ECONOMIC ORDER QUANTITY (EOQ)
Is an amount of quantities delivered from supplier of materials. Economic order quantities is given by a formula below;-
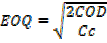
Where
C = ordering cost per order
D = Demand per annual
Cc = carrying cost per item per annum
Examples
Find the economic order quantity where demand is 20,000 units per annum, the ordering cost is Tshs. 500 per order; the carrying cost per item per annum is Tshs. 120
Solution
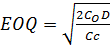
Demand per annum = 20,000 units (10,000)
Carrying cost per item = Tshs. 120 (100)
Ordering cost = Tshs. 500 (180)
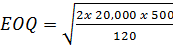
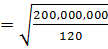
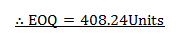
STOCK TAKING
This is a process of verifying the balances of items held in stock at the end to the pre- determined period by counting, weighing and measuring. Stock taking can be divided into three (3) categories
1. ANNUAL STOKING
This is done once per year to find the ending balance for the purpose of preparing financial report.
2. PERIODIC STOCK TAKING
This is an activity of finding the balances of stock for an interval period.
3. PERPETUAL STOCK TAKING
This is the continuous stock taking of recording the transactions made of receiving and issuing of materials in stock.
CALCULATING CONTROL LEVELS
1. LEAD TIME
Is the period of time between ordering and replacement. i.e. when goods are available for use.
2. RE-ORDER LEVEL
Is the level of stock at which a further replacement order should be placed.
Re-order level = maximum usage x maximum level time.
Minimum level = Re-order- (Normal consumption x lead time).
TURN – OVER
Turn-over refers to total sales at a certain period of time.
Turn-over = price x Quantity
= P x Q
RATE OF STOCK TURN OVER
This is the number of times the average volume of stock held has been turned over. i.e. Sold during a given period.
Rate of stock turn over = 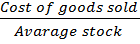
GROSS PROFIT
This is the excess of sales (turn over) the cost of sales.
G.P = Total sales – cost of sales.
Example 1.
Given
Sales = 12,000
Purchases = 100,000
Gross profit = 120,000 – 100,000
= 20,000
Example 2
Given the following date of a firm opening stock at the beginning of the year = 250,000
Purchases = 300,000
Closing stock at the end of the year = 20,000
Goods returned to supplier (Returns outwards) =10,000
Goods returned by customers (returns inwards) = 20,000
Total sales = 800,000
Find gross profit
DR TRADING A/C CR
|
Opening stock 250,000 Add: Purchases 300,000 Less : returns outwards 10,000 Net purchases 290,000 Goods available for sale 540,000 Less: closing stock 20,000 Cost of goods sold 520,000 Gross profit 260,000 780,000
|
Sales 80,0000 Less: returns inwards 20,000 Net sales 780,000 780,000 |
edu.uptymez.com
NET PROFIT
This is the revenue which remains after making deductions of expenses running a business.
In order to calculate net profit, a profit and loss A/c must be drawn up, showing on the credit side the gross profit brought forward from the trading A/c and on the debt side, the various expenses such as rent, rates, taxes, wages, insurance, interest on loans (if any), advertising , light and heat, depreciation etc.
Net profit = gross profit – expenses
BUSINESS CALCULATIONS
(a)MARK-UP
This is gross profit as a percentage to cost price.
Mark-up = 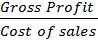 x 100
x 100
Example
Given
Cost price = 50,000
Gross profit = 25,000
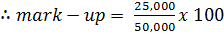
= 50%
(b)MARGIN
This is the gross profit as a percentage to sales price.
Margin =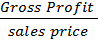 x 100
x 100
Example:
Given
Selling price = 100,000
Gross profit = 20,000
Margin 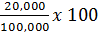
= 20%
DISCOUNTS
This is the allowance given to the trade on the goods purchases. There are 3 types of discounts.
(a) TRADE DISCOUNT
This is an allowance (deduction) made if goods are sold by one businessman to another businessman on goods whose price is either fixed or controlled or is generals known.
Example
Mr. Bukagile sells his products at Tshs. 1000 per unit. He gives trade discount of 10%. If a customer bought 50 units the trade discount will be:-
(50 x 1000) x 10%
= 5000
(b) QUANTITY DISCOUNT
This is the discount allowed in additional to a trade discount if the quantity of goods sold is large.
Example
A wholesaler selling soda may allow trade discount to retailers of 20% to quantities less than 50 crates and additional quantity discount of 5% to any amount exceeding 50 crates.
(c) CASH DISCOUNT
This is a discount given to induce the trader to pay promptly.
Example: 5% discount will be allowed if payment is made within 1 month, 2% if payment is made after 1 month and 1% if payment is made after a month.
TYPES OF CASH DISCOUNT
(i) DISCOUNT ALLOWED
This is the amount which is allowed to the debtor. It is an expense to a business.
(ii) DISCOUNT RECEIVED
This is a discount which is received from creditors.
DOCUMENTS USED IN WARE-HOUSING
1.Ware-house warrant.
This is a document authorizing the removal of goods. This is a document issued to the importer after storing his goods in a ware-house.
2.In-bond notes.
This is a document that shows the amount of goods which are in a ware-house.