 6 bits
(1x 6)/8 = 8x/8
= 3/4
= 0.75 bytes
iii) 1 kb = 1000 bytes
x = 0. 75 byte
x = (0.75 bytes x 1kb)/1000
x = 0.00075 kb
b) Isha ghandhi = 12 characters
i) 1 bit = 2 characters
x = 12 characters
(2x character)/2 = (1 bit x 12 character)/2
= 6 bits
ii) 1 byte = 8 bits
x? = 6bits
= 6/8
∴ x = 0.75
iii) 1kb =1000 bytes
? = 0.75 bytes
(1kb x 0.75 bytes)/100 = (1000x bytes)/1000
= 0.00075kb
HARD DISK STRUCTURE
– Physically, the hard disk consists of several metallic platters that are permanently sealed into a disk drive container.
– Binary data on a hard disk is recorded magnetically on invisible closed concentric circles called “Tracks”
– Each track on the disk is further divided into smaller, more manageable units called “sectors”. A sector is the smallest addressable unit on a disk and is exactly 512 bytes in size.
CLUSTER SIZE AND PERFORMANCE
The performance of a hard disk is directly related to the cluster size in general smaller cluster sizes result in a more efficient use of hard disk space , but can also lead to fragmentation in large files if the cluster are not stored continuously (side by side) on the hard disk.
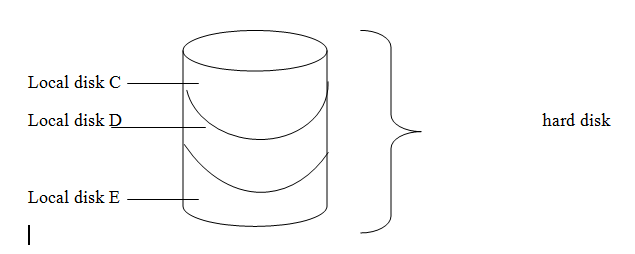
PARTITIONS
A hard disk may be split into several smaller logical called partitions. Each partition on a hard disk is treated like a separate disk.
For example: A hard disk could be divided up into partitions as shown on the right.
ACCESS TIME
Seek time is a measure of how long it takes the head assembly to travel to track of the disk that contain data.
Access time can be improved by increasing rotational speed (thus reducing latency) and reducing the time spent seeking.
DATA TRANSFER RATE
HDD data transfer rate depend up on the rotational speed of the platers and the recording density.

