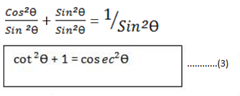Trigonometry is the study of angle measurement and functions that depends on angle.
The fundamental trigonometric ratios are
Sine (sin)
Cosine (Cos)
Tangent (Tan)
Others are cosecant (cosec)
Secant (sec)
Cotangent (cot )
Let θ be the angle in a right angled triangle; then we say
Sin θ
COS θ
Tan θ
And  = Cosecant θ = Cosec θ
= Cosecant θ = Cosec θ
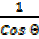 = secant = sec θ
= secant = sec θ
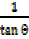 = Cotangent θ = cot θ
= Cotangent θ = cot θ
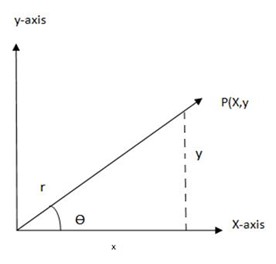
Consider a right angled triangle below
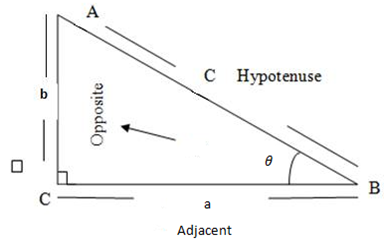
Sin θ = 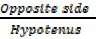 =
=  ………..(i)
………..(i)
cos θ = 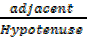 =
= 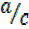 ……….(ii)
……….(ii)
tan θ= 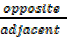 =
= 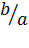 …………(iii)
…………(iii)
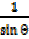 = cosec θ=
= cosec θ= 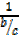 =
= 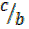 (iv)
(iv)
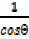 = sec θ =
= sec θ =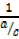 =
= 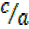 (v)
(v)
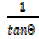 = cot θ =
= cot θ = 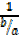 =
= 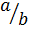 (vi)
(vi)
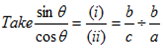
But 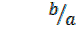 = tanθ
= tanθ
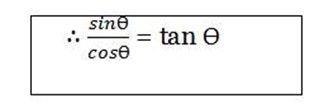
SPECIAL ANGLES
These are the angles which we can find their trigonometric ratios without mathematical tables or scientific calculators.
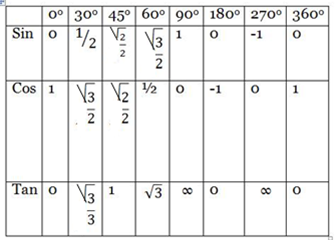
The angles are 00, 300, 450, 600, 900, 1800, 2700, 3600.
Finding the trigonometric ratios for special angles.
Case 1: Consider 300 and 600
Here use an equilateral triangle with unit sides
That is
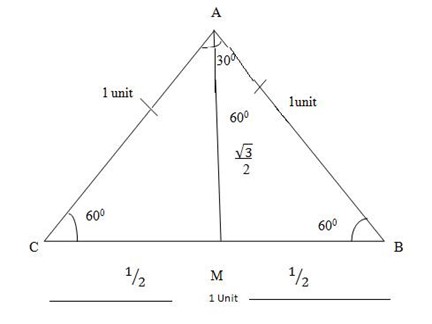
From  AMB (right angled)
AMB (right angled)
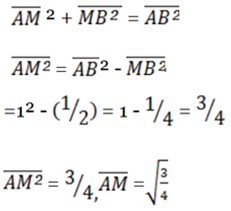
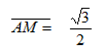
Then from the fig above
Sin 300 = 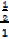 =
= 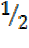
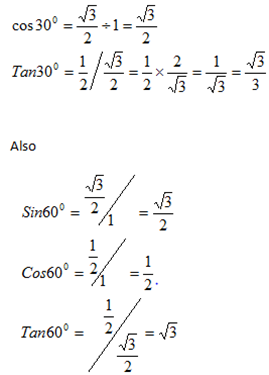
Case 2 Consider 450
Here use are square with unit sides (1 unit)
That is
From 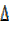 ABC (right angled)
ABC (right angled)
 =
= 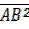 +
+ 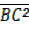
 = 1² + 1² = 2
= 1² + 1² = 2
 =
= 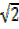
Then sin 450 = 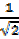 =
=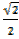
Cos 450 = 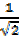 =
= 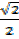
Tan 450 = 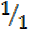 = 1
= 1
Trigonometric ratios for 00, 900, 1800 and 2700 and 3600.
Here use a unit circle ‘Discussed also in O level’
A unit circle is a circle with radius (1 unit)
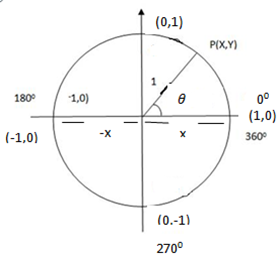
Suppose p(x,y) is a point in a unit circle
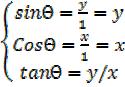
Generally in a unit circle
X = cosine value of an angle
Y= sine value of an angle
 = Tangent of an angle
= Tangent of an angle
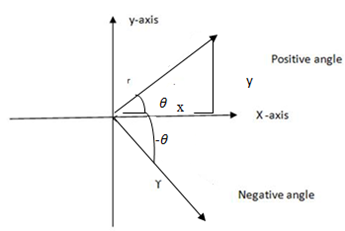
Angle measurement can be in two ways.
Clockwise direction (-ve angles)
Anticlockwise direction (+ve angles)
From a unit circle we use
X= cosine value of an angle
Y= sine value of an angle
Hence consider angles 00, 900, 1800, 2700, 3600 and their corresponding coordinates in a unit circle.
00 means
means 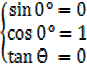
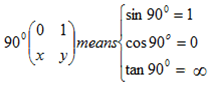
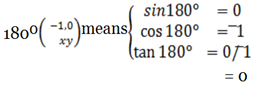
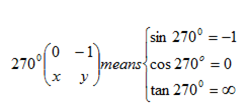
360° means
means 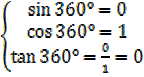
Summary:-
The concept of picture and negative angles.
But sine function and tangent function are odd functions
Cosine function is an even function
Fig above
From Sin θ =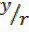
Sin ( -θ) = –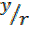 = -sinθ
= -sinθ
cos θ = 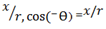
cos(-θ) = Cos θ
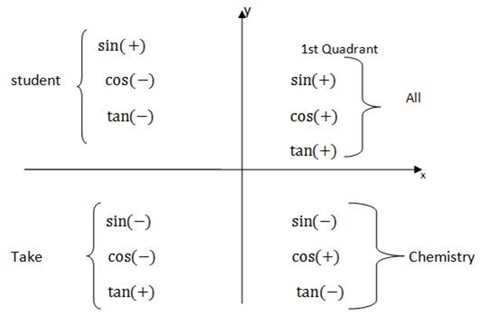
THE IDEA OF QUADRANTS
The idea is discussed in O’Level form IV Basic Mathematics, but let us recall the idea.
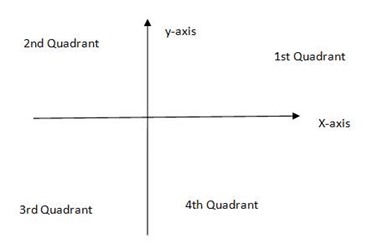
1st Quadrant Angles
The range of the angles is 0°< θ<900
The all trig ratios are positive and are obtained directly from four figure (mathematical figure
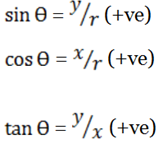
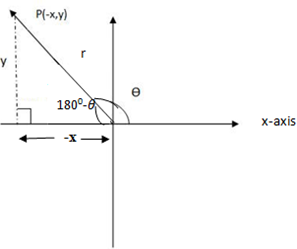
2nd Quadrant angles
The range of the angles is 900 < θ <1800
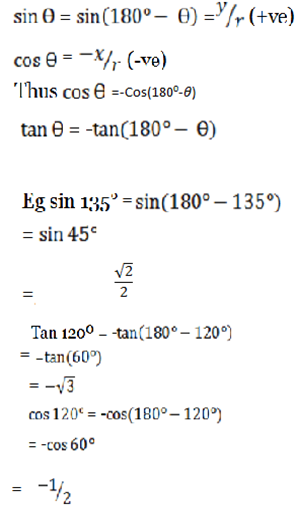
3rd Quadrant
Ranges from 180°< θ< 270°
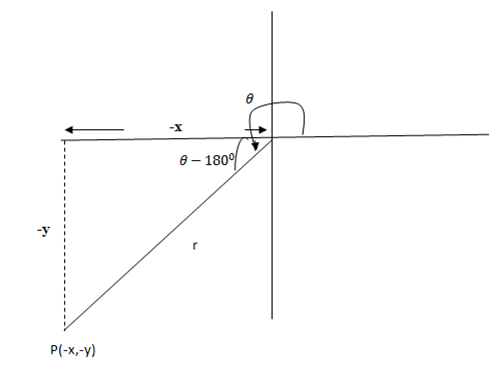
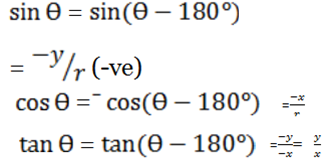
4th Quadrant
Ranges from 270°<θ<360°
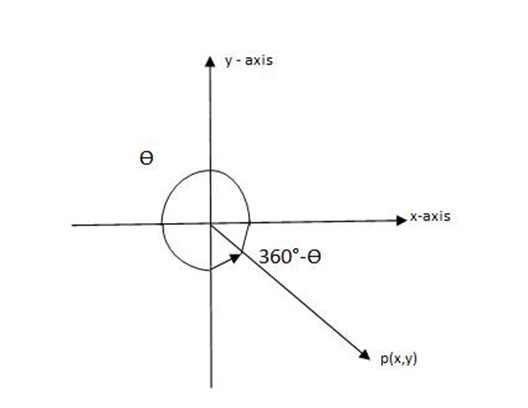
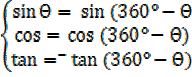
Eg: Sin 315° = -Sin (360° -315°)
=-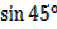
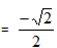
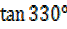 = -tan (360° – 330°
= -tan (360° – 330°
= -tan 30°
= 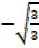
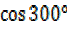 =
= 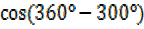
=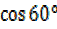 =
= 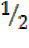
PYTHAGORAS THEOREM (IDENTITY)
Consider a right angled 
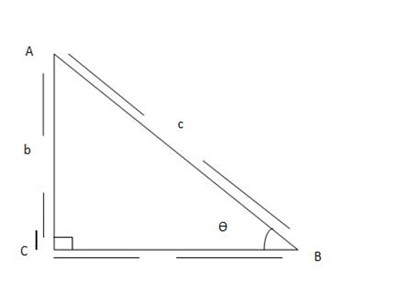
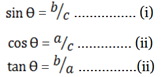
From Pythagoras theorem
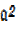 + b² = c²
+ b² = c²
Dividing by C²
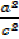 +
+ 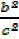 =
= 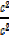
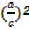 + (
+ (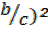 = 1————–∗
= 1————–∗
Substitute equations (i) and (ii) into (*)
Then we get
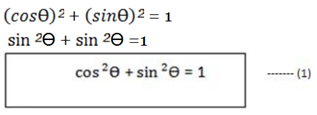
Is the Pythagoras Identity.
Dividing equation (1) by 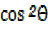

dividing equation (i) by Sin2θ