What is mole?
Mole is a unit of measurements as any other units,
Example Pair, dozen, gross etc
1mole = 6.02 x 1023 particles
Definition;
A mole is the amount of a substance as many as particles of elementary entities contained in 12g of carbon-12 isotopes. The particles can be atoms, molecules, electrons or ions. This is a unit mole which was introduced by Avogadro
as 6.02 x 1023 particles
Example; 1 mole of water (H2O) contains 6.02 x 1023 molecules
1 mole of sodium (Na) contains 6.02 x 1023 atoms
1 mole of CuCl2 contains 6.02 x 1023 ions
1 mole of Fe contains 6.02 x 1023 electrons
MOLAR MASS OF A SUBSTANCE
Molar mass: is the mass of I mole of any element or compound
Its SI unit is g/mol. It is denoted by M
For example; Na = its molar mass = 23g/mol
NaCl = its molar mass = 58.5g /mole
Na2SO4 = its molar mass = (23 x 2) + (32) + (16 x 4) = 142g/mol
NB: Molar masses and relative molecular mass of a substance are calculated from the formula of that substance.
QUESTION;
Calculate the molar of the following
1. Na2CO3. 10 H2O
11. Al2 (SO4)3
Al = 27, S = 32, O = 16, Na = 23, C = 12, H = 1
2. Calculate the number of molecules in i. 8g of oxygen gas
ii. 11g of CO2
3. If the number of ions in CuCl2 is 3.02 x 10 23, what was the mass of CuCl2
ANSWERS:
- Na2CO3.10H2O
edu.uptymez.com
(23 x 2) + 12 + (16 x 3) + 10 [(1 x 2) + 16]
46 + 12 + 48 + 180
106 + 180 = 286g/mol
ii) Al2 (SO4)3
(27 x 2) + 3 (32 + (16 x 4))
54 + 3(96)
54 + 288 = 342g/mol
Iii). 8g of oxygen gas
O2 = 16 x 2 = 32 = 6.02 x 1023
8 =?

= 1.505 x 10 23 molecules
IV). 11g of CO2
CO2 = 12 + 32 = 44 = 6.02 x 1023
11 =?
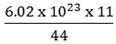
= 1.505 x 1023 molecules
CuCl2
64 + (35.5 x 2) = 64 + 71 = 135 = 6.02 x 1023
? = 1023
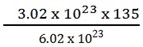
= 67.5 g/mol
RELATIVE MOLAR MASS (Mr)
This is the mass of one molecule of a compound compared with the mass of one atom of carbon – 12.
It has no units
Molar mass (M) = Relative molecular mass (Mr)
Molar mass of an element = relative atomic mass (Ar)
Example; Na M of Na = 23gmol-1
Ar of Na = 23
M or CH4 = 16gmol-1
Mr of CH4 = 16
M of H2O = 18gmole
Mr of H2O = 18
Example;
1. Calculating the molar mass of (NH4)2CO3 given that N = 14, H= 1, C = 12, O = 16.
Solution
(NH4)2CO3
(14g x 2) + (1g x 8) + 12g + (16g x 3)
28g/mol + 8g/mol + 12g/mole + 48g/mol
= 96g/mole
Molar mass of a compound
This is the sum of constituent atoms (elements)
AMOUNT OF A SUBSTANCE OR NUMBER OF MOLES (n)
Number of moles, n is the mass of the sample of a substance divided by the molar mass of that substance
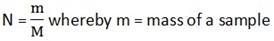
M = Molar mass of substance
N = number of moles (amount of substance)
Example;
What is the amount of substance in
a) 180g of carbon
m = 180g
M = 12gmol-1
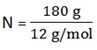
n = 15mol
b) 180g of CO2
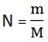
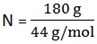
n = 4.09 mol
QUESTIONS:
Finding the mass of each of the following substance
a) 2.4 mol of NaOH
b) 3.2 x 10-3 mol of N
c) 0.780 mol of Ca(CN)2
d) 7.00 mol of H2O2
How many moles are in each of the following?
a) 0.800g of Ca
b) 79.3g of Cl2
c) 5.96g of KOH
d) 937g of Ca(C2H3O2)2
NUMBER OF PARTICLES (N) IN A GIVEN AMOUNT OF SUBSTANCE (n)
To find the number of particles in a given amount of substance we use the expression
N = n.L
Where: n = number of moles
N = number of particles in a substance
L = Avogadro’s no = 6.02 x 1023 mol-1
QUESTION:
1. How many particles are there in 20g of Ca?
Solution
Find n in 20g of Ca
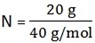
N = 0.5 mol
From the expression
N = nL
= 0.5 mol x 6.02 x 1023 mol-1
= 3.01 x 1023
2. How many molecules are there in 80g of the NaOH?
MOLAR VOLUME (Vm)
MOLAR GAS VOLUME
This is the volume occupied by one mole of a gas at standard temperature and pressure and is 22.4 dm3 or 22.4l
1dm3 = 1l = 1000cm3
Standard temp = 00c (273K)
Standard pressure = 1 atm (760 mm Hg)
Avogadro’s law states “At the same temperature and pressure volumes of all gases contain the same number of particles”
In calculating the amount of substance n, using molar volume (vm), the expression used is

Example; Find the amount of substance present in
a) 18.8 dm3 of CO2 at s.t.p
b) 48.8 dm3 of O2 at s.t.p
Solution

Where; V = volume of a gas
Vm = molar volume of a gas
n = amount of substance
V = 18. 8 dm3
Vm = 22.4 dm3/ mol
n =?
Substituting the volume in the expression
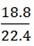
n = 0.839 mol
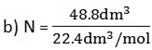
n = 2.18 mol
THE MOLE IN STOICHIOMETRIC CALCULATIONS
A balance chemical equation tells us a great of quantitative information
Consider the following equation us a great deal of quantitative information
Consider the following balanced equation
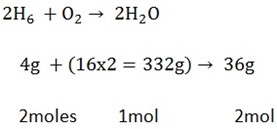
Stoichiometry- is the quantitative relationship of reacting substances
Stoichiometric coefficients = moles
A balanced equation is used in calculating different quantities
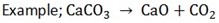
From the above balanced equation, calculate the weight of CaO and Volume of CO2 at s.t.p which will be produced by heating 75g of CaCO3
(Ca = 40, C = 12, O = 16)
Solution
Finding the molecule mass
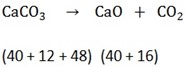
Molecular mass of CaCO3 = 100g
CaO = 56g
From the equation:
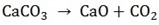
1 mol 1mol 1mol
100g 56g
15g x?
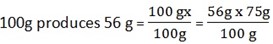
75g produces ?
x=42g
If 100g/mol = 22.4dm3
75g/mol =?
= 16.8 dm3
QUESTION
a) How many ions are in 10g of Al2(SO4)3?
b) How many fluorides are in 1.46mols of AIF3?
Solution;
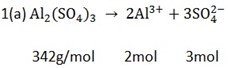
342 g/mol = 5 mol of ions
10 g = ?
If 342 g = 1 mol
10 g = x
x = 0.0292 mol of Al2 (SO4)3
If 1 mol of Al2 (SO4)3 = 5mol of ions
0.0292mol of Al2 (SO4) 3 = ?
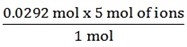
= 0.0146 mol of ions
N = nL
= 0.046 mol x 6.02 x 1023 mol-1
= 8.79 x 1023
SOLUTION AND MOLAR CONCENTRATION
Solution is a mixture of solvent and solute.
Solute – Is a solid crystal component which dissolved into solvent.
Solvent – Is a liquid component which dissolve solute. (water is a common universal solvent).
So that when we prepare a standard solution, we must measure both two component. A solute measured in grams of weight and solvent in liter, dm3 or cm3 of its volume. The quantity of solute that may dissolved by 1litre of solvent make a standard solution.
STANDARD SOLUTION
Is a solution of known concentration. Standard solution has been prepared by accurate measurement and the concentration of solute in the solution is described into two ways.
i. Weight concentration in grams.
ii. Particles concentration in mole.
i. WEIGHT CONCENTRATION
This concentration abbreviated as conc. of a grams dissolved in one litre (g/dm3 or g/L).
e.g 30g/L or 15g/dm3
Example;
Allen dissolved two spoons of sugar into the tea drink. If capacity of cup is 200cm3 and a spoon carry 25g, what is the concentration of sugar in the tea?
Solution
carrying capacity = 25g
25 x 2 = 50g
Therefore, weight of solute = 50g
Volume of solvent = 200cm3
But,

MOLARITY (MOLAR CONCENTRATION)
This is a concentration of particles contained in one litre of the solution. (mol/L or M)
Example;
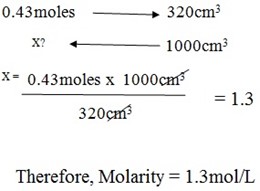
The Allen spin a common salt in the bowl filled by 320cm3 of water to make a solution. If the same spoon used, determine a molarity of salt in the solution.
Solution
Volume of water = 320cm3
Weigh of salt = 25g
But, Moles = weight of component/Molar mass (W/Mr)
n = 25g/58.5g
n = 0.43moles
Therefore,
RELATIONSHIP OF WEIGHT AND MOLAR CONCENTRATION
From,
Molarity = moles/Volume in litre
M = n/V in L
But,
n = W/Mr
Therefore,
M = W/Mr X 1/V in L
But,
W/V in L = Conc
Therefore,
M = Conc/Mr
So that,
Molarity = Conc/ Molar mas
Where by,
n = no of moles
V = Volume in liter
Mr = Molar mass
W = Weight of component in grams
Assignment
Find the molarity of each component if both had a concentration of 72g/dm3 .
(a) H2SO4
(b) Na2CO3
(c) NaHCO3
(d) KCl
