CIRCLE
Length of an Arc
Consider the following
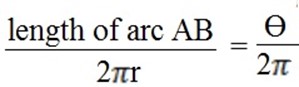
2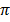 (length of arc AB) = θ x 2
(length of arc AB) = θ x 2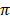 r
r
Length of arc AB = rθ
Area of a circular sector
Pg. 141 drawing
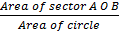 =
= 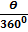
Where: area of circle = 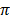 r2 and 360o = 2
r2 and 360o = 2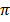
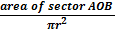 =
= 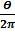
Area of sector AOB x 2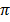 = θ x
= θ x 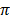 r2
r2
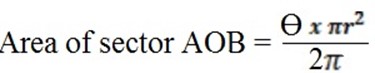
Area of sector AOB =  r2θ
r2θ
Where θ is in radians and r is the radius of the circle
Example 1.15
Find the arc length of a circle of radius r which is subtended by a central angle θ for each of the following
a) r = 3cm and θ = 45o
b) r = 6cm and θ = 180o
Use 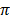 = 3.14
= 3.14
Solution
a) 1 = rθ
1 = 3 x 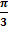 cm or
cm or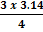 =
= 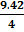 = 2.354 cm
= 2.354 cm
b) arc length, 1 = r θ
1 = 6 x 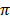
1 = 6 x 3.14
= 18.84cm
Example 1.16
Find the area of the sector of a circle with radius 6cm and subtended by an angle of 60o use 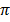 = 3.14
= 3.14
Solution
Area =  r2θ
r2θ
= ½ x 6 x 6 
= 6 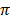 cm2
cm2
Since 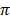 = 3.14
= 3.14
Therefore, area = 3.14 x 6
= 18.84cm2
Trigonometric Equation
Example 1.17
Solve sin θ = ½ for 0o ≤ θ ≤ 360o
Solution
Sin θ = ½
θ = Sin-1 ( ½)
θ = 30o, 150o
Example 1.18
Solve 2sin θ – 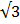 = 0 for 0 ≤ θ ≤ 360
= 0 for 0 ≤ θ ≤ 360
Solution
2 sin θ = 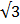
Sin θ = 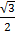
θ = 60o, 120o
Example 1.19
2cos2 θ + 3cos θ – 2 = 0
Solution
This equation is quadratic in cos θ
Factorize the equation
2cos2 θ + 3cos θ – 2 = 0
Let cos θ = t
2t2 + 3t – 2 = 0
2t2 + 4t – t – 2 = 0
2t (t + 2) – (t + 2) = 0
(t + 2) (2t – 1) = 0
t = -2 or 2t = 1
t = -2 or t = ½
But, t = Cos θ
Cos θ = -2
θ = undefined or no solution since the minimum value of cos θ = -1
Cos θ = ½ = θ = 60o, 300o
θ = (60o, 300o)
Example
Solve Cos 2 θ Cos θ + Sin 2θ = 1, where 0≤ θ ≤ 360o
Solution
Use the compound angle formula Cos (A – B) = Cos A Cos B + Sin A Sin B
Thus, Cos 2 θ Cos θ + Sin θ = Cos (2θ – θ) = Cos θ
Cos θ = 1
θ = (0o, 360o)
Trigonometric functions
Let x be angle in degree or radians and f (x) be the image of x. Then the functions defined as f (x) = sin x, f (x) = cos x and f (x) =tan are called trigonometric functions. These functions can be graphed just like any other functions. Values of angles should be on the horizontal axis and images values should be on the vertical axis.
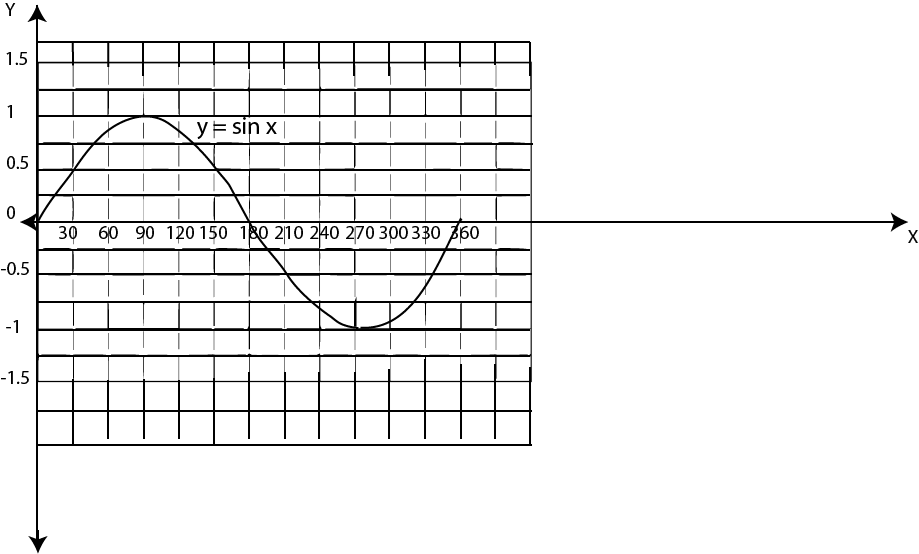
Sine functions f (x) = sin x
To graph sine functions, draw a table of values in which x values will be angles and y = f (x) will be images of these angles. The angles may be in degrees or radians. Table 8.1 has values that suit a function y = sin x, (The y – values are correct to one decimal place)
| x | 0 | 30 | 45 | 60 | 90 | 120 | 135 | 150 | 180 | 210 | 225 | 240 | 270 |
| ysinx | 0 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1 | 1 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0 | -0.5 | -0.7 | -0.9 | -1 |
edu.uptymez.com
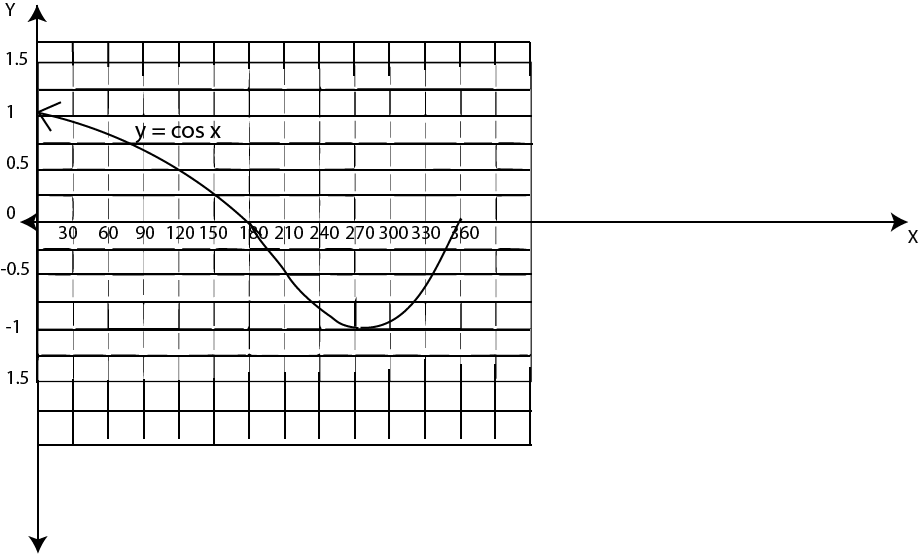
Cosine function y = cos x
To graph cosine function follow the procedure followed in drawing sine functions. Table 8.2 contains values for y = cos x. In table 8.2 values are given to one decimal place.
Note
1. The domain of y = sin x and y = cos x is set of real numbers and range is (-1 ≤ y ≤ 1).
2. These functions are periodic, they repeat after every one complete revolution (360o)
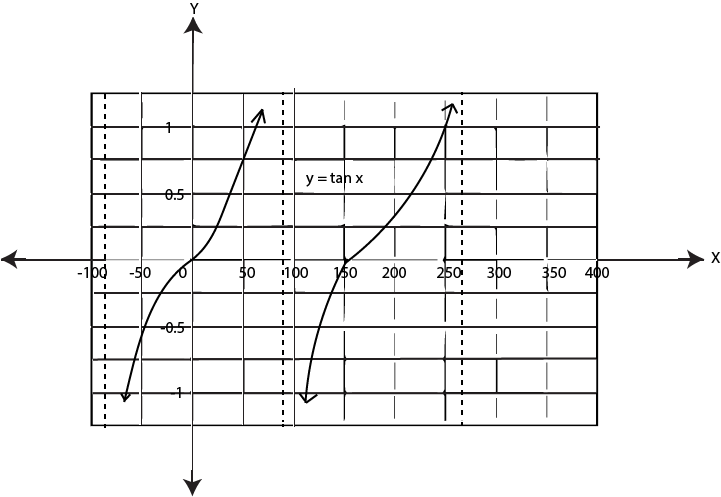
Graph of y = tan x
To graph y = tan x draw a table values and plot the point required then join the points
with given correct to one decimal places.
| xn | 90 | 60 | -45 | 30 | 0 | 30 | 45 | 60 | 90 | 120 | 135 | 150 | 180 |
| Y tan x | 1.7 | -30 | -1 | 0 | -0.6 | 1 | 1.7 |  |
-1.7 | -1 | -0.6 | 0 |
edu.uptymez.com
Note
1. The range of y = tan x is a set of real numbers
2. The domain is (x: x ≠ 90o, x ≠ 270, x ≠ 450…)
3. The tangent function is periodic too. It repeats itself after every 180o
4. At x = 90o, x = 450o etc, the functions not defined. These values are its asymptotes. It tends to approach these values but never touches them
Exercise
1. State the range and period for each of the following
a) y = cos x
b) y = ½ cos 2x
c) y = ½ cos x
d) y = 3 sin x
e) y = 3 – sin x
j) y = 1 + sin 