EXTERNAL FORCES THAT AFFECT THE EARTH
External forces are the forces that operate on the surface of the Earth. The external forces leads to the modifications and formations of various land forms or land scape.
These external forces that operate on the earth′s surface include:-
WEATHERING
Is the disintegration of rock exposed on the earth’s surface by the agents of weather particularly temperature and pressure release.
TYPES OF WEATHERING
There are three types of weathering. These are
I.Physical or mechanical weathering
Is the disintegration of rocks into smaller particles by mechanical means but without involving changes in temperature.
Mechanical weathering include the following processes
a)Insulation thermal expansion weathering – is the weathering which brought by temperature change.
During the day time the rocks expands and contract during the night leading to the creaking and breaking of the rock into small particles.
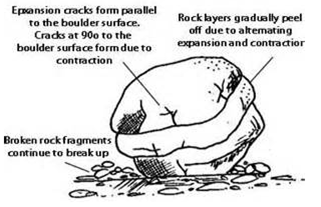
b) Exfoliation is the peeling off of outer layer of the rock like onion.
This is due to the fact that when the temperature is high the outer layer of rock warm faster than the inner layers and cool more rapidly. This cause the outer thickness to peel and form the smooth round hill called Exfociation dumes.
The rock particles deposited around the bottom of the dome is called Talus or scree

c) Granular disintegration
Is the breaking up of the rock which is consist of different minerals. These mineral contracts and expand separately through temperature changes.
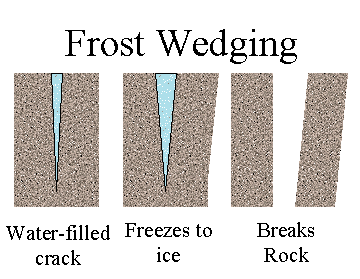
d) Frost action
This is common in temperature areas well as highlands and deserts.
When the temperature falls water in the cracks of the rock freezes. On free zing it expands leading to the widdening of the cracks. As the freezing repeating rocks breaks into fraguments or particles.
e) Pressure release
This take place where denudation has taken place to a great extent. As the materials are removed in certain area the pressure is released due to the reduction in weight. The rocks become weak and easly disentegrated by other process like exfoliation.
f) Salt crystallization
This take place when salt crystals deposited in the rock cracks or pores during evaporation. As the deposition goes on the crystals become large and exert stress upon the rock cause it to disintegrate.
This process is common in desert where there is capillary action or along the coast where there is constant supply of salt.
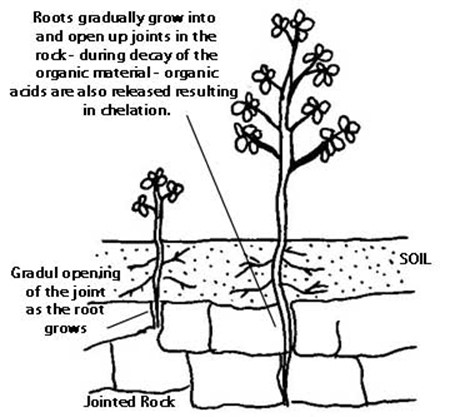
Biological weathering
Is the weathering where by the disintegaration of rock into small particles is influenced by plants and animals
Chemical weathering
Is the process which involves the decomposition or decay of the rock by chemical means.
FACTORS EFFECTING THE RATE OF WEATHERING
1.Nature of rock. The nature of rock include
•Mineral composition
•Plane of weakness
•Cementation
•colour
2.Climate. This is concerned with rainfall nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution. Areas with heavy rainfall the rate of weathering is h3.Plants and animals.Plant root penetration result disintegration of rocks. Animals borrowings and decaying of dead animal result rock decomposion.
4.Reliefs steepness of the land also determines the rate of weathering is high compared to low lands where deposition is common.
Chemical weathering processes
a) Oxidation. Is the oxidation of rock minerals particular iron when combine with oxygen in the presence of water.
b) Carbonation. Is the decomposition on of rocks particularly limestone with carbondioxide gas.
c) Solution Some rocks such as salt rocks are soluble in water and simply dissolve leading to the disappear once of the rocks.
d) Hydration is the process in which certain minerals absorb water and well causing internal stress and fructuring of rocks.
e) Hydrolysis. Is the reaction between water and mineral elements that is between hydrogen ion (H+) and the ions of minerals. It is common in felspar minerals which compensation potash soda or lime and silica
Effects of Weathering
1.Formation of various
2.features Soil formatio Eg:- Clints and Grikes in limestone region
3.It influences the rate of erosion.
4.It provide building material Eg:- Cement, blocks
5.It attract tourist since weathering result the formation of various features
MASS WASTING.
Mass wasting is the down slope movement of weathered rock materials due to the influence of gravity. The movement is not influenced or effected by transport agents such as wind or running water.
– When the movement of this nature occurs after the materials have been lubricated by rainwater or water from melting snow, it is referred to as mass movement. This force involved in mass wasting is that of gravity.
– In mass wasting, water acts as a lubricant and helps the materials to overcome the initial resistance where by the initial resistance is the friction between the materials and the underlying rock mass.
The movement can either be slow or sudden and rapid. The type (nature).
TYPES OF MASS WASTING
There are two types of mass wasting
I. Slow wass wasting
II. Rapid mass wasting
Slow mass wasting
This is the slow but stendy movement of rock debt is and soil down the stop.
This form involve the following processes.
a) Soil creep. This is the steady movement involving soil and other fine materials along a very gentle slope.
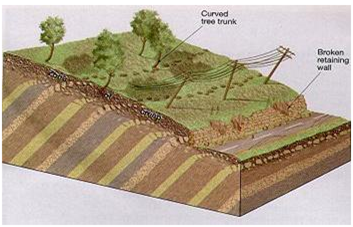
Evidence that soil creep is taking place are
•Fence posts and telephones poles
•Stone walls
•Accumulation of soil at the base of slope.
b) Talus creep – is the mass of broken rock particles rock pieces that accumulated at the base of a rock mass such as a cliff.
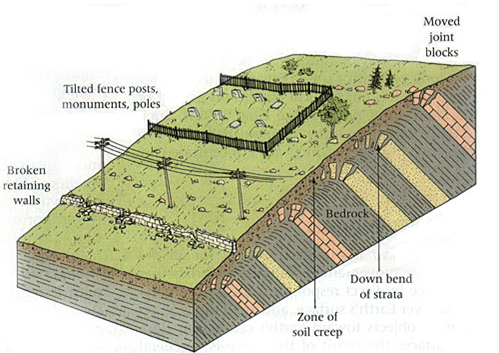
c) Rock creep
Individual rock blocks moves down the slope slowly especially where the rock block lying over clay materials.
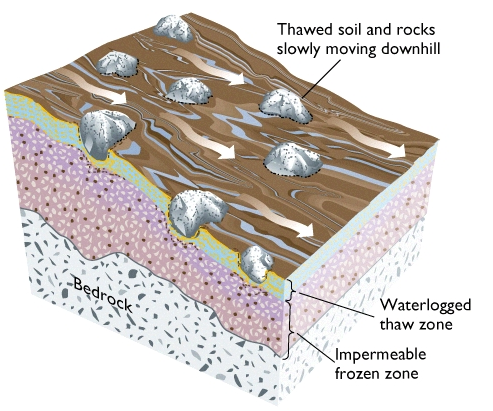
d) Solifluction
This is the movement of a mixture of soil, gravels and weathered rock down a moderate slope and the materials aare saturated with water.
Rapid mass wasting
This is the movement of materials in sudden and very fast way.
It involves processes like flowing, sloding or falling. Rapid mass wasting include the following.
a)Earth flow.
Materials on the earth’s surface get so saturated with water that they begin to flow down the will under the influence of gravity. This occurs in hummid region.
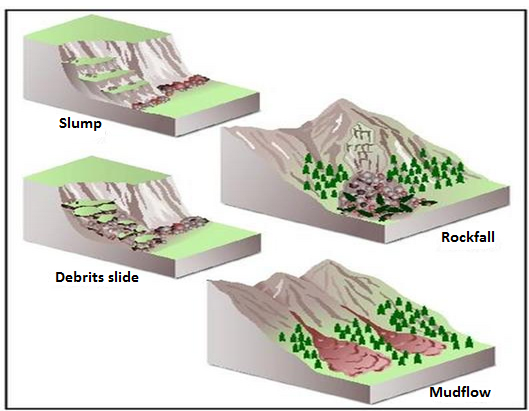
b)Mudflow.
This is a flow of large quantities of mud down the slopes especial where the soil is bare
c)Landslide
This is a rapid movement of a large mass of earth and rocks down a hill or mountain inside.
Forms of landslide.
i. Slump
This is the shearing or tearing away of rock materials. Usually occurs along a concave plance. It involve the large mass of soil, rock and other loose materials and vegetation.
ii.Debris slide.
This involve the movement of a whole mass of accumulated rock debris and other loose materials that produced through wealthering down a hill slope.
iii. Rock slide
The movement of rock mass sits on a fault or a weakened bedding plane on relative gentle slope.
iv. Rock falls
This is the rapid falling of individual rock brocks or boulders fleely form a steep slope.
v. Debris fall
This is the free falling of loose materials of various size from the top of a very sleep slope and cliff to the bottom of the slopes due to growty.
vi. Avalanches
This is the sudden sliding and falling of a large mass of snow Ice and loose rock materials down a montariside.
Factors influencing mass wasting
a) The nature and weight of the materials rapid mass wasting will occur 18 the weathered rock materials are very deep
b) Amount of water
If materials are more saturated with water are more likely to move than they are dry
c) The angle of slope
The steeper the slope, the faster the movement of materials
d) Climate
Mass wasting can be determined by the amount and nature of rainfall of an area receives. Areas receiving heavy experiences massive mass wasting.
e) Vegetation
Plant cover hold materials hence reduce amount of movement, hence bare surface experience active mass wasting.
f) Human activities
Eg. Cultivation Construction grazing animals mining and clearing of vegetation render the surface bare and unprotected, shake the land cause materials to move.
Effects of mass wasting on the environment
1) Soil erosion. As materials move down the slope especially where rapid movement is involved, they remove some soil to other area.
2) Formation of new landforms.The process can lead to the formation of scars and depression.
3) Formation of lakes.Materials of land slides can be accumulated and form a barrier to the flowing river hence eventually form lake due to accumulation of water blocked.
4) Formation of fertile soil.The material from fertile land accumulated at destination form fertile soil. At the place.
5) Demage of property.Various forms of mass wasting lead to the damage of propartly like telephone lines and power transmission
6) Loss of life.
iii. (a) EROSION AND DEPOSITION BY RUNNING WATER.
Erosion – Refers to the breaking and wearing a way of exposed rocks by moving water (rives and waves), the wind and moving ice and wind. Water, wind and ice are called effects of erosion.
Deposition – It is the process which sediment, soil, rocks is accumulated to a certain place.
Running water – The process associated with running water fluvial process. Running water can take form of over land flow (surface runoff) or channel them (river). In the surface runoff water flows on the surface forming uniform cover while in channel flow (river) water flows in the specific channels.
i. Over land flow (surface Runoff)
Is more effective on bio and upper slopes and undergo the following types of erosion
(a) Sheet erosion
– Remove the uniform cover of the soil
– It is common in gentle sloping areas, which are bare of vegetation.
(b) Rill erosion
– Produces small groves on the surface called mills and it takes place after sheet erosion has produced a mumble of tiny streamlets.
(c) Gully erosion
– Take place leading to the production of deep trough into land, this is more concentrated, if vell erosion has not been checked by planting trees.
Surface Run –off and its features Produced
i. Rills – These are small channels produced on the surface due to rill erosion
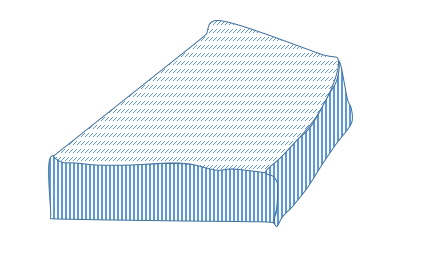
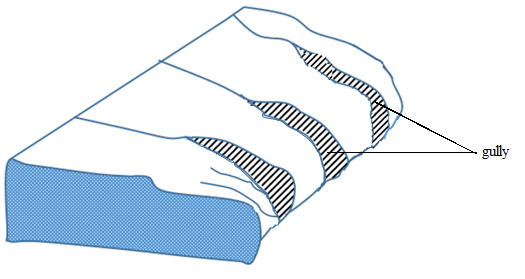
ii. Gullies
Are deep steep – Sided through produced by gully erosion, they are formed when rills are depended and widened by more concentrated erosion.
iii. Bad lands
This is the landscape which has been proken up by many gullies and channels due to erosion.
iv. Inserbeng
Round topped hills produced as remounts of hard rock after All other pants have been eroded.
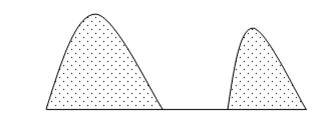
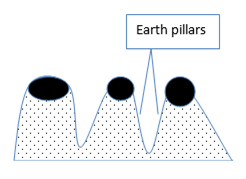
v. Earth pillars are columnar (tower like) structures standing vertically on the surface due to the removal or erosion of clay and boulders on soft rocks.