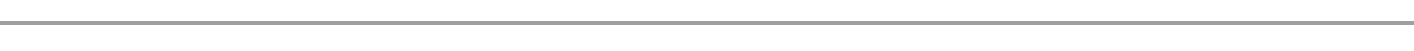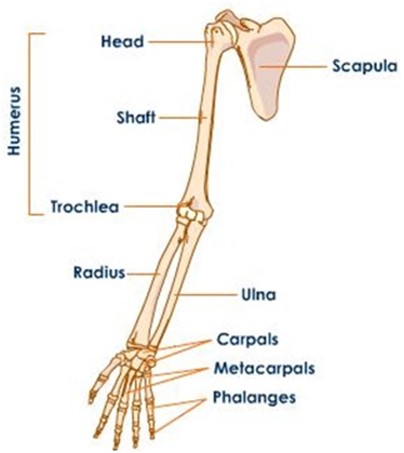
SKELETON OF HUMAN HIND LIMB
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS
- Bone
edu.uptymez.com
This is a hard, tough connective tissue composed of minerals salts; calcium and phosphate.
2. Cartilage
This is a soft bone found in the trachea, ear, and nose and at the end of the bones especially at joints to reduce friction.
3. Ligaments
These are fibrous tissues which join one bone to another. Ligaments are elastic to allow movement at a joint.
4. Tendon
This is a tough connective tissue which attaches a muscle to bone. Tendons are inelastic to firmly attach muscles to the bones
5. Joints
This is area/region where bones meet. Joints provide articulation between bones making movement possible
Types of joints
1) Movable joints
2) Immovable joints
1. Fixed/ immovable joints
These are joints that do not allow movement of bones. E.g. Pelvic girdles and sutures (bones found in the skull)
2. Movable joints
These are joints which allow movement of bones E.g. Hip joint and shoulder joint
Types of movable joints
These are classified according to movement of bones at joint in different shapes or structure.
There are four types of movable joints
a) Ball and Socket joints
b) Hinge joints
c) Glinding joints
d) Pivot joints (peg and socket joints)
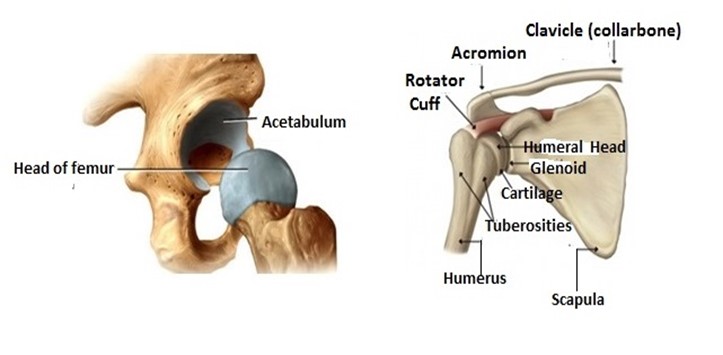
a) Ball and Socket joint
Is the type of movable joint which allow movement of bones to take place in many direction.
These types of joints allow the greatest flexibility of all joints e.g. hip joint, shoulder joint
It is called the ball and socket joints because the round head which looks like a ball of one bone it’s a socket of another bone. At the shoulder, the rounded head of the Humerus fits into the socket of the pectoral bone. Some joints have synovial fluid which reduces friction by lubricating the bones, e.g. hip joint shoulder and knee join
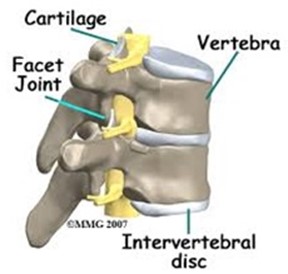
b) Glinding joints (sliding)
These are bones that occur between the vertebrae. This type of joints found where two or more bones surface move over each other. It allows movement in two directions. It occurs at the wrist and ankle and allows hand and foot to be moved up and down or to be rotated only slightly.
They lack fluid between them, and instead they have a layer of cartilage between them that reduce friction
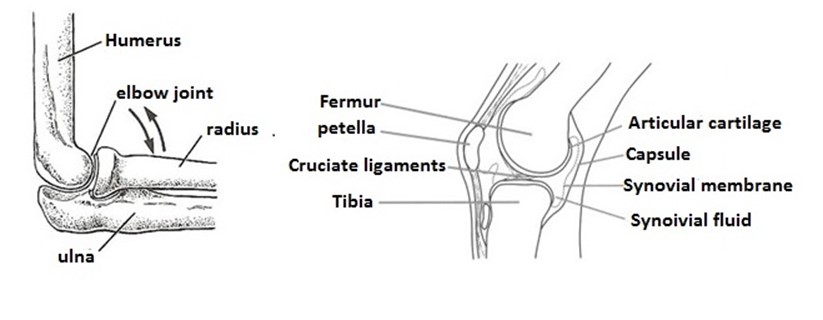
c) Hinge joints
Is a joint which allows only movement of bones to one direction, it is called hinge joint because it operates like the hinge of a door in which a door is allowed to move in one direction only. A joint of this type is found at the elbow, knee, finger, knuckles are between the phalanges of toes.
d) Pivot joint (on the neck)
The skull is pivot at the first cervical vertebra (atlas). The joint allow the head to move sideways. E.g. when a person he shake his head and say no. It allows nodding movement.
Adaptations of joints to movement
- Freely movable joints such as those of the limbs may therefore cause dislocation hence movement joint involves more than one bone. Dislocation and friction is presented by the ligament which holds the bones together.
-
It may also cause knocking of bones against each other, and strain in the bones due to compression of the bones are not well protected.
In freely movable joints such as those of limbs, dislocation is prevented by the ligament which holds together bones.
-
Joints which support weight are provided with cushion. The cushion absorbs compression due to weight. Cushioning in the joint is provided by the disc (in the intervertebral column) of cartilage as in the case in joints of the vertebrae.
MUSCLES
Muscle is a tissue of consisting of cells that have the capacity to contract and exert a pull
Types of muscles
I. Skeletal muscle (voluntary)
II. Cardiac muscle (involuntary)
III. Smooth muscle (involuntary)
Muscles are tissues that cover the skeleton
edu.uptymez.com
The skeleton alone can’t bring about locomotion and movement of the body in order to bring about movement there must be muscles. These muscles are attached to the bones. Muscles are composed of many elongated cells called muscles fibres which are able to contract and relax.
During relaxation of muscles can be stretched but they show elasticity which allows the regain to their original size and shape after being stretched.
Muscles are made up of specialized tissues which are known contractile tissue. When these tissues contract, they become shorter and tighter as a result they cause movement
1. SKELETAL MUSCLE
These are muscles which are attached to bones of the skeleton. Are made up of long fibre and cover the skeleton are also known as striated/ voluntary muscles because they are controlled by the will.
Skeleton muscles can contract and relax quickly but get fatigue quickly
Functions
-
Skeletal muscles are concerned with movement of the limbs and parts of the skeleton

edu.uptymez.com
2. SMOOTH MUSCLE
These are muscles found on the wall of internal organs
- Such internal organs are alimentary canal, bladder, uterus, sperm ducts and blood vessel e. t. c.
- Smooth muscles are controlled by involuntary nervous system meaning they cannot contract at will. So they are involuntary muscles.
-
Smooth muscles contract slowly and they get fatigue relatively slowly
edu.uptymez.com
Functions of smooth muscle
-
They contract and relax to cause movement in different organs e.g. peristalsis in the alimentary canal cause movement of the materials through the canal with the help of smooth muscle
edu.uptymez.com
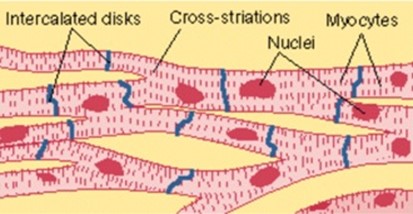
3. CARDIAC MUSCLE
These are muscles which are found only in the heart. Their muscles are made up of muscle fibres which branch and connect to each other like a network (interconnecting network)
Cardiac muscle has the capacity to contract and relax through its life without becoming fatigued. (They contract softening from fatigue)
The contractions of these muscles are not (initiated) helped by the nervous system so they are involuntary muscle.
MUSCLE AND MOVEMENT
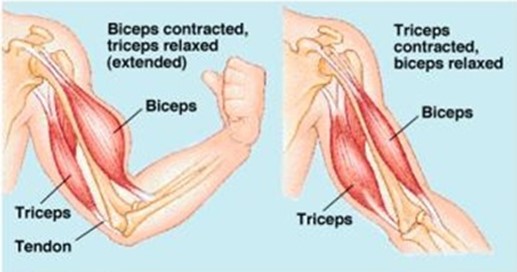
The skeleton alone cannot bring about locomotion and movement of the body parts such as arms, finger and jaws when the aim is straightened.
The muscles above the arm become thin while those below become thick. The bending and straightened of the arm is brought by two sets of muscles located above and below the Humerus.
The muscles above the Humerus are called biceps and those at the back are called triceps.
Bending of the arm is brought about by contraction of muscle in which they are called flexor and relaxation of triceps muscles are called extensor for the arm to straighten the triceps contract biceps relax.
Muscle which work as pair in opposition to one another are called antagonistic pairs. Their antagonistic action is necessary to bring continued movement. Therefore biceps and triceps are known as antagonistic muscles. Muscles are attached to bones at both ends by strong in elastic fibres called tendons.
Contraction and Relaxation of Biceps and Triceps during bending and strengthen of the arm
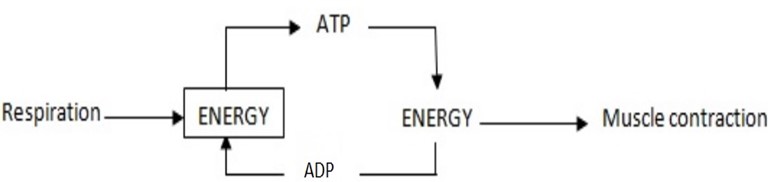
Muscles contraction
- For muscle to contract, energy is required. This energy is derived from respiration and it is found in the muscle cells in the form of ATP.
- During muscle contraction ATP is broken down to ADP, there by releasing the energy. The released energy is used to cause the muscle tissue to contract.
edu.uptymez.com
MUSCLE CRAMPS
These are sudden, involuntary contractions of muscles or groups of muscles.
The tissue may become hard and knotted cramp in skeletal muscle may occur after a period of prolonged exercise e.g. swimming also it may be caused by lack of salt in the body. Stretching and warming the affected muscles can help to cease the cramp
Causes of muscle cramp
- Dehydration
- Lack of magnesium
- Muscle fatigue
- Excessive exercise
edu.uptymez.com
Prevention of muscle cramps
- Stretching of muscle more often
- Do a lot of physical exercise
- Taking salt through a solution of water
edu.uptymez.com
GROWTH OF CURVATURE (MOVEMENT IN PLANTS)
Since most plants remain fixed to the ground, they are incapable of moving from one place to another.
However their leaves stems and roots may show growth responses. These response results in part of the plants growing away from or toward a stimulus is growth of curvature
Growth movement enables plants to obtain their requirement despite of being fixed in one place.
Growth curvature movements are the result of tropic responses
The tropic movement is the case where a plant moves either towards or away from the stimulus. If the response is toward the stimulus is referred to as (+) positive response.
If the response is away from the stimulus it is referred to as (-) negative responses.
Movement or growth of curvature is categorized in two groups. Which are following;
- Tropic movement or tropism
- Nastic movement
edu.uptymez.com
- Tropism is movement by plant organs in response to unilateral stimulus in which the direction of the movement is related to the direction of the stimulus.
edu.uptymez.com
Tropic Movement includes
i) Phototropism
This is the growth movement in response to the source of light
ii) Hydrotropism
This is the movement by which roots growth toward water
iii) Geotropism
This is the movement in response to the stimulus of gravity
iv) Chemotropism
This is the growth movement in response to source of chemicals
v) Haptotropism
Movement due to touch
II. Nastic movement
Is referred to as non – directional response.
Example of nastic responses are the opening and closing of flower and leaves of certain plants in response to changes in light intensity and temperature, closing of flowers of carmorous plants when touched. Also closing and opening of dandelion flower in response to changes in humidity.
Tropic and nastic movement of plants are response to external stimulus
Importance of Tropical Movement
- Exposes the leaves of the plant to trap maximum sunlight for photosynthesis
- Enables plants with weak stem to obtain mechanical support
edu.uptymez.com