EFFECT OF SOLUTE ON VAPOR PRESSURE BY OSWALD’S METHOD
Consider the solution made by dissolving solute in a given solvent. Then the dry air being passed through the two component
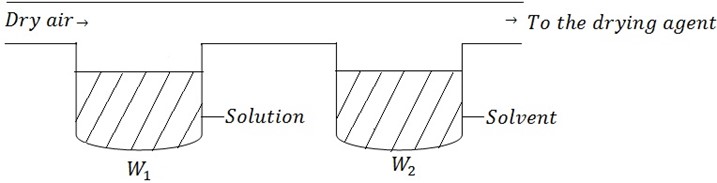
The passage of dry air cause the loss in mass (weight).
Let:
W1 be loss in mass of solution.
W2 be loss in mass of solvent.
Also the Po is be the vapor pressure of solvent
P be the vapor pressure of solution
W1 α P
W1 α P0 – P
W1 = KP But k =1
W1 = p ————(i)
W2 = k (Po -P) k =1
W2 = Po – P ———(ii)
Now
Add the two equations
W1 + W2 = Po – P + P
W1 + W2 = Po
From Raoults,
Relative lowering of
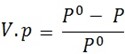
But Po – P = W2 and Po = W1 + W2
Hence;
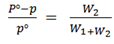
Where
Po is the V.p of solvent
P is the V.p of solution
W1 is the loss in mass of solution
W2 is the loss in mass of solvent
Example 6
A current of dry air was passed through a solution of 2.64g of benzoic acid in 30g of ether (C2H5OC2H5) and then through pure ether. The loss in weight of the solution was 0.64g and that of ether was 0.0345g. Calculate the molecular mass of benzoic acid (122g/mol).
Solution
Weight of solution W1 = 0. 645g
Weight of solvent W2 = 0.0345g
Mass of solution m = 2.64g
Mass of solvent M = 30g
Mr of ether (C2H5OC2H5) = 74g/mol
But


Example 7
A stream of dry air was passed through a bulb containing a solution of 7.5g of aromatic compound in 75cm3 of water and through another globe containing pure water. The loss in mass in the first globe was 2.81g and in the second globe was 0.054g. Calculate the Molar mass of aromatic compound 93.6.
Solution
Mass of solution = 7.5g
Mass of solvent = 75g
Loss in mass of solution = W1 = 2.81g
Loss in mass of solvent = W2 = 0.054g
From Oswald’s law;

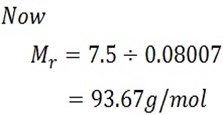
Example 8
In a experiment air was drown successively through a solution of sugar (38.89g per 100g H2O) and the distilled water, and then through anhydrous calcium chloride. It was found that water lost was 0.0921g and the calcium chloride globe gained 110g. Calculate the molar mass of sugar
Solution
Mass of sugar = 38.89g, W1 + W2 = 5.16g
Mass of water 100g, W2 = 0.0921g
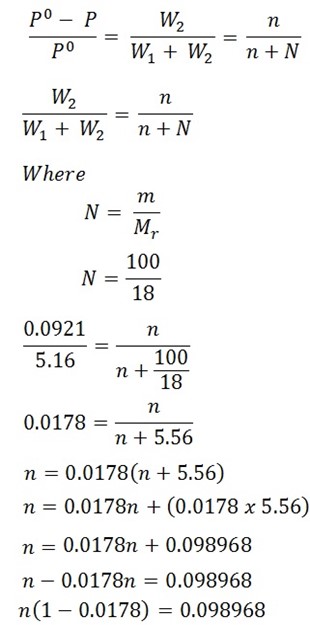

2. BOILING POINT ELEVATION
What is boiling point?
Boiling point is the temperature at which liquid boils where by the vapor pressure of that liquid is equal to the atmospheric pressure.
Effect of solute(impurities) to the boiling point of the liquid.
When solute particles are added to the liquid, the solution formed. The boiling point of the solution formed is increased by some oC. The boiling point is elevated due to the increase in collision of solute molecules and liquid molecules. Finally the temperature being raised.
The difference between the boiling point of the solution and the boiling point of the liquid is what we call Boiling point elevation
The boiling point is denoted by ΔT
ΔT = T2 – T1
Where by;
T 2 is the boiling point of solution
T 1 is the boiling point of solution
Note
ΔT is always positive.
The relationship between boiling point elevation and the amount of solute added
This relationship can be explained by two laws which are;
i) Blagden’s law
ii) Raoult’s law
i) BLAGDEN’S LAW
It states that;
“The change in temperature caused by addition of solute is directly proportional to the amount of solute being added”
If the amount is represented by m
From Blagden’s law

ii) RAOULT’S LAW OF BOILING
POINT ELEVATION
It state that;
“The change in temperature caused by the addition of solute particles is inversely proportional the molecular weight of the solute added”
From Raoult’s law

What is Molality?
Molality is the number of moles of solute per 1kg of the solvent.
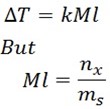
Where
ms mass of solvent in kg
nx number of moles of solute
If ms is given in ‘g’
Then it has to be converted to kg
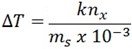
But
K is called boiling point elevation constant or ebullioscopic constant (k)

Definition
Molar elevation constant is the boiling point elevation produced when 1 mole of solute is dissolved in 1kg of the solvent.
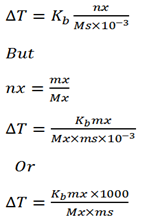
Example 1
a) Define the following
i) Boiling point
ii) Boiling point elevation constant
iii) Ebullioscopic constant
Answer
i) Boiling point is the temperature at which liquid boils where by the vapor pressure of that liquid is equal to the atmosphere pressure.
ii) Boiling point elevation constant is the temperature change when 1 mole of solute is dissolved 1kg of the solvent.
iii) Ebullioscopic constant is the boiling point elevation obtained when 1 mole of solute is dissolved in 1kg of the solvent.
b) What is the boiling point of the solution containing 3moles of sugar in 1000g of water (Kb for H2O is 0.52).
Solution
Number of moles of solute nx = 3
Kb = 0.52
Mas of solvent = 1000g
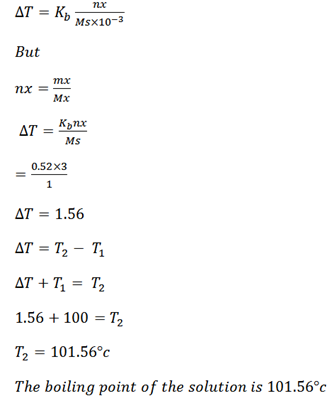
Example 2
When 1g of solute was added in 10g of water the boiling point elevation was 1.2oC. Calculate the molar mass of solute if the ebullioscopic constant of water is 0.52
Solution
Mass of solute mx = 1g
Mass of solvent = 1og
B.P elevation T = 1.2oC
Kb of solvent = 0.52.
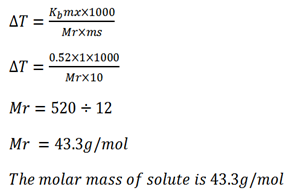
Example 3.
A solution containing 18.4g glycerine per 100g of water boil at 101.04oC. Calculate the molar mass of glycerine .
Kb for 0.52oC kgmol-1
Solution
Mass of solute mx = 18.4g (T1 = B.P of H2O)
Mass of solute ms = 100g
B.P of solution T2 = 101.04oC
Kb of solvent = 0.52
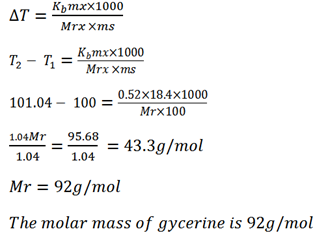
Example 4
The boiling point of a solution containing 0.2g of substance X in 20g of ether is 0.17k higher than that of the pure ether . Calculate the molecular mass of X . The boiling point constant of ether per 1kg is 2.16k (127. 8g/mol).
Solution
Mass of solute = 0.2g
Mass of solvent = 20g
B .P elevation ΔT = 0.17k
Kb of ether (solvent) = 2.16
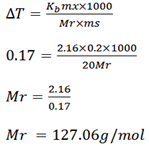
Example 5
Acetone boils at 56.38oC and a solution of 1.41g of an organic solid in 20g of acetone boils at 56.88oC . If k for acetone per 100g is 16.7oC . Calculate the mass of one mole of the organic solid.
Solution
B .P of solvent T1 = 56.38oC
B.P of solution T2 = 56.88oC
Mass of solute = 1.41g
Mass of solvent = 20g
Kb of solvent = 1.67
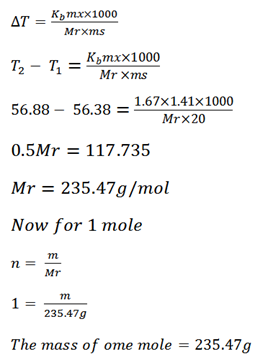
3. FREEZING POINT DEPRESSION
What is freezing point?
Is the temperature at which liquid change into solid state /freeze.
Effect of solute on the freezing property of the liquid
When solute is added to a certain liquid, the freezing point of the liquid is lowered. This is because the solute particles disturb the intermolecular forces between the molecules of the liquids.
The difference between the freezing point of the solvent (pure liquid) and that of solution is what we call freezing point
Depression
Freezing point depression is denoted by ΔT
ΔT = T2 – T1
Where;
T1 is the freezing point of solvent
T2 is the freezing point of solution
The freezing point depression (T) is related to the amount of solute added by the following expression
Note
The some derivation as in boiling point elevation
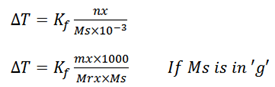
Definition
Freezing point depression equation;
Kf is freezing point constant or Cryoscopic constant.
Definition
Cryoscopic constant is the temperature expressed when the molar weight of solute dissolved in a kg of solvent.
Example 1
Ethanoic acid has the freezing point of 16.63oC on adding 2.5g of solute to 40g of the acid, The freezing point was lowered to 11.48oC. Calculate the molar mass of the solute if kf is 3.9oC kgmol-1
Solution
F.P of ethanoic T1 = 16. 63oC
Mass of solute = 2. 5g
Mass of solvent = 40g
Lowered F.P T2 = 11.48oC
Kf of the solvent = 3.9oC kgmol-1
ΔT = T2 – T1
= 11.48 – 16.63o
= -5.150C
Now
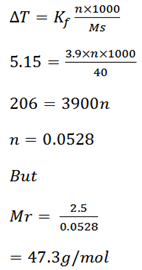
Example 2
When 0.946g of organic substance was added in 15g of water resulting into the solution which was found to have the freezing point of -0.651oC ( kf is 3.9 ).
i) Calculate the molar mass of solute (179.2)
ii) What is the molecular formula of solute (mf) if its empirical formula is CH2O?
Solution
Mass of solute = 0.946g
Mass of solvent = 15g
F. P of solution = -0.651oC
Kf of solvent = 1.86
F.P of solvent = 0oC
T = T2 T1
T = 0.651 – 0
T = –0.651
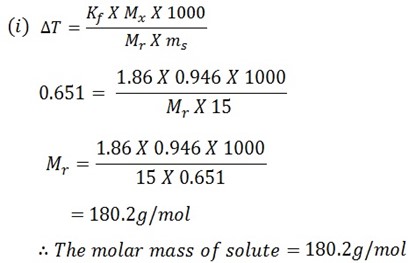
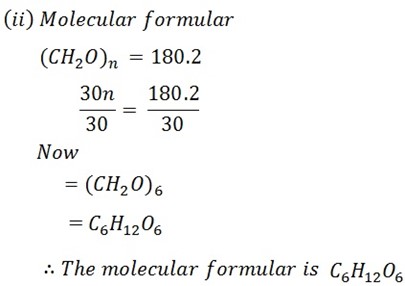
Example 3
Define the following terms
i) Boiling point.
ii) Freezing point.
iii) Freezing point depression.
iv) Cryoscopic constant.
Answers
i) Boiling point Is the temperature st which liquid boils where by the vapor pressure of that liquid is equal to the atmospheric pressure.
ii) Freezing point Is the temperature at which liquid change into solid state. e.g f.P of water is OoC.
iii) Freezing point depression Is the difference between the freezing point of the solution and that of the solvent (pure liquid).
iv) Cryoscopic constant Is the temperature depressed when the molar weight of solute is dissolved in a kilogram of solvent.
b) 7.85g of the compound Y having the empirical formula of C5H4 was dissolved in 310g of benzene (C6H6) . If the freezing point of the solution is 1.05oC below that of pure benzene.
i) Determine the molecular mass Y.
ii) Find the molecular formula of Y if Kf for C6H6 is 5.12oC kg mol-1