Definition;
Volumetric analysis, is the process of determining the amount of substance in term of volume and concentration of reacting solutions.
Concentration;
This is the amount of substance per one dm3 (litre) of solution
Units are g/dm3, mole/dm3
Types of concentration
1. Molar concentration (morality) is the amount of substance in moles per one dm3 of solution (mol dm -3) it is denoted by M
For example; 0.1M H2SO4, 2M H2SO4 etc
Mass concentration is the amount of substance in games per one dm3 of solution (g/dm3)
Question:
a) Define (I) concentration (ii) molarity
b) Calculate mass concentration of the following
i) 4g of NaOH in 400cm3 of solution
ii) 10g of H2SO4 in 2dm3
iii) 2g of HCl in 4l
Solution

a) Give the meaning and SI units of molarity
b) What is the molarity of a solution containing?
i) 0.05mole in 80 cm3
ii) 0.25mole in 2dm3
iii) 0.5mole in 4l
Solution
2b). given n = 0.05mol
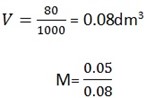
= 0.625mol/dm3
STANDARD VOLUMETRIC APPARATUS
The apparatus needed in volumetric analysis include
- Retort stand and clamps
- White tiles
- Burette – This is calibrated from 0 to 50 cm3 it measures volume of an acid
- Pipette – common capacity volumes are 25 cm3 or 20cm3. It measures volume of a base.
- Conical flask
- Filter funnel
- Reagent bottles
- Volumetric flask
- Wash bottle
- Measuring cylinder
- Beakers
- Watch glass
edu.uptymez.com
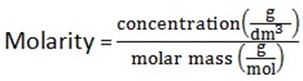
STANDARD SOLUTION
A standard solution is the one whose concentration is exactly known
For example; 10g of NaOH in 1dm3 of solution
10g of KOH in 2dm3 of solution
The molarity of the above substance can be calculated because their concentration (in gdm-3) and formulae are known
MOLAR SOLUTION
A molar solution is the solution which contains one mole of a solute dissolve in one dm3 of solution
Example; 4Og of NaOH dissolved in 1dm3 of solution
98g of H2SO4 dissolved in 1 litre of solution
132g of (NH4) 2 SO4 dissolved in 1L of solution
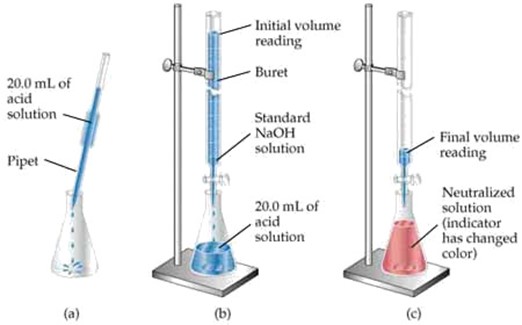
TITRATION OF ACIDS AND BASES
Titration: is the process of adding an acid to a base until an indicator shows that the reaction is complete
What is acid base titration?
What is titration?
This is a process of adding one solution to another until an indicator shows that the reaction is complete
CHOICE OF INDICATORS IN ACID – BASE TITRATION
|
ACID/ BASE |
EXAMPLE |
SUITABLE INDICATOR |
|
Strong acid/ strong base |
HCl / NaOH |
Any indicator |
|
Weak acid/ strong |
Acetic acid/CH3COOH/ KOH |
Phenolphthalein p.o.p |
|
Strong acid/ weak base |
H2SO4/NH3 /(NH4 OH) |
Methyl orange |
|
Weak acid/ weak base |
CH3COOH/NH4OH |
No satisfactory indicator |
edu.uptymez.com
In an acid – base titration, the solution of the known concentration is added gradually to a solution of unknown concentration. When the unknown solution is exactly neutralized as shown by the color change of the indicator then at this point the number of moles of the solution with known concentration, for example; acid is equal to the number of moles of solution with unknown concentration, for example; Base. This point is known as End – point of titration.
MOLAR RATIO
The amount of moles present in the two different solution A and B can be symbolized as nA and nB.
But the moles in standard solution,
n = M x V
Where by,
M = Molarity
V = Volume taken
Therefore,
nA = MA x VA
nB = MB x VB
So that,
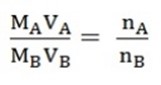
This is called molar ratio formula which can be used in titration to determine any unknown, if five items are known. But always nA and nB identified from the balanced chemical equation of compound A and B.
QUESTION
1. 24cm3 of a solution of 0.1M KOH were exactly neutralized by 30cm3 of solution of sulphuric acid
i) mol/dm3 ii) g/dm3
Solution;
Make the equation;
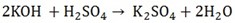
nB = 2 nA = 1
VB = 24cm3 VA = 30cm3
MB = 0.1M MA =?
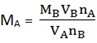
MA = 0.04mol/dm3
ii) Concentration of acid in g/dm3
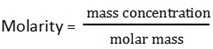
Mass concentration = molarity x molar mass
= 0.04mol/dm3 x 98g/mol
= 3.92 g/dm3
ASSIGNMENT:
LAMBAT GENERAL QUESTION 29 ON WARDS
QUESTION
25cm3 of X2CO3 contains 10.6g/dm3 required 23.00 cm3 and 0.217M of HCL for complete neutralization calculating
i)The molarity of X2CO3 solution
ii) The molar mass of X2CO3
iii) The atomic mass of X
iv)Name of element X
Solution
i) X2Co3 + 2HCL  2xCl + H2O + CO2
2xCl + H2O + CO2
nB = 1 MA = 0.217
VB = 25cm3 nA = 2
MB =? VA = 23cm3
nA = nB
MA VA = MB VB
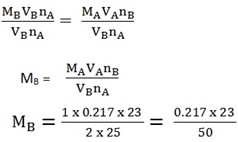
= 0.09982mol/dm3
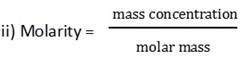
0.09982 = 10.6
1 = M
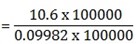
= 106g/mol = 106.2g/mol
iii) X2 CO3
2x + 12 + 48 = 106
2x + 60=106
2x = 46
x = 23
= 23g
iv)The name of element X is Sodium (Na)
PERCENTAGE COMPOSITIONS OF PURE AND IMPURE COMPONENTS
The pure substance may be composed in pure substances without affecting its chemical properties. Through volumetric analysis a percentage composition may be determined.
– Percentage purity
– Percentage impurity.
Where by,

Density = mass concentration per cm3
EXAMPLES;
3g of impure Na2CO3 were made up to 250 cm3 of solution; 25cm3 of this solution required 21.0 cm3 of 0.105M HCl for complete neutralization
i) Write down the balanced equation for the reaction
ii) Calculate the molarity of pure Na2CO3
iii) Calculate concentration of pure Na2CO3
iv) Calculate % purity of Na2CO3
v) Calculate % impurity of Na2CO3
Solution i and ii
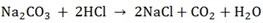
nB = 1 nA = 2
MB =? MA = 0.105
VB = 25cm3 VA = 21cm3
nA = nB
MAVA = MBVB
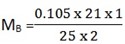
= 0.0441 M (pure Na2C03)
It’s pure because sand wouldn’t react with the acid
(iii) Concentration = molarity x molar mass
= 0.0441 M x 106g/mol
= 4.67g/dm3
iv) 3.0g=250cm3
x = 1000cm3
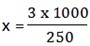
x = 12 g/dm3

Percentage purity = 38.9%
Percentage impurity= 100% – 38.9%
= 61.1 %
DILUTION LAW.
Is the law that describe or direct how to change and decrease molar concentration of the solution. The law state that “The product of initial concentration and its volume is equal to the product of final concentration and its volume”
M1 V1 = M2V2
Where, M1 = initial concentration
M2 = final concentration
V1 = initial volume
V2 = final volume
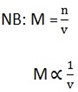
Example.
1. To what volume must 300cm3 of 6.0M NaOH be diluted to give a 0.40M solution?
Solution
M1 = 6.0M V1 = 300cm3
M2 = 0.04M V2 =?
M1V1 = M2V2
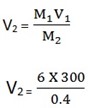
V2 = 4500cm3
DETERMINING WATER OF CRYSTALLIZATION.
Water of crystallization is the water that is bound within the crystals of substances. This water can be removed by heating. titration reaction are used to determine the amount of water of crystallization in a substance.
Questions
1. Determine the number of molecules of water of crystallization in the sample (Na2CO3 . XH2O). If R.M.M is 286g/mol.
Solution
Na2CO3 . XH2O
2(Na) + C + 3(O) + X(H2O) = 286
2(23) + 12 + 3(16) + X(18) = 286
106 + X(18) = 286
18X = 286 – 106
18X = 180
X = 180/18
X = 10
Therefore, the number of moles of water = 10
2. a) How many grams of concentrated HBr should be used to prepare 500ml of 0.6 M HBr solution?
b) Find the volume of stored solution.
Solution
a) Given purity = 48%
D = 1.5g
V = 500ml
M = 0.6M
n = M x V
= 0.5l x 0.6mol/l
= 0.3mol
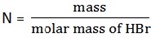
m = 0.3mol x 81g/mol = 24.3g
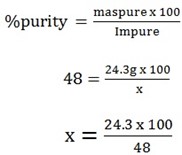
x = 50.6g
b) D = 1.5g/ml
m = 50.6g
v =?
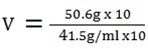
V = 33.7ml
3. 1.5g of an acid Hx was dissolved in water and its solution made to 250cm3. If 30.2cm3 of this acid solution neutralized 25cm3 of 0.115M KOH, Calculate,
i) Molarity of Hx
ii) Molecule weight of Hx
iii) Name of radical x
Solution
i) VA = 30.2cm3 VB = 25cm3
MA =? MB = 0.115M
Mass of HX = 1.5g
KOH + HX KX + H2O
nB = 1
nA = 1 thus MA VA = MB
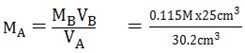
= 0.095M

X = 6g/dm3 x 1000
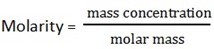
Molar weight = 63g/mol
iii) x must be a radical and the common ones are HCl, HNO3, H2SO4, H3PO4, so it’s either HNO3 or HCl.
But HNO3 = 63g/mol
Thus, x is nitrate (v) ion (NO3–)
