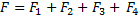Definition
Vectors are any quantity that possess both magnitude and direction .
Example
(i) Displacement
(ii) Velocity
(iii) Acceleration
REPRESENTATION OF A VECTOR
The vector quantity is always described by using two capital letters with respect to arrow on top or small letters with respect to bar at the bottom.


 n
n
A B
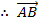 or
or 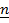
COMPONENTS OF VECTORS.
This depends on the dimension of vector as follows;
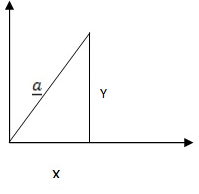
(i) For two dimensions namely as 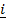 and
and 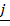
Where 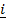 =x- value
=x- value
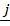 = y – value
= y – value
e.g. 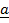 = (x,y) coordinate form
= (x,y) coordinate form
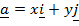 component form
component form
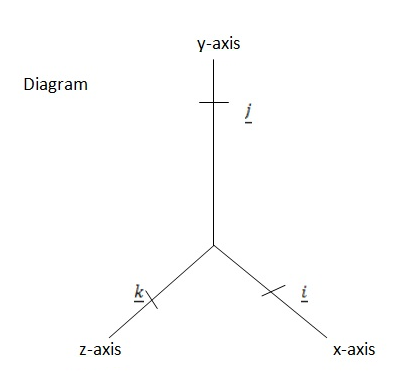
Diagram
For three dimensions
Re: 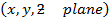
This involves three components namely as 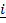 ,
, 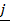 and
and 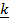
Where,
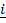 = x – value
= x – value
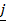 = y – value
= y – value
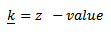
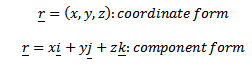
TERMINOLOGIES APPLIED IN VECTOR ANALYSIS
1. PARALLEL VECTORS
These are vectors having the same direction.
e.g
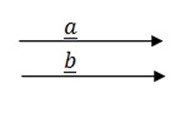
2. EQUAL VECTORS
These are vectors having the same magnitude and direction.
e.g.
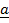 = 5N
= 5N
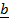 = 5N
= 5N
3. NEGATIVE (OPPOSITE) VECTORS
These are vectors having the same magnitude but opposite direction.
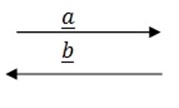
Hence
(i) 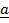 =-
=-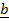 (vector in opposite direction
(vector in opposite direction
(ii) 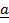 =
= 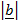 = b vector on the same direction
= b vector on the same direction
FREE VECTORS
These are vectors which originate from different points.
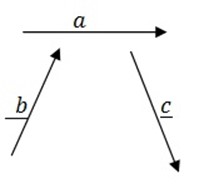
POSITION VECTORS
These are vectors which originate from the same points.
NB:
– Position vector of 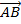 =
= 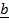 –
– 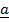
– Position vector of 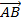 =
=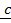 –
– 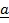
– Position vector of 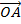 =
= 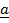 –
– 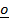
– Position vector of 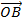 =
= 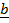 –
– 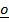
NULL VECTORS
These are vectors which have a magnitude of zero ( length of zero) or
These are vectors which contain zero point
Eg.
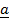 = (0,0)
= (0,0)
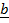 = (0,0,0)
= (0,0,0)
COLLINEAR VECTORS
– These are vectors which lie on the same line.
i.e. 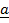
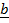
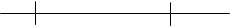
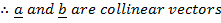
COPLANAR VECTORS
These are vectors which lie on the same plane.

 ,
, 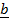 and
and 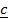 are coplanar vector
are coplanar vector
NB:
Consider the vector diagram below;
Where

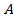 = initial (starting) point
= initial (starting) point
B = Final (terminal) point
OPERATION IN VECTORS
These are
(i) Addition
(ii) Subtraction
(iii) Multiplication
i. ADDITION OF VECTORS
Suppose two dimensional vectors
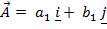
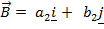
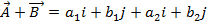
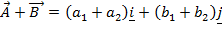
Suppose three dimensional vectors
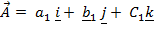
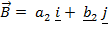 +
+ 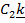
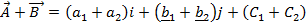 k
k
RESULTANT VECTOR
Is the single vector which represents the effect of all vectors acting at a point.
Consider 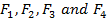 are acting at a point
are acting at a point
Hence
Where F is the result force/ vector