II. PUBLIC EXPENDITURE.
Refers to the spending by the government .it is categorized into two groups.
-
Recurrent expenditure.
Refers to government expenditure on public consumption like in education, salaries, health etc
-
Development expenditure
Is the expenditure by government on development projects like roads, in communication etc.
Roles of government expenditure (why should spend?)
- To regulate economic activities
- It influencing the allocation of resources
- To enable government to maintain it enterprises and property
- Provide essential goods and services to the public.
- Stabilizing the economy
- Motivating the government employee in terms of reward, seminar etc
- To balance the national development.
edu.uptymez.com
III. NATIONAL BUDGET
- It is the estimate of the government revenue and expenditure within a given year (financial year)
- This is a statement showing anticipated receipts and anticipated payments.
edu.uptymez.com
TYPES OF NATIONAL BUDGET.
There two main types of government budget (Balanced and unbalanced budget which includes (Deficit surplus budget)).
- Surplus budget
edu.uptymez.com
This refers to budget in which the anticipated revenue is great than anticipated expenditure. This surplus budget implies that
- There is going to be a reduction in price level
- There is reduction in money supply
- There is reduction in economic activities
-
There is going to be grants and gifts to other countries
This kind of budget is not found in LDCs.
edu.uptymez.com
Qn, Why do countries plan for surplus budget, what are the objectives of surplus budget.
- Their aimed at reducing money supply (circulation)
- To enable government finance development projects in the future
- To enable government give grants, loans to other countries
- To correct balance of payments
- To disnglish-swahili/courage” target=”_blank”>courage consumption of some goods
- To control inflation through reducing aggregate demand
- To help the government to get money and repay debts.
edu.uptymez.com
Surplus budget may lead to the following problems;
- Unemployment
- Depression
- Decrease in money supply leading decrease in investment and saving
- Decrease in aggregate demand leading to decrease in production
-
Increase in tax rate to maximize revenue.
Deficit budget
Refers to the budget in which the anticipated revenue is less than anticipated expenditure. It occurs when government estimated expenditure is greater than estimated revenue.This is mainly occur in developing countries like Tanzania.
Balanced budget is when the anticipated budget is equal to anticipated expenditure.Government estimated revenue Government proposed expenditure.Most of the classical economist advocated balanced budget,which was based on the policy of ‘line within means’.According to them,government revenue should not fall short of expenditure.
edu.uptymez.com
This implies that;
- The government is going to borrow more money within a financial year
- There is going to be an increase in money supply resulting from increase in expenditure
- There will be increase in price level
- There will be increase in aggregate demand and unemployment
- The government may sale its assets.
edu.uptymez.com
Qn. Why having a deficit budget in LDC’S.
- A deficit budget is aimed at increasing level of aggregate demand
- Increase level of supply
- Aim at controlling deflation
- Reducing the tax burden
- Encouraging borrowing
- Shifting the economy from depression recovery
- Increasing economic activities
edu.uptymez.com
Qn. What are the causes of budgetary deficit in Tanzania
Qn. Discuss the functions of the budget
PUBLIC DEBTS.
Is the total borrowing by the government. This includes internal and external borrowing.
CLASSIFICATION OF DEBTS
1. INTERNAL DEBTS.
Is the total money which the government borrows from individual and institutions within the country.
2. EXTERNAL DEBTS
Is the borrowing of a money outside the country e.g. from WB, IMF, ADB (African development bank)
3. REPRODUCTIVE DEBTS.
These are debts which the government uses for productive activities that will generate revenue to repay back the debts.
4. NON REPRODUCTIVE DEBTS (dead weight)
This are debts used to finance activities that do not give the return e.g. weapons.
5. SHORT TERM DEBTS.
This is debts paid within short time.
6. LONG TERM DEBTS
These are debts paid after a long period of time for example 10year – 50year.
7. A FUNDED DEBTS
These are debts in which a specific time of repaying debts is not fixed to get the loan.
8. UN-FUNDED DEBTS
These are debts in which date of redemption is stated while receiving the loan.
9. VOLUNTARY AND COMPOLSORY DEBT
REDEMPTION OF PUBLIC DEBTS
Redemption of public debt refers to the payment of public debts
WAYS USED IN REDEMPTION OF PUBLIC DEPT.
1. REPUDIATION.
Repudiation is form of debt redemption where the government refuse to pay debts.
2. BY CONVERSION.
Is the form of debts redemption where the government takes new loan with low interest and paying the previous loan with higher interest.
3. NEGOTIATIONS ON DEBTS.
This refers to cancellation of a debt
4. USE OF SURPLUS BUDGET
Where the expenditure is less than revenue and extra amount of money is left for paying debt.
5. CAPITAL LEVY.
Is where the government imposes taxation on asset like building and the revenue is used to pay the debts.
6. SINK FUND
Is the situation where the government invest a given amount of money in the bank to get compound interest and hence use the amount obtained to pay a debts.
7. PRIVATIZATION OF PUBLIC GOODS.
The money obtained from privatization is used for debts repayment.
8. USE OF GRANTS AND GIFTS RECEIVED
9. SELLING SECURITY TO THE GOVERNMENT
10. USE OF ACCUMULATED FOREIGN RESERVES.
CAUSES AND JUSTIFICATION OF PUBLIC DEBTS.
Qn. Why do LDC’s government depend on borrowings?
-To increase revenue since tax revenue is not enough to finance government activities in LDCS.
-To reduce the tax burden from tax payers
-To correct balance of payment deficit,
-To reduce printing of more money by the government to avoid inflation.
-In order to overcome natural calamities such as drought etc.
-To help the government attain economic growth through the finding of more economic activities hence economic growth
-Enable the government persuade its development plan
-To balance the budget and cover budgetary deficits.
-To enable the government repay loan conversion
-To control economic depression through increase in aggregate demand result from increase in unemployment opportunities.
Qn. Discuss the roles played by public borrowing in LDC.
-It leads to over dependency
-It reduces money available for consumption and investment.
-Debts worsen the country balance of payment position.
-If the dept is not used reproductively it becomes a burden to the government and its people.
-Most of the debts are always in the form of a tied aid i.e. debt with conditions (strings attached)
-When the debt is long-term its burden is shifted to another generation
-There is a burden of paying interest and other cost in debts administration.
Qn. Discuss the measure your country is using to reduce debt burden?
Qn. Discuss why external debts have been increasing instead decreasing in LDCS
FISCAL POLICY.
-This is the use of taxation, government expenditure and public borrowing to influence the economic activity of a given country.
How fiscal policy work (mechanism of fiscal policy)
It works in two ways i.e. expand economic and to contract economy.
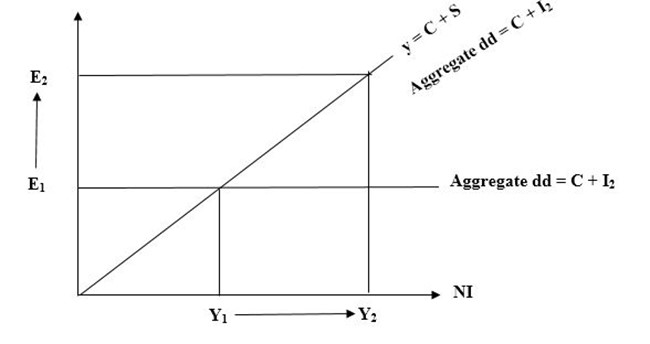
EXPANSION FISCAL POLICY
This is a situation where there is increase of government expenditure and decrease in tax. It is aimed at increasing aggregate demand.
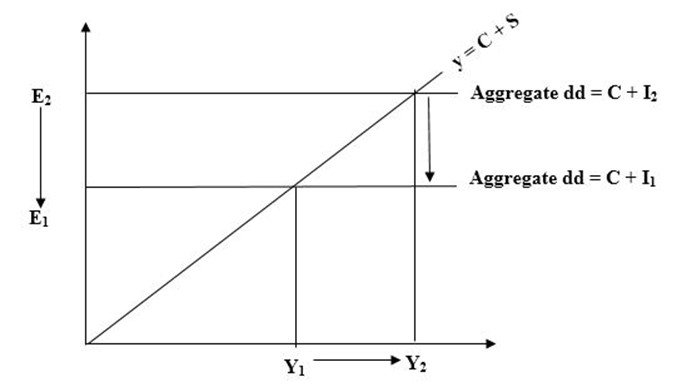
II. CONTRACTION FISCAL POLICY.
It aimed at reducing aggregate demand where there is increase in tax and decrease in expenditure.
Qn. Discuss how fiscal policy can be used to bring economic development hint (use roles of tools of fiscal policy)