NOMENCLATURE OF ALCOHOLS
• Rules of naming alcohols are the same as those alkanes with the following modifications
i. The parent chain must contain hydroxyl group 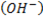
ii. In numbering carbons start at the end closer to hydroxyl group.
iii. Position of hydroxyl group should be indicated by using Arabic numerals.
iv. In giving a name of alcohol, the name must end with suffix ol ( after removing e from corresponding name of hydrocarbon)
Example
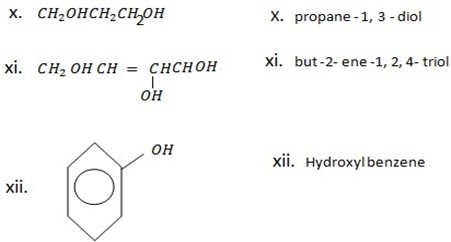
Give systematic (IUPAC) name of the following organic compounds.

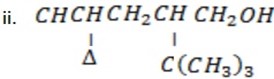
4 – Cyclopropyl- 2 tertbutylpentanol.
OR ( 4- Cyclopropyl – 2- terbuty-pentan-1-ol
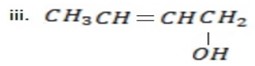
Pent – 3 con 1- 01
OR (3 – pentanol).
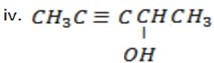
Pent – 3 – yn – 2- ol.
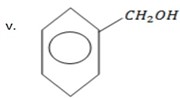
1 – Pheny methanol.
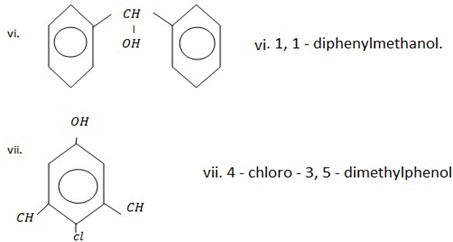
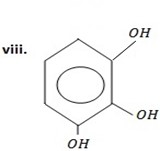
2,3 – dihydroxyl phenol OR (1,2,3,- trihydroxylbenzene)
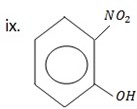
2 – nitrophenol.
PREPARATION OF ALCOHOLS
a) REACTION BETWEEN MOIST SILVER OXIDE AN HALOALKANE.
Generally
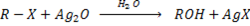
Example
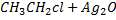
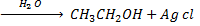
b) REACTION BETWEEN HALOALKANE AND ALKALINE SOLUTION.
• Haloalkane react with alkaline solution like NaOH and KOH yielding alcohol
E.g. In case of NaOH
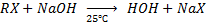
Example
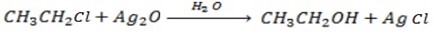
c) ACIDIC HYDROLYSIS OF ALKENE ( REACTION BETWEEN ALKENE AND WATER UNDER PRESENCE OF SULPHURIC ACID).
Generally
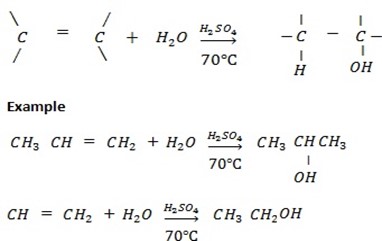
d) REDUCTION OF CARBONYL COMPOUNDS
• Carbonyl compounds react with reducing agent like 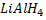 alcohols.
alcohols.
Generally
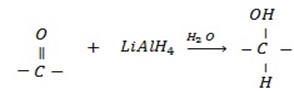
• Aldehydes give primary alcohol.
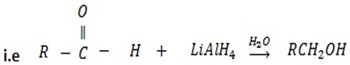
While
• Ketones give secondary alcohol.
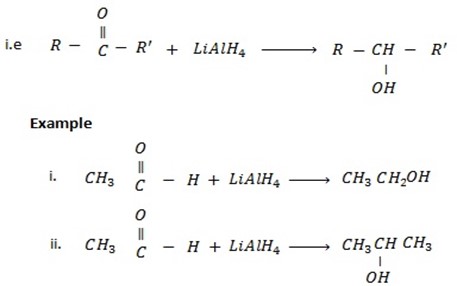
e) REDUCTION OF CARBOXYLIC ACID
• Carboxylic acids react with strong reducing agent like 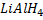 forming primary alcohols.
forming primary alcohols.
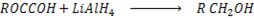
Example
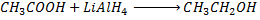
NOTE
In above reaction if 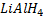 is in limited amount ( or weak reducing agent is used instead of
is in limited amount ( or weak reducing agent is used instead of 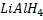 ) aldehyde is formed instead of alcohol.
) aldehyde is formed instead of alcohol.
f) REACTION BETWEEN GRIGINARD REAGENT AND CARBOXYLIC COMPOUNDS ACID FOLLOWED BY ACIDIC HYDROLYSIS
Generally
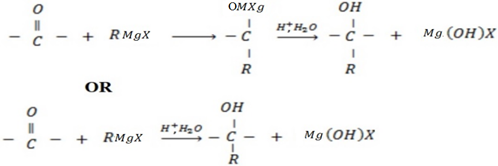
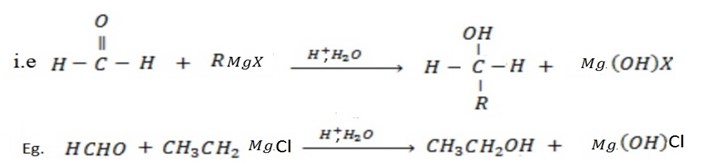
• If the aldehyde used is methanol, primary alcohol is formed.
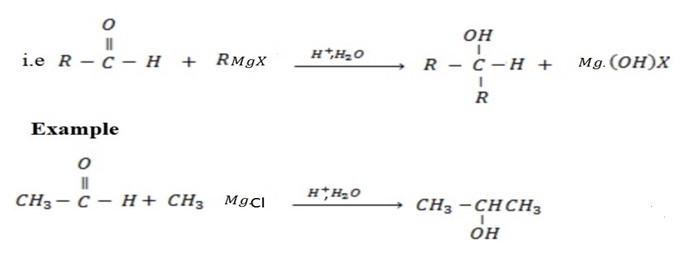
• If higher member of aldehyde is used, secondary alcohol is formed.
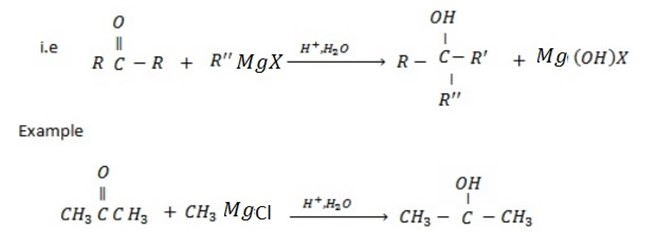
• If the carbonyl compound which is used is Ketone, tertiary alcohol is formed.
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF ALCOHOLS
• Boiling point of alcohol increase with an increase of number of carbon ( As number of carbon increase the molecular weight also increase)
E.g
Boiling point of 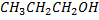 is large than the
is large than the 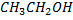
– The less branched alcohol has higher boiling point than that alcohol which is more branched.
Example

– The more branched has lower boiling point due to the following reason,
i. Poor package of carbon atoms
ii. Minimum surface area as it attain more spherical shape hence heating become easier
-In comparison to alcohol and corresponding carbon member of alkene ( with approximately the same molecular weight) alcohol have higher boiling due to presence of hydrogen bond in alcohol.
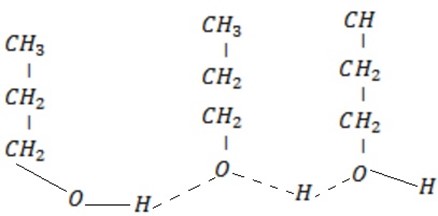

– For polyhydric alcohols. Alcohol with more than one OH– group has the boiling point increase, with number of hydroxyl groups due to increase in position of making hydrogen bond.
Example.
Explain the following the B.P ( boiling point) of ethyl glycol is highest among the compound given below although is little in the molecular weight.
| compound | Formula | Molecular weight | Boiling point in oc |
| Ethylene glycol | 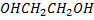 |
62 | 197 |
| Propanol | 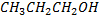 |
60 | 97 |
| Butane | 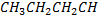 |
58 | -0.5 |
edu.uptymez.com
ANS
Boiling point of alcohol increase with an increase in number of  group.
group.
(for polyhydric alcohol) due to increase in number of position of making hydrogen bonding, ethylene glycol has two  groups so compare to 1- propanol which has only one
groups so compare to 1- propanol which has only one  group. Ethylene glycol, have many position of making hydrogen bonding and hence the boiling will be higher, in case of butane it has group, there is no hydrogen bonding at all that is why has lowest boiling point compound.
group. Ethylene glycol, have many position of making hydrogen bonding and hence the boiling will be higher, in case of butane it has group, there is no hydrogen bonding at all that is why has lowest boiling point compound.
Solubility of alcohol in water decrease with an increase hydrophobic group ( increase number of carbons due to an increase of non polar covalent character).
In increase of polyhydric alcohols solubility increase with an increase in number of  group as a result of increasing number of position of making hydrogen bonding.
group as a result of increasing number of position of making hydrogen bonding.
Example. NECTA 1993 PP1
Explain the solubility of alcohol increase with order
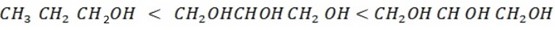
For Polyhydric alcohol solubility increase with an increase in number of position of making hydrogen bonding that is why solubility of given compound increase in that order (i.e the longer the number of group the higher the solubility will be).Alcohol exist as coloured liquid compound because hence easily exposed